Difference between revisions of "Basic Principles of The Method of Moments"
Kazem Sabet (Talk | contribs) (→Multilayer Green’s Functions) |
Kazem Sabet (Talk | contribs) (→Discretization Of Electric & Magnetic Currents) |
||
| Line 198: | Line 198: | ||
Similar expressions can be derived for the T<sup>(EM)</sup>, U<sup>(HJ)</sup> and Y<sup>(HM)</sup>elements of the MoM matrix. | Similar expressions can be derived for the T<sup>(EM)</sup>, U<sup>(HJ)</sup> and Y<sup>(HM)</sup>elements of the MoM matrix. | ||
| − | == Discretization | + | == Discretization of Electric & Magnetic Currents == |
The right choice of the basis functions to represent the elementary currents is very important. It will determine the accuracy and computational efficiency of the resulting numerical solution. Rooftop basis functions are one of the most popular types of basis functions used in a variety of MoM formulations. The surface currents (whether electric or magnetic) are discretized using 2D rooftop basis functions shown in the figure below: | The right choice of the basis functions to represent the elementary currents is very important. It will determine the accuracy and computational efficiency of the resulting numerical solution. Rooftop basis functions are one of the most popular types of basis functions used in a variety of MoM formulations. The surface currents (whether electric or magnetic) are discretized using 2D rooftop basis functions shown in the figure below: | ||
| − | [[File:image055_tn.png | + | <table> |
| − | + | <tr> | |
| − | Rooftop or RWG basis functions built over two rectangular, triangular or mixed cells. | + | <td> [[File:image055_tn.png|thumb|480px|Rooftop or RWG basis functions built over two rectangular, triangular or mixed cells.]] </td> |
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | </table> | ||
The rooftop basis functions are defined over two adjacent cells with a common edge of length. If the two cells are triangular, then the so-called RWG functions are obtained. It is also possible to define rooftop functions over two adjacent rectangular cells or two adjacent rectangular and triangular cells with a common edge. On a rectangular cell, the function is defined as having a (descending or ascending) linear profile in one direction and a constant profile in the other perpendicular direction. | The rooftop basis functions are defined over two adjacent cells with a common edge of length. If the two cells are triangular, then the so-called RWG functions are obtained. It is also possible to define rooftop functions over two adjacent rectangular cells or two adjacent rectangular and triangular cells with a common edge. On a rectangular cell, the function is defined as having a (descending or ascending) linear profile in one direction and a constant profile in the other perpendicular direction. | ||
| Line 211: | Line 213: | ||
[[File:image065_tn.png]][[File:image066_tn.png]] | [[File:image065_tn.png]][[File:image066_tn.png]] | ||
| + | <table> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td> [[File:image065_tn.png|thumb|480px|Prismatic basis functions built over single triangular and rectangular cells.]] </td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | </table> | ||
Prismatic basis functions built over single triangular and rectangular cells. | Prismatic basis functions built over single triangular and rectangular cells. | ||
Revision as of 16:03, 11 June 2017
Contents
- 1 An Overview of the Method of Moments
- 2 Free-Space Green’s Function
- 3 3D Integral Equations
- 4 Galerkin Testing
- 5 Pocklington’s Integral Equations for Wire Structures
- 6 Discretization Of Wire Structures
- 7 Multilayer Green’s Functions
- 8 Planar Integral Equations
- 9 Numerical Solution of Integral Equations
- 10 Discretization of Electric & Magnetic Currents
- 11 The Rectangular Mesh Advantage
- 12 Computing The Near Fields in Planar MoM
- 13 Computing The Far Fields in Planar MoM
- 14 Periodic Planar MoM Simulation
- 15 EM.Cube's Linear System Solvers
An Overview of the Method of Moments
The Method of Moments (MoM) is a rigorous, full-wave numerical technique for solving open boundary electromagnetic problems. Using this technique, you can analyze electromagnetic radiation, scattering and wave propagation problems with relatively short computation times and modest computing resources. The method of moments is an integral equation technique; it solves the integral form of Maxwell’s equations as opposed to their differential forms that are used in the finite element or finite difference time domain methods.
In a 3D MoM simulation, the currents or fields on the surface of a structure are the unknowns of the problem. The given structure is immersed in the free space, and the unbounded background medium is modeled using the free-space Green's functions. The unknown physical or equivalent currents are discretized as a collection of elementary currents with small finite spatial extents. Such elementary currents are called basis functions. They obviously have a vectorial nature and must satisfy Maxwell's equations and the relevant boundary conditions individually. The actual currents on the surface of the given structure (the solution of the problem) are expressed as a superposition of these elementary currents with initially unknown amplitudes. Through the MoM solution, you find these unknown amplitudes, from which you can then calculate the currents or fields everywhere in the structure.
EM.Libera offers two distinct 3D MoM simulation engines. The Wire MoM solver is based on Pocklington's integral equation. The Surface MoM solver uses a number of surface integral equation formulations of Maxwell's equations. In particular, it uses an electric field integral equation (EFIE), magnetic field integral equation (MFIE), or combined field integral equation (CFIE) for modeling PEC regions. On the other hand, the so-called Poggio-Miller-Chang-Harrington-Wu-Tsai (PMCHWT) technique is utilized for modeling dielectric regions. Equivalent electric and magnetic currents are assumed on the surface of the dielectric objects to formulate their assocaited interior and exterior boundary value problems.
