Difference between revisions of "EM.Illumina"
Kazem Sabet (Talk | contribs) (→Building the Physical Structure in EM.Illumina) |
Kazem Sabet (Talk | contribs) (→EM.Illumina's Excitation Sources) |
||
| Line 188: | Line 188: | ||
Click on each category to learn more details about it in the [[Glossary of EM.Cube's Excitation Sources]]. | Click on each category to learn more details about it in the [[Glossary of EM.Cube's Excitation Sources]]. | ||
| − | A short Hertzian dipole is the simplest way of exciting a structure in EM.Illumina. A short dipole source acts like an infinitesimally small ideal current source. The total radiated power by your dipole source is calculated and displayed in Watts in its property dialog. Your physical structure in EM.Illumina can also be excited by an incident plane wave. In particular, you need a plane wave source to compute the radar cross section of a target. The direction of incidence is defined by the θ and φ angles of the unit propagation vector in the spherical coordinate system. The default values of the incidence angles are θ = 180° and φ = 0° corresponding to a normally incident plane wave propagating along the -Z direction with a +X-polarized E-vector. Huygens sources are virtual equivalent sources that capture the radiated electric and magnetic fields from another structure that was previously analyzed in another [[EM.Cube]] computational module. | + | A short Hertzian dipole is the simplest way of exciting a structure in EM.Illumina. A short dipole source acts like an infinitesimally small ideal current source. The total radiated power by your dipole source is calculated and displayed in Watts in its property dialog. Your physical structure in EM.Illumina can also be excited by an incident plane wave. In particular, you need a plane wave source to compute the radar cross section of a target. The direction of incidence is defined by the θ and φ angles of the unit propagation vector in the spherical coordinate system. The default values of the incidence angles are θ = 180° and φ = 0° corresponding to a normally incident plane wave propagating along the -Z direction with a +X-polarized E-vector. Huygens sources are virtual equivalent sources that capture the radiated electric and magnetic fields from another structure that was previously analyzed in another [[EM.Cube]] computational module. |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
== EM.Illumina's Simulation Data & Observables == | == EM.Illumina's Simulation Data & Observables == | ||
Revision as of 02:45, 6 September 2016
A Fast Asymptotic Solver For Large-Scale Scattering Problems
Contents
- 1 Product Overview
- 2 EM.Illumina Features at a Glance
- 3 A Physical Optics Simulation Primer
- 4 Building the Physical Structure in EM.Illumina
- 5 EM.Illumina's Excitation Sources
- 6 EM.Illumina's Simulation Data & Observables
- 7 Discretizing the Physical Structure in EM.Illumina
- 8 Running PO Simulations in EM.Illumina
Product Overview
EM.Illumina in a Nutshell
EM.Illumina is a 3D electromagnetic simulator for modeling large free-space structures. It features a high frequency asymptotic solver based on Physical Optics (PO) for simulation of electromagnetic scattering from large metallic structures and impedance surfaces. You can use EM.Illumina to compute the radar cross section (RCS) of large target structures like aircraft or vehicles or simulate the radiation of antennas in the presence of large platforms.
EM.Illumina provides a computationally efficient alternative for extremely large structures when a full-wave solution becomes prohibitively expensive. Based on a high frequency asymptotic physical optics formulation, it assumes that an incident source generates currents on a metallic structure, which in turn reradiate into the free space. A challenging step in establishing the PO currents is the determination of the lit and shadowed points on complex scatterer geometries. Ray tracing from each source to the points on the scatterers to determine whether they are lit or shadowed is a time consuming task. To avoid this difficulty, EM.Illumina's simulator uses a novel Iterative Physical Optics (IPO) formulation, which automatically accounts for multiple shadowing effects.The IPO technique can effectively capture dominant, near-field, multiple scattering effects from electrically large targets.
![]() Click here to access EM.Illumina Tutorial Gateway.
Click here to access EM.Illumina Tutorial Gateway.