In EM.Picasso, the background structure is a planar layered substrate that consists of one or more laterally infinite material layers always stacked along the Z-axis. In other words, the dimensions of the layers are infinite along the X and Y axes. Your substrate can be a dielectric half-space, or a single conductor-backed dielectric layer (as in microstrip components or patch antennas), or simply the unbounded free space, or any arbitrary multilayer stack-up configuration. In the special case of a free space substrate, EM.Picasso behaves similar to EM.Libera's Surface MoM simulator. Metallic traces are placed at the boundaries between the substrate or superstrate layers. These are modeled by perfect electric conductor (PEC) traces or conductive sheet traces of finite thickness and finite conductivity. Some layers might be separated by infinite perfectly conducting ground planes. The two sides of a ground plane can be electromagnetically coupled through one or more slots (apertures). Such slots are modeled by magnetic surface currents. Furthermore, the metallic traces can be interconnected or connected to ground planes using embedded objects. Such objects can be used to model circuit vias, plated-through holes or dielectric inserts. These are modeled as volume polarization currents.
In a planar MoM simulation, the unknown electric and magnetic currents are discretized as a collection of elementary currents with small finite spatial extents. As a result, the governing integral equations reduce to a system of linear algebraic equations, whose solution determines the amplitudes of all the elementary currents defined over the planar structure's mesh. Once the total currents are known, you can calculate the fields everywhere in the structure.
Free-Space Green’s Function
The Green’s functions are the analytical solutions of boundary value problems when they are excited by an elementary source. This is usually an infinitesimally small vectorial point source. In order for the Green’s functions to be computationally useful, they must have analytical closed forms. This can be a mathematical expression or a more complex recursive process. It is no surprise that only very few electromagnetic boundary value problems have closed-form Green’s functions. The total electric (E) field can be expressed in terms of the electric current in the following way:
- [math] \mathbf{E = E^{inc}} + \mathbf{\iiint_V \overline{\overline{G}}_{EJ}(r|r') \cdot J(r') } d \nu' + \mathbf{\iiint_V \overline{\overline{G}}_{EM}(r|r') \cdot M(r') } d \nu' [/math]
- [math] \mathbf{H = H^{inc}} + \mathbf{\iiint_V \overline{\overline{G}}_{HJ}(r|r') \cdot J(r') } d \nu' + \mathbf{\iiint_V \overline{\overline{G}}_{HM}(r|r') \cdot M(r') } d \nu' [/math]
where is the dyadic Green’s functions for electric fields due to electric current sources and Ei is the incident or impressed electric field. The incident or impressed field provides the excitation of the structure. It may come from an incident plane wave or a gap source on a line, etc. The simplest background structure is the unbounded free space, which is represented by the following Green’s function:
- [math] \mathbf{ \overline{\overline{G}}_{EJ}(r|r') = (\overline{\overline{I}} + \nabla\nabla) } G_{\Lambda} (\mathbf{r|r'}), \quad G_{\Lambda} (\mathbf{r|r'}) = \frac{ e^{-jk_0 \mathbf{|r-r'|}} }{ 4\pi \mathbf{|r-r'|} } [/math]
where [math]\mathbf{\overline{\overline{I}}}[/math] is the unit dyad, [math]\nabla[/math] is the gradient operator, r and r' are the position vectors of the observation and source points, respectively, and k0 is the free-space propagation constant. This implies that electromagnetic waves propagate in free space in a spherical form away from the source. Note that the Green’s function has a singularity at the source, i.e. when r = r'. This singularity must be removed when solving the integral equations.
3D Integral Equations
In the more general formulation of the field integration equations, both electric and magnetic currents are included. In that case, the total electric and magnetic fields are given by the following equations:
- [math] \mathbf{E = E^{i}} + \mathbf{\iiint_V \overline{\overline{G}}_{EJ}(r|r') \cdot J(r') } + \mathbf{\iiint_V \overline{\overline{G}}_{EM}(r|r') \cdot M(r') } [/math]
- [math] \mathbf{H = H^{i}} + \mathbf{\iiint_V \overline{\overline{G}}_{HJ}(r|r') \cdot J(r') } + \mathbf{\iiint_V \overline{\overline{G}}_{HM}(r|r') \cdot M(r') } [/math]
The above coupled equations involve four types of dyadic Green's functions that represent the electric and magnetic field radiated by an electric or a magnetic current. The incident or impressed electric and magnetic fields Ei and Hi exist independently of the given structures and are related to each other depending on the type of excitation source.
Enforcing the boundary conditions on the integral definitions of the E and H fields results in a system of integral equations as follows:
- [math] \mathcal{L}_E(\mathbf{E}) = \mathcal{L}_E \left( \mathbf{E^{i}} + \mathbf{\iiint_V \overline{\overline{G}}_{EJ}(r|r') \cdot J(r') } + \mathbf{\iiint_V \overline{\overline{G}}_{EM}(r|r') \cdot M(r') } \right) = 0 [/math]
- [math] \mathcal{L}_H(\mathbf{H}) = \mathcal{L}_H \left( \mathbf{H^{i}} + \mathbf{\iiint_V \overline{\overline{G}}_{HJ}(r|r') \cdot J(r') } + \mathbf{\iiint_V \overline{\overline{G}}_{HM}(r|r') \cdot M(r') } \right) = 0 [/math]
where [math]\mathcal{L}_E(E)[/math] is the boundary value operator for the electric field and [math]\mathcal{L}_H(H)[/math] is the boundary value operator for the magnetic field. For example, they may require that the tangential components the E field vanish on perfect electric conductors. Or they may require that the tangential components the E and H fields be continuous across an aperture in a perfect ground plane. Given the fact that the dyadic Green’s functions and the incident or impressed fields are all known, one can solve the above system of integral equations to find the unknown currents J and M. Therefore, through these relationships you can easily cast the above integral equations in terms of unknown E and H fields.
Galerkin Testing
The integral equation derived in the previous section can be solved numerically by discretizing the computational domain using a proper meshing scheme. The original functional equation is reduced to a set of discretized linear algebraic equations over elementary cells. The unknown quantities are found by solving this system of linear equations, and many other parameters can be computed thereafter. This method of numerical solution of integral equations is known as the Method of Moments (MoM). In this method, the unknown electric current is represented by an expansion of basis functions as follows:
- [math] \mathbf{J(r)} = \sum_{n=1}^N {I_n}^{(J)} \mathbf{ {f_n}^{(J)}(r) }[/math]
where [math]\mathbf{ {f_n}^{(J)} }[/math] are the generalized vector basis functions for the expansion of electric currents, and [math]{I_n}^{(J)}[/math] are the unknown complex amplitudes of these basis functions, which have to be determined. Substituting these expansions yields the following discretized integral equation:
- [math] \mathcal{L}_E \left( \mathbf{E^i} +\iiint_V \mathbf{ \overline{\overline{G}}_{EJ}(r|r') } \cdot \sum_{n=1}^N {I_n}^{(J)} \mathbf{ {f_n}^{(J)}(r') } \, d\nu' \right) = 0 [/math]
In order to solve the above equation, the method of moments uses Galerkin's technique to turn it into a set of linear algebraic equations. This is accomplished by testing the above equations using the basis functions, leading to the following linear system:
- [math]\mathbf{[Z] \cdot [I] = [V]}[/math]
where
- [math] Z_{ij} = \iiint_{V_i} \mathbf{ {f_i}^{(J)}(r) } \, d\nu \cdot \iiint_{V_j} \mathbf{ \overline{\overline{G}}_{EJ}(r|r') \cdot {f_j}^{(J)}(r') } \, d\nu' [/math]
and
- [math] V_i = \iiint_{V_i} \mathbf{ {f_i}^{(J)}(r) \cdot E^i(r) } \, d\nu [/math]
Using a rooftop expansion of the currents on the wires, we can discretize the Pocklington integral equation. In order to convert the discretized integral equation into a system of linear system of algebraic equations, we use Galerkin’s testing process, in which the testing functions are chosen to be identical to the expansion basis functions. However, to avoid the source singularity at r=r’, the expansion functions are placed at the center of the wires, while the test functions are evaluated on the surface of the wires, assuming a finite non-zero radius for all wires. The solution vector [I] is then found as:
- [math]\mathbf{[I] = [Z]^{-1} \cdot [V] } [/math]
where [Z]-1 is the inverse of the impedance matrix and [V] is the excitation vector.
Pocklington’s Integral Equations for Wire Structures
Wire structures are made of linear PEC elements. These may consist of actual physical wires such as a dipole or loop antenna or a wireframe representation of a surface or solid object. In a wire structure, the unknown electric currents are one-dimensional. The integral equation is derived by forcing the tangential component of the electric field to vanish on the surface of the wire. This leads to the following simpler integral equation:
- [math] \mathbf{ \hat{I} \cdot E^i } - jk_0 Z_0 \int_C \left( G_A \mathbf{(r|r')} I(l') \mathbf{ \hat{l} \cdot \hat{l}' } + \frac{1}{{k_0}^2} \frac{\partial G_A}{\partial l} \frac{\partial I}{\partial l'} \right) \, dl' = 0 [/math]
where GA is the free space Green’s function, I(l) is the unknown linear current in the wire and C is the contour of the wire. and [math]\hat{l}'[/math] are the unit vectors along the wire contour. Note that GA has a singularity when r = r’, which must be either removed or avoided as will be explained later.