EM.Illumina as the Physical Optics Module of EM.Cube
EM.Illumina is the high-frequency, asymptotic Physical Optics Module of EM.Cube, a comprehensive, integrated, modular electromagnetic modeling environment. EM.Illumina shares the visual interface, 3D parametric CAD modeler, data visualization tools, and many more utilities and features collectively known as CubeCAD with all of EM.Cube's other computational modules.
EM.Illumina's simulator is seamlessly interfaced with EM.CUBE's other simulattion engines. This module is the ideal place to define Huygens sources. These are based on Huygens surface data that are generated using a full-wave simulator like EM.Tempo, EM.Picasso or EM.Libera.
![]() Click here to learn more about EM.Cube Modeling Environment.
Click here to learn more about EM.Cube Modeling Environment.
![]() Click here to learn more about the basic functionality of CubeCAD.
Click here to learn more about the basic functionality of CubeCAD.
EM.Illumina Features at a Glance
Structure Definition
- Metal (PEC) solids and surfaces in free space
- PMC and impedance surfaces in free space
- Import STL CAD files as native polymesh structures
- Huygens blocks imported from full-wave modules
Sources
- Short dipoles
- Import previously generated wire mesh solution as collection of short dipoles
- Plane wave excitation with linear and circular polarizations
- Multi-ray excitation capability (ray data imported from EM.Terrano or external files)
- Huygens sources imported from PO or other modules with arbitrary rotation and array configuration
Mesh Generation
- Surface triangular mesh with control over tessellation parameters
- Local mesh editing of polymesh objects
Physical Optics Simulation
- Physical Optics solution of metal scatterers and impedance surfaces
- Conventional Geometrical Optics - Physical Optics (GOPO) solver
- Novel iterative PO solver for fast simulation of multiple shadowing effects and multi-bounce reflections
- Calculation of near fields, far fields and scattering cross section (bistatic and monostatic RCS)
- Frequency and angular sweeps with data animation
- Parametric sweep with variable object properties or source parameters
- Multi-variable and multi-goal optimization of structure
- Remote simulation capability
- Both Windows and Linux versions of PO simulation engine available
Data Generation & Visualization
- Electric and magnetic surface current distributions on metallic or impedance surfaces
- Near field intensity plots (vectorial - amplitude & phase)
- Huygens surface data generation for use in PO or other EM.Cube modules
- Far field radiation patterns: 3D pattern visualization and 2-D Cartesian and polar graphs
- Bi-static and monostatic radar cross section: 3D visualization and 2D graphs
- Custom output parameters defined as mathematical expressions of standard outputs
A Physical Optics Simulation Primer
Physical Optics as an Asymptotic Technique
Asymptotic methods are usually valid at high frequencies as k0 R = 2π R/λ0 >> 1, where R is the distance between the source and observation points, k0 is the free-space propagation constant and λ0 is the free-space wavelength. Under such conditions, electromagnetic fields and waves start to behave more like optical fields and waves. Asymptotic methods are typically inspired by optical analysis. Two important examples of asymptotic methods are the Shoot-and-Bounce-Rays (SBR) method and Physical Optics (PO). The SBR method is a ray tracing method based on Geometrical Optics (GO) and forms the basis of the simulation engine of EM.Terrano.
In the Physical Optics (PO) method, a scatterer surface is illuminated by an incident source, and it is modeled by equivalent electric and magnetic surface currents. This concept is based on the fundamental equivalence theorem of electromagnetics. According to the Huygens principle, the equivalent electric and magnetic surface currents are derived from the tangential components of magnetic and electric fields on a given closed surface, respectively. A simple PO analysis involves only perfect electric conductors, and only electric surface currents related to the tangential magnetic fields are considered. EM.Illumina assumes that a source like a short dipole radiator or an incident plane wave induces currents on the surface of the metallic structure. These induced currents, in turn, reradiate into the free space and produce the scattered fields. In the case of an impedance surface, both surface electric and magnetic currents are induced on the surface of the scatterer.