Discretization Of Wire Structures
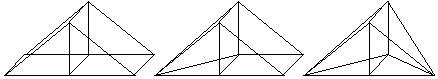
The right choice of the basis functions that are used to represent the elementary currents is very important. It will determine the accuracy and computational efficiency of the resulting numerical solution. Rooftop basis functions are one of the more popular types of basis functions used in a variety of MoM formulations. The simplest rooftop function is the one-dimensional triangular functions defined as in the figure below:
This function provides a linear interpolation of the unknown currents or fields in one dimension. Note that the function vanishes at it two ends. This is a desirable feature for basis functions that represent electric currents on metallic wires as the current must vanish at the two ends of a wire. The total current on the wire can be approximated in a linear fashion by a set of one-dimensional rooftop functions as shown in the figure below:
This can be written as
- [math] I(l) = \sum_{n=1}^N a_n f_n(l) \mathbf{\hat{s}_n} [/math]
where l is the length coordinate along the wire with l=0 at its start point. [math]f_n(l)[/math] is the scaled and translated version of the linear basis function [math]f(l)[/math] shown in the previous figure. [math]\mathbf{\hat{s}_n}[/math] is the unit vector along wire.
Multilayer Green’s Functions
The Green’s functions are the solutions of boundary value problems when they are excited by an elementary source. This is usually assumed to be an infinitesimally small vectorial point source. In order for Green’s functions to be computationally useful, they must have analytical closed forms like a mathematical expression, or one should be able to compute them using a recursive process. It turns out that only very few boundary value problems have closed-form Green’s functions. Planar layered structures with laterally infinite extents are one of those few cases, which can be represented by recursive dyadic Green's functions.
In general, a structure may support both electric (J) and magnetic (M) currents. The total electric (E) and magnetic (H) fields can be expressed in terms of the electric and magnetic currents in the following way:
- [math]E = E^{inc} + \iiint\limits_V \overline{\overline{G}}_{EJ}(r|r') \cdot J(r') \, dv' + \iiint\limits_V \overline{\overline{G}}_{EM}(r|r') \cdot M(r') \, dv'[/math]
- [math]H = H^{inc} + \iiint\limits_V \overline{\overline{G}}_{HJ}(r|r') \cdot J(r') \, dv' + \iiint\limits_V \overline{\overline{G}}_{HM}(r|r') \cdot M(r') \, dv'[/math]
where GEJ, GEM, GHJ, GHM are the dyadic Green’s functions for the electric and magnetic currents due to electric and magnetic current source, respectively, and Ei and Hi are the incident or impressed electric and magnetic fields, respectively. In these equations, r is the position vector of the observation point and r' is the position vector of the source point. V is the volume that contains all the sources and the volume integration is performed with respect to the primed coordinates. The incident or impressed fields provide the excitation of the structure. They may come from an incident plane wave or a gap source on a microstrip line, a short dipole, etc. The complexity of the Green’s functions depends on what is considered as the background structure. If you remove all the unknown currents from the structure, you are left with the background structure.
Planar Integral Equations
To derive a system of integral equations, we enforce the boundary conditions on the integral definitions of the E and H fields as follows:
- [math]L_E(E) = L_E \bigg\{ E^{inc} + \iiint\limits_V \overline{\overline{G}}_{EJ}(r|r') \cdot J(r') \, dv' + \iiint\limits_V \overline{\overline{G}}_{EM}(r|r') \cdot M(r') \, dv' \bigg\} [/math]
- [math]L_H(H) = L_H \bigg\{ H^{inc} + \iiint\limits_V \overline{\overline{G}}_{HJ}(r|r') \cdot J(r') \, dv' + \iiint\limits_V \overline{\overline{G}}_{HM}(r|r') \cdot M(r') \, dv' \bigg\} [/math]
where LE is the boundary value operator for the electric field and LH is the boundary value operator for the magnetic field. For example, LE may require that the tangential components of the Efield vanish on perfect conductors:
- [math] \hat{n} \times \hat{n} \times \mathbf{E} = 0, \quad \mathbf{r} \in PEC [/math]
Or LE and LH may require that the tangential components of the E and H fields be continuous across an aperture in a perfect ground plane:
- [math]\begin{cases} \hat{n} \times \hat{n} \times (\mathbf{E}^+ - \mathbf{E}^-) = 0 \\ \hat{n} \times \hat{n} \times (\mathbf{H}^+ - \mathbf{H}^-) = 0 \end{cases} \quad \Rightarrow \quad \mathbf{M}^+(r) = \mathbf{M}^-(r), \quad r \in PMC [/math]
Given the fact that the dyadic Green’s functions and the incident or impressed fields are all known, one can solve the above system of integral equations to find the unknown currents J and M.
In EM.Picasso, magnetic currents are always surface current with units of V/m. Electric currents, however, can be surface currents with units of A/m as in the case of metallic traces like microstrip lines, or they can be volume currents with units of A/m2 as in the case of perfectly conducting vias. Dielectric inserts are modeled as volume polarization currents that are related to the electric field E in the following manner:
- [math]\mathbf{J}_p(r) = jk_0 Y_0(\varepsilon_r - \varepsilon_b)\mathbf{E}(r)[/math]
where k0 is the free space propagation constant, [math]Y_0 = \tfrac{1}{Z_0} = \tfrac{1}{120\pi}[/math] is the free space intrinsic admittance, εr is the permittivity of the dielectric insert, and εb is the permittivity of its background layer. In a 2.5-D formulation, it is assumed that the volume currents have only a vertical component along the Z direction, and their circumferential components are negligible.
Numerical Solution of Integral Equations
The planar integral equations derived earlier can be solved numerically by discretizing the unknown currents using a proper meshing scheme. The original functional equations are reduced to discretized linear algebraic equations over elementary cells. The unknown quantities are found by solving this system of linear equations, and many other parameters can be computed thereafter. This method of numerical solution of integral equations is known as the Method of Moments (MoM). In this method, the unknown electric and magnetic currents are represented by expansions of basis functions as follows:
- [math]J(r) = \sum_{n=1}^N I_n^{(J)} f_n^{(J)} (r)[/math]
- [math]M(r) = \sum_{k=1}^K V_k^{(M)} f_k^{(M)} (r)[/math]
where [math]f_n^{(J)}[/math] and [math]f_k^{(M)}[/math] are the generalized vector basis functions for the expansion of electric and magnetic currents, respectively, and [math]I_n^{(J)}[/math] and [math]V_k^{(M)}[/math] are the unknown amplitudes of these basis functions, which have to be determined. Substituting these expansions into the integral equations generates a set of discretized integral equations, which can further be converted to a system of linear algebraic equations. This is accomplished by testing the discretized integral equations using the a set of test functions. In the method of moments, the Galerkin technique is typically used, which chooses the expansion basis functions as test functions. This leads to the following linear system:
- [math] \begin{bmatrix} Z^{(EJ)} & T^{(EM)} \\ U^{(HJ)} & Y^{(HM)} \end{bmatrix} \cdot \begin{bmatrix} I^{(J)} \\ V^{(M)} \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} V^{(E)} \\ I^{(M)} \end{bmatrix} [/math]
where
- [math] Z_{ij}^{(EJ)} = \iiint\limits_{V_i} dv f_i^{(J)}(r) \cdot \iiint\limits_{V_j} dv' \overline{\overline{G}}_{EJ}(r|r') \cdot f_i^{(J)}(r')[/math]
and
- [math] V_i^{(E)} = \iiint\limits_{V_i} dv f_i^{(J)}(r) \cdot E^{inc}(r) [/math]
- [math] I_i^{(H)} = \iiint\limits_{V_i} dv f_i^{(M)}(r) \cdot H^{inc}(r) [/math]
Similar expressions can be derived for the T(EM), U(HJ) and Y(HM)elements of the MoM matrix.
Discretization of Electric & Magnetic Currents
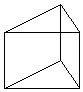
The right choice of the basis functions to represent the elementary currents is very important. It will determine the accuracy and computational efficiency of the resulting numerical solution. Rooftop basis functions are one of the most popular types of basis functions used in a variety of MoM formulations. The surface currents (whether electric or magnetic) are discretized using 2D rooftop basis functions shown in the figure below:
The rooftop basis functions are defined over two adjacent cells with a common edge of length. If the two cells are triangular, then the so-called RWG functions are obtained. It is also possible to define rooftop functions over two adjacent rectangular cells or two adjacent rectangular and triangular cells with a common edge. On a rectangular cell, the function is defined as having a (descending or ascending) linear profile in one direction and a constant profile in the other perpendicular direction.
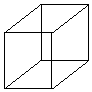
The volume polarization currents in 2.5-D MoM have a vertical direction along the Z-axis. These are discretized using prismatic basis functions that have either a rectangular or triangular base with a constant profile along the Z-axis.
Prismatic basis functions built over single triangular and rectangular cells.
The Rectangular Mesh Advantage
Rectangular cells offer a major advantage over triangular cells for numerical MoM simulation of planar structures. This is due to the fact that the dyadic Green's functions of planar layered background structures are space-invariant on the transverse plane. Recall that the elements of the moment matrix are given by the following equation:
- [math] Z_{ij}^{(\mu \nu)} = \iiint_{V_i} d\nu f_i^{(\mu)}(r) \cdot \iiint_{V_j}d\nu ' \overline{\overline{G}}_{\mu \nu}(r|r') \cdot f_j^{(v)}(r') [/math]
where the spatial-domain dyadic Green's functions are a function of the observation and source coordinates, rand r' . The MoM matrix elements can indeed be interpreted as interactions between two elementary basis functions fi(r) and fj(r') on that particular background structure. The spatial-domain dyadic Green's functions can themselves be expressed in terms of the spectral-domain dyadic Green's functions as follows:
- [math] \overline{\overline{G}}_{\mu \nu}(r|r') = \frac{1}{(2\pi)^2} \int\limits_{-\infty}^{\infty} \int\limits_{-\infty}^{\infty} \tilde{\overline{\overline{G}}}_{\mu \nu} (k_p, z|z') e^{-j[k_x(x-x')+k_y(y-y')]} \, dk_x \, dk_y , \quad {k_p}^2 = {k_x}^2 + {k_y}^2 [/math]