A challenging step in establishing the PO currents is the determination of the lit and shadow points on complex scatterer geometries. The conventional physical optics method (GO-PO) uses geometrical optics ray tracing from each source to the points on the scatterers to determine whether they fall into the lit or shadow regions. But this can become a time consuming task as the size of the computational problem grows. Besides GO-PO, EM.Illumina also offers a novel Iterative Physical Optics (IPO) solver, which dispenses with the GO part of GO-PO and automatically accounts for multiple shadowing effects using an iterative algorithm.
![]() Click here to lean more about the Theory of Physical Optics.
Click here to lean more about the Theory of Physical Optics.
Advantages & Limitations of EM.Illumina's PO Solver
EM.Illumina provides a computationally efficient alternative to full-wave solutions for extremely large structures when full-wave analysis becomes prohibitively expensive. For simple scatterer geometries, EM.Illumina's GO-PO solver is fairly adequate. But for complex geometries that involve multiple shadowing effects, the IPO solver must be utilized. The IPO technique can effectively capture dominant, near-field, multiple scattering effects from electrically large targets with concave surfaces. You have to remember that Physical Optics is a surface simulator. This is not a problem for PEC and PMC objects, which have zero internal fields, or even impedance surfaces, where you can satisfy the boundary conditions on one side of a surface only. PO analysis cannot handle the fields inside dielectric objects. Additionally, most coupling effects between adjacent scatterers are ignored.
Building the Physical Structure in EM.Illumina
The Variety of Surface Types in EM.Illumina
EM.Illumina organizes physical objects by their surface type. Any object in EM.Illumina is assumed to be made of one of the three surface types:
| Material Type | Applications | Geometric Object Types Allowed |
|---|---|---|
| Perfect Electric Conductor (PEC) Surface | Modeling perfect metal surfaces | Solid and surface objects |
| Perfect Magnetic Conductor (PMC) Surface | Modeling perfect magnetic surfaces | Solid and surface objects |
| Impedance Surface | Modeling impedance surfaces as an equivalent to the surface of dielectric objects | Solid and surface objects |
Click on each category to learn more details about it in the Glossary of EM.Cube's Materials & Physical Object Types.
EM.Illumina can only handle surface and solid CAD objects. Only the outer surface of solid objects is considered in the PO simulation. No line or curve objects are allowed in the project workspace; or else, they will be ignored during the PO simulation.
Organizing Geometric Objects by Surface Type
You can define several PEC, PMC or impedance surface groups with different colors and impedance values. All the objects created and drawn under a group share the same color and other properties. Once a new surface node has been created on the navigation tree, it becomes the "Active" surface group of the project workspace, which is always listed in bold letters. When you draw a new CAD object such as a Box or a Sphere, it is inserted under the currently active surface type. There is only one surface group that is active at any time. Any surface type can be made active by right clicking on its name in the navigation tree and selecting the Activate item of the contextual menu. It is recommended that you first create surface groups, and then draw new objects under the active surface group. However, if you start a new EM.Illumina project from scratch, and start drawing a new object without having previously defined any surface groups, a new default PEC surface group is created and added to the navigation tree to hold your new CAD object.
![]() Click here to learn more about Moving Objects among Surface Groups.
Click here to learn more about Moving Objects among Surface Groups.
| |
In EM.Cube, you can import external CAD models (such as STEP, IGES, STL models, etc.) only to CubeCAD. From CubeCAD, you can then move the imported objects to EM.Illumina. |
EM.Illumina's Excitation Sources
EM.Illumina provides three types of sources for the excitation of your physical optics simulation:
| Source Type | Applications | Restrictions |
|---|---|---|
| Hertzian Short Dipole Source | Almost omni-directional physical radiator | None, stand-alone source |
| Plane Wave Source | Used for modeling scattering | None, stand-alone source |
| Huygens Source | Used for modeling equivalent sourced imported from other EM.Cube modules | Imported from a Huygens surface data file |
Click on each category to learn more details about it in the Glossary of EM.Cube's Excitation Sources.