where the doubly infinite integration is performed with respect to the spectral variables kx and ky. As can be seen from the above expression, the spatial-domain dyadic Green's functions are functions of z, z', as well as (x-x') and (y-y'). The MoM matrix elements can now be transformed into the spectral domain as
- [math] Z_{ij}^{(\mu \nu)} = \dfrac{1}{(2\pi)^2} \int\limits_{-\infty}^{\infty} \int\limits_{-\infty}^{\infty} \tilde{f}_i^{(\mu)} (k_x, k_y) \cdot \tilde{\overline{\overline{G}}}_{\mu \nu} (k_{\rho}, z|z') \cdot \tilde{f}_j^{(\nu)} (k_x, k_y) \, dk_x \, dk_y [/math]
where the tilde symbol signifies the Fourier transform of a function defined as
- [math] \tilde{f}(k_x, k_y) = \dfrac{1}{(2\pi)^2} \int\limits_{-\infty}^{\infty} \int\limits_{-\infty}^{\infty} f(x,y) e^{j(k_x x + k_y y)} \, dx \, dy [/math]
Rectangular cells have simple Fourier transforms. The rooftop basis functions are triangular functions in the direction of current flow and constant in the perpendicular direction. This means that their Fourier transform is a product of a sinc-squared function along one spectral direction and a sinc function along the other. You can see from the figure below that if one deals with a rectangular mesh of identical cells (all equal and parallel), then the interactions among the rooftop basis functions become a functions of the index differences and not the absolute indices:
- [math] Z_{(i,k)|(j,l)} = Z \Big\langle f_{i,k}(x,y)| f_{j,l}(x', y') \Big\rangle = Z_{(i-j)|(k-l)} [/math]
In the above equation, the vectorial rooftop basis functions have explicit, double indices: i and k along the local X and Y directions, respectively, for the test (observation) basis function, and j and l along the local X and Y directions, respectively, for the expansion (source) basis function. Thus, uniform rectangular cells, i.e. structured rectangular cells of identical size aligned in the same direction, can speed up the planar MoM simulation significantly due to these symmetry and the invariance properties. For example, all the self-interactions are identical regardless of the location of a rooftop basis function. This reduces the matrix fill process for a total of N rooftop basis functions from an N2 process to one of order N.
Pairs of rooftop basis functions that have identical MoM interactions.
Computing The Near Fields in Planar MoM
Once all the current distributions are known in a planar structure, the electric and magnetic fields can be calculated everywhere in that structure using the dyadic Greens's functions of the background structure:
- [math] \begin{align} \mathbf{E(r) = E_{inc}(r)} + & \sum_{n=1}^N I_n^{(J)} \iiint_V \overline{\overline{G}}_{EJ}(r|r') \cdot f_n^{(J)}(r') \, d\nu' + \\ & \sum_{k=1}^K V_n^{(M)} \iiint_V \overline{\overline{G}}_{EM}(r|r') \cdot f_k^{(M)}(r') \, d\nu' \end{align} [/math]
- [math] \begin{align} \mathbf{H(r) = H_{inc}(r)} + & \sum_{n=1}^N I_n^{(J)} \iiint_V \overline{\overline{G}}_{HJ}(r|r') \cdot f_n^{(J)}(r') \, d\nu' + \\ & \sum_{k=1}^K V_n^{(M)} \iiint_V \overline{\overline{G}} {HM}(r|r') \cdot f_k^{(M)}(r') \, d\nu' \end{align} [/math]
The above equations can be cast into the spectral domain as follows:
- [math] \begin{align} \mathbf{E(r) = E_{inc}(r)} + \frac{1}{(2\pi)^2} \int\limits_{-\infty}^{\infty} \int\limits_{-\infty}^{\infty} \bigg[ & \sum_{n=1}^N I_n^{(J)} \tilde{\overline{\overline{G}}}_{EJ}(k_{\rho}, z|z') \cdot \tilde{f}_n^{(J)}(k_x, k_y) + \\ & \sum_{k=1}^K V_n^{(M)} \tilde{\overline{\overline{G}}}_{EM}(k_{\rho}, z|z') \cdot \tilde{f}_k^{(M)}(k_x, k_y) \bigg] \, dk_x \, dk_y \end{align} [/math]
- [math] \begin{align} \mathbf{H(r) = H_{inc}(r)} + \frac{1}{(2\pi)^2} \int\limits_{-\infty}^{\infty} \int\limits_{-\infty}^{\infty} \bigg[ & \sum_{n=1}^N I_n^{(J)} \tilde{\overline{\overline{G}}}_{HJ}(k_{\rho}, z|z') \cdot \tilde{f}_n^{(J)}(k_x, k_y) + \\ & \sum_{k=1}^K V_n^{(M)} \tilde{\overline{\overline{G}}}_{HM}(k_{\rho}, z|z') \cdot \tilde{f}_k^{(M)}(k_x, k_y) \bigg] \, dk_x \, dk_y \end{align} [/math]
Calculation of the near-zone fields (fields at the vicinity of the unknown currents) is done at the post-processing stage and in a Cartesian coordinate systems. These calculations involve doubly infinite spectral-domain integrals, which are computed numerically. As was mentioned earlier, EM.Cube's planar MoM engine rather uses a polar integration scheme, where the radial spectral variable kρ is integrated over the interval [0, Mk0], M being a large enough number to represent infinity, and the angular spectral variable t is integrated over the interval [0, 2π]. You also saw some of the numerical parameters related to this spectral-domain integration scheme.
Computing The Far Fields in Planar MoM
Unlike differential-based methods, MoM simulators do not need a radiation box to calculate the far field data. The far-zone fields are calculated directly by integrating the currents on the traces and across the embedded objects using the asymptotic form of the background structure’s dyadic Green's functions:
- [math] \mathbf{E^{ff}(r)} = \iiint_V \mathbf{ \overline{\overline{G}}_{EJ,ff}(r|r') \cdot J(r') } \, d\nu ' + \iiint_V \mathbf{ \overline{\overline{G}}_{EM,ff}(r|r') \cdot M(r') } \, d\nu '[/math]
- [math] \mathbf{H^{ff}(r)} = \dfrac{1}{\eta_0} \mathbf{ \hat{r} \times E^{ff}(r) }[/math]
where η0 = 120π is the characteristic impedance of the free space. As can be seen from the above equations, the far fields have the form of a TEM wave propagating in the radial direction away from the origin of coordinates. This means that the far-field magnetic field is always perpendicular to the electric field and the propagation vector, which in this case happens to be the radial unit vector in the spherical coordinate system. In other words, one only needs to know the far-zone electric field and can easily calculate the far-zone magnetic field from it. In EM.Cube's mixed potential integral equation formulation, the far-zone electric field can be expressed in terms of the asymptotic form of the vector electric and magnetic potentials A and F:
- [math]\mathbf{E^{ff}}(x,y,z) = j k_0 \eta_0 \hat{r} \times [\hat{r} \times \mathbf{A}(r \to \infty)] + j k_0 \hat{r} \times \mathbf{F}(r \to \infty)[/math]
The asymptotic form of these vector potentials are calculated using the "Method of Stationary Phase" when k0r → ∞. In that case, one can use the approximation:
- [math] k_0 |\mathbf{r-r'}| \approx k_0 (r - \mathbf{\hat{r} \cdot r'}) [/math]
After applying the stationary phase method, one can extract the spherical wave factor exp(-jk0r)/r from the far-zone electric field, leaving the rest as functions of the spherical angles θ and φ. In other words, the far field is normalized to r, the distance from the field observation point to the origin. It is customary to express the far fields in spherical components Eθ and Eφ. Note that the outward propagating, TEM-type, far fields do not have radial components, i.e. Er = 0.
- [math] \mathbf{E_{\theta}}(\theta, \phi) = \cos\theta \cos\phi E_x + \cos\theta \sin\phi E_y - \sin\theta E_z [/math]
- [math] \mathbf{E_{\phi}}(\theta, \phi) = -\sin\phi E_x + \cos\phi E_y [/math]
Periodic Planar MoM Simulation
In the case of an infinite periodic planar structure, the field equations can be written in the following form:
- [math] \mathbf{E(r) = E^{inc}(r)} + \sum_{m=-\infty}^{\infty} \sum_{n=-\infty}^{\infty} \bigg[ \iiint_V \mathbf{ \overline{\overline{G}}_{EJ}(r|r') \cdot J_{mn}(r') } \, d\nu' + \iiint_V \mathbf{ \overline{\overline{G}}_{EM}(r|r') \cdot M_{mn}(r') } \, d\nu' \bigg] [/math]
- [math] \mathbf{H(r) = H^{inc}(r)} + \sum_{m=-\infty}^{\infty} \sum_{n=-\infty}^{\infty} \bigg[ \iiint_V \mathbf{ \overline{\overline{G}}_{HJ}(r|r') \cdot J_{mn}(r') } \, d\nu' + \iiint_V \mathbf{ \overline{\overline{G}}_{HM}(r|r') \cdot M_{mn}(r') } \, d\nu' \bigg] [/math]
where
- [math]\mathbf{J_{mn}(r) = J_{mn}}(x,y,z) = \mathbf{J_{00}}(x+m S_x, y+n S_y, z) e^{j(m k_{x00} S_x + n k_{y00} S_y)}[/math]
- [math]\mathbf{M_{mn}(r) = M_{mn}}(x,y,z) = \mathbf{M_{00}}(x+m S_x, y+n S_y, z) e^{j(m k_{x00} S_x + n k_{y00} S_y)}[/math]
and
- [math] -\infty \lt m, n \lt \infty [/math]
In the above equations, [math]\mathbf{J_{00}(r)}[/math] and [math]\mathbf{M_{00}(r)}[/math] are the periodic unit cell's electric and magnetic currents that are repeated everywhere in space on a rectangular lattice with periods Sx and Sy along the X and Y directions, respectively. [math]k_{x00}[/math] and [math]k_{y00}[/math] are the periodic propagation constants along the X and Y directions, respectively, and they are given by:
- [math] k_{x00} = k_0 \sin\theta \cos\phi [/math]
- [math] k_{y00} = k_0 \sin\theta \sin\phi [/math]
where θ and φ are the beam scan angles in the case of periodic excitation of lumped sources, or they are the spherical angles of incidence in the case of a plane wave source illuminating the periodic structure. Using the infinite summations, one can define periodic dyadic Green's functions in the spectral domain in the following manner:
- [math] \mathbf{ \overline{\overline{G}}_{\mu \nu}^{PER} (r|r') } = \frac{1}{S_x S_y} \sum_{m=-\infty}^{\infty} \sum_{n=-\infty}^{\infty} \mathbf{ \tilde{\overline{\overline{G}}}_{\mu \nu} } (k_x, k_y, z|z') e^{-j[k_{xm}(x-x') + k_{yn}(y-y')]} [/math]
where
- [math] k_{xm} = k_{x00} + \frac{2\pi m}{S_x} \quad \text{and} \quad k_{ym} = k_{y00} + \frac{2\pi m}{S_y} [/math]