A short Hertzian dipole is the simplest way of exciting a structure in EM.Illumina. A short dipole source acts like an infinitesimally small ideal current source. The total radiated power by your dipole source is calculated and displayed in Watts in its property dialog. Your physical structure in EM.Illumina can also be excited by an incident plane wave. In particular, you need a plane wave source to compute the radar cross section of a target. The direction of incidence is defined by the θ and φ angles of the unit propagation vector in the spherical coordinate system. The default values of the incidence angles are θ = 180° and φ = 0° corresponding to a normally incident plane wave propagating along the -Z direction with a +X-polarized E-vector. Huygens sources are virtual equivalent sources that capture the radiated electric and magnetic fields from another structure that was previously analyzed in another EM.Cube computational module.
EM.Illumina's Simulation Data & Observables
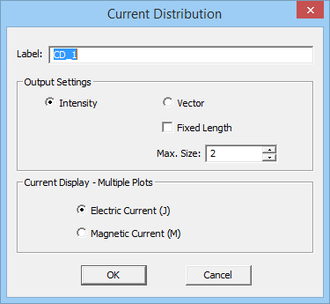
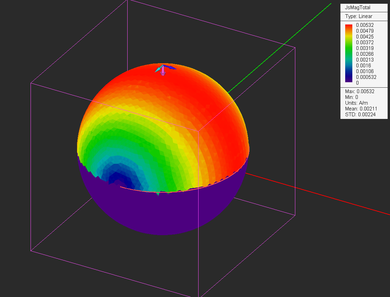
EM.Illumina does not produce any output data on its own unless you define one or more observables for your simulation project. The primary output data in the Physical Optics method are the electric and magnetic surface current distributions on the surface of your structure. At the end of a PO simulation, EM.Illumina generates a number of output data files that contain all the computed simulation data. Once the current distributions are known, EM.Illumina can compute near-field distributions as well as far-field quantities such as radiation patterns and radar cross section (RCS).
EM.Illumina currently provides the following observables:
| Simulation Data Type | Observable Type | Applications | Restrictions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Current Distribution Maps | Current Distribution | Computing electric surface current distribution on PEC and impedance surfaces and magnetic surface current distribution on PMC and impedance surfaces | None |
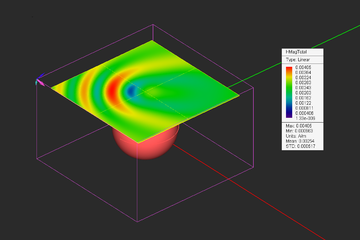
| Near-Field Distribution Maps | Near-Field Sensor | Computing electric and magnetic field components on a specified plane in the frequency domain | None |
| Far-Field Radiation Characteristics | Far-Field Radiation Pattern | Computing the radiation pattern and additional radiation characteristics such as directivity, axial ratio, side lobe levels, etc. | None |
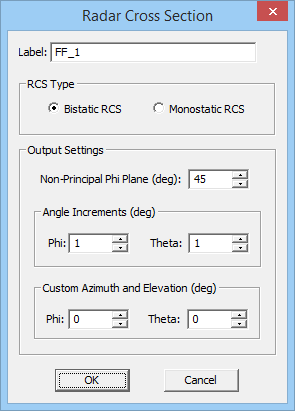
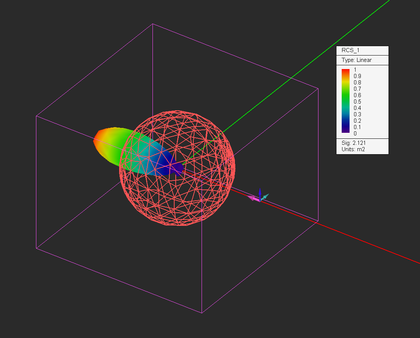
| Far-Field Scattering Characteristics | Radar Cross Section (RCS) | Computing the bistatic and monostatic RCS of a target | Requires a plane wave source |
| Huygens Surface | Huygens Surface | Collecting tangential field data on a box to be used later as a Huygens source in other EM.Cube modules | None |
Click on each category to learn more details about it in the Glossary of EM.Cube's Simulation Observables.
Current distributions are visualized on the surface of PO mesh cells, and the magnitude and phase of the electric and magnetic surface currents are plotted for all the objects. A single current distribution node in the navigation tree holds the current distribution data for all the objects in the project workspace. Since the currents are plotted on the surface of the individual mesh cells, some parts of the plots may be blocked by and hidden inside smooth and curved objects. To be able to view those parts, you may have to freeze the obstructing objects or switch to the mesh view mode.
EM.Illumina allows you to visualize the near fields at a predefined field sensor plane of arbitrary dimensions. Calculation of near fields is a post-processing process and may take a considerable amount of time depending on the resolution that you specify.
![]() Click here to learn more about Defining a Field Sensor Observable.
Click here to learn more about Defining a Field Sensor Observable.
![]() Click here to learn more about Visualizing 3D Near Field Maps.
Click here to learn more about Visualizing 3D Near Field Maps.
You need to define a far field observable if you want to plot the radiation patterns of your physical structure. After a PO simulation is finished, three 3D radiation patterns plots are displayed in the project workspace and are overlaid on your physical structure. These are the Theta and Phi components of the far-zone electric fields as well as the total far field.
![]() Click here to learn more about Far Field Observables.
Click here to learn more about Far Field Observables.
![]() Click here to learn more about Visualizing 3D Radiation Patterns.
Click here to learn more about Visualizing 3D Radiation Patterns.
![]() Click here to learn more about Plotting 2D Radiation Graphs.
Click here to learn more about Plotting 2D Radiation Graphs.
When your physical structure is excited by a plane wave source, the calculated far field data indeed represent the scattered fields. EM.Illumina can calculate two types of RCS for each structure: Bi-Static RCS and Mono-Static RCS. In bi-static RCS, the structure is illuminated by a plane wave at incidence angles θ0 and φ0, and the RCS is measured and plotted at all θ and φ angles. In mono-static RCS, the structure is illuminated by a plane wave at incidence angles θ0 and φ0, and the RCS is measured and plotted at the echo angles 180°-θ0; and φ0. It is clear that in the case of mono-static RCS, the PO simulation engine runs an internal angular sweep, whereby the values of the plane wave incidence angles θ and φ are varied over the entire intervals [0°, 180°] and [0°, 360°], respectively, and the backscatter RCS is recorded.
To calculate RCS, first you have to define an RCS observable instead of a radiation pattern. At the end of a PO simulation, the thee RCS plots σθ, σφ, and σtot are added under the far field section of the navigation tree. Keep in mind that computing the 3D mono-static RCS may take an enormous amount of computation time.
![]() Click here to learn more about Computing Radar Cross Section.
Click here to learn more about Computing Radar Cross Section.
![]() Click here to learn more about Plotting 2D RCS Graphs.
Click here to learn more about Plotting 2D RCS Graphs.