The above doubly infinite periodic Green's functions are said to be expressed in terms of "Floquet Modes". The exact formulation involves an infinite set of these periodic Floquet modes. During the MoM matrix fill process for a periodic structure, a finite number of Floquet modes are calculated. By default, EM.Cube's planar MoM engine considers Mx = My = 25. This implies a total of 51 modes along the X direction and a total of 51 modes along the Y direction, or a grand total of 512 = 2,601 Floquet modes. You can increase the number of Floquet modes for your project from the Planar MoM Engine Settings Dialog. In the section titled "Periodic Simulation", you can change the values of Number of Floquet Modes in the two boxes designated X and Y.
EM.Cube's Linear System Solvers
After the MoM impedance matrix [Z] (not to be confused with the impedance parameters) and excitation vector [V] have been computed through the matrix fill process, the planar MoM simulation engine is ready to solve the system of linear equations:
- [math] \mathbf{[Z]}_{N\times N} \cdot \mathbf{[I]}_{N\times 1} = \mathbf{[V]}_{N\times 1} [/math]
where [I] is the solution vector, which contains the unknown amplitudes of all the basis functions that represent the unknown electric and magnetic currents of finite extents in your planar structure. In the above equation, N is the dimension of the linear system and equal to the total number of basis functions in the planar mesh. EM.Cube's linear solvers compute the solution vector[I] of the above system. You can instruct EM.Cube to write the MoM matrix and excitation and solution vectors into output data files for your examination. To do so, check the box labeled "Output MoM Matrix and Vectors" in the Matrix Fill section of the Planar MoM Engine Settings dialog. These are written into three files called mom.dat1, exc.dat1 and soln.dat1, respectively.
There are a large number of numerical methods for solving systems of linear equations. These methods are generally divided into two groups: direct solvers and iterative solvers. Iterative solvers are usually based on matrix-vector multiplications. Direct solvers typically work faster for matrices of smal to medium size (N<3,000). EM.Picasso offers five linear solvers:
- LU Decomposition Method
- Biconjugate Gradient Method (BiCG)
- Preconditioned Stabilized Biconjugate Gradient Method (BCG-STAB)
- Generalized Minimal Residual Method (GMRES)
- Transpose-Free Quasi-Minimum Residual Method (TFQMR)
Of the above list, LU is a direct solver, while the rest are iterative solvers. BiCG is a relatively fast iterative solver, but it works only for symmetric matrices. You cannot use BiCG for periodic structures or planar structures that contain both metal and slot traces at different planes, as their MoM matrices are not symmetric. The three solvers BCG-STAB, GMRES and TtFQMR work well for both symmetric and asymmetric matrices and they also belong to a class of solvers called Krylov Sub-space Methods. In particular, the GMRES method always provides guaranteed unconditional convergence.
EM.Picasso, by default, provides a "Automatic" solver option that picks the best method based on the settings and size of the numerical problem. For linear systems with a size less than N = 3,000, the LU solver is used. For larger systems, BiCG is used when dealing with symmetric matrices, and GMRES is used for asymmetric matrices. If the size of the linear system exceeds N = 15,000, the sparse version of the iterative solvers is used, utilizing a row-indexed sparse storage scheme. You can override the automatic solver option and manually set you own solver type. This is done using the Solver Type drop-down list in the "Linear System Solver" section of the Planar MoM Engine Settings dialog. There are also a number of other parameters related to the solvers. The default value of Tolerance of Iterative Solver is 1E-3, which can be increased for more ill-conditioned systems. The maximum number of iterations is usually expressed as a multiple of the systems size. The default value of Max No. of Solver Iterations / System Size is 3. For extremely large systems, sparse versions of iterative solvers are used. In this case, the elements of the matrix are thresholded with respect to the larges element. The default value of Threshold for Sparse Solver is 1E-6, meaning that all the matrix elements whose magnitude is less than 1E-6 times the large matrix elements are set equal to zero. There are two more parameters that are related to the Automatic Solver option. These are " User Iterative Solver When System Size >" with a default value of 3,000 and " Use Sparse Storage When System Size > " with a default value of 15,000. In other words, you control the automatic solver when to switch between direct and iterative solvers and when to switch to the sparse version of iterative solvers.