Discretizing the Physical Structure in EM.Illumina
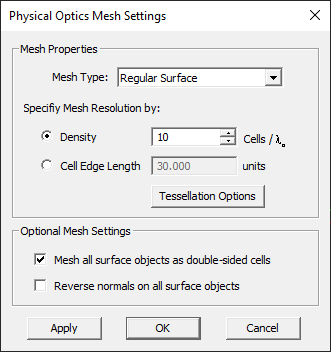
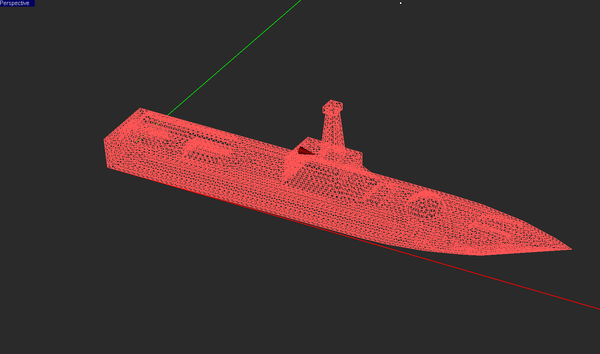
EM.Illumina uses a triangular surface mesh to discretize the structure of your project workspace. The mesh generating algorithm tries to generate regularized triangular cells with almost equal surface areas across the entire structure. You can control the cell size using the "Mesh Density" parameter. By default, the mesh density is expressed in terms of the free-space wavelength. The default mesh density is 10 cells per wavelength. In the Physical Optics method, the electric and magnetic surface currents, J and M, are assumed to be constant on the surface of each triangular cell. On flat surfaces, the unit normal vectors to all the cells are identical. Incident plane waves or other relatively uniform source fields induce uniform PO currents on all these cells. Therefore, a high resolution mesh may not be necessary on flat surface or faces. Accurate discretization of curved objects like spheres or ellipsoids, however, requires a high mesh density.
Since EM.Illumina is a surface simulator, only the exterior surface of solid CAD objects is discretized, as the interior volume is not taken into account in a PO analysis. By contrast, surface CAD objects are assumed to be double-sided. In other words, the default PO mesh of a surface object consists of coinciding double cells, one representing the upper or positive side and the other representing the lower or negative side. This may lead to a very large number of cells. EM.Illumina's mesh generator has settings that allow you to treat all mesh cells as double-sided or all single-sided. You can do that in the Mesh Settings dialog by checking the boxes labeled All Double-Sided Cells and All Single-Sided Cells. This is useful when your project workspace contains well-organized and well-oriented surface CAD objects only. In the single-sided case, it is very important that all the normals to the cells point towards the source. Otherwise, your surfaces fall in the shadow region, and no currents will be computed on them. By checking the box labeled Reverse Normal, you instruct EM.Illumina to reverse the direction of the normal vectors globally at the surface of all the cells.
![]() Click here to learn more about EM.Illumina's Triangular Surface Mesh Generator .
Click here to learn more about EM.Illumina's Triangular Surface Mesh Generator .
Running PO Simulations in EM.Illumina
EM.Illumina's Simulation Modes
Once you have set up your structure in EM.Illumina, have defined sources and observables and have examined the quality of the structure's mesh, you are ready to run a Physical Optics simulation. EM.Illumina offers five simulation modes:
| Simulation Mode | Usage | Number of Engine Runs | Frequency | Restrictions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single-Frequency Analysis | Simulates the physical structure "As Is" | Single run | Runs at the center frequency fc | None |
| Frequency Sweep | Varies the operating frequency of the PO solver | Multiple runs | Runs at a specified set of frequency samples | None |
| Parametric Sweep | Varies the value(s) of one or more project variables | Multiple runs | Runs at the center frequency fc | None |
| Optimization | Optimizes the value(s) of one or more project variables to achieve a design goal | Multiple runs | Runs at the center frequency fc | None |
| HDMR Sweep | Varies the value(s) of one or more project variables to generate a compact model | Multiple runs | Runs at the center frequency fc | None |
You can set the simulation mode from EM.Illumina's "Simulation Run Dialog". A single-frequency analysis is a single-run simulation. All the other simulation modes in the above list are considered multi-run simulations. If you run a simulation without having defined any observables, no data will be generated at the end of the simulation. In multi-run simulation modes, certain parameters are varied and a collection of simulation data files are generated. At the end of a sweep simulation, you can graph the simulation results in EM.Grid or you can animate the 3D simulation data from the navigation tree.
Running A Single-Frequency PO Analysis
To open EM.Illumina's Simulation Run dialog, click the Run ![]() button of the Simulate Toolbar or select Menu > Simulate > Run...or use the keyboard shortcut Ctrl+R. To start the simulation click the Run button of this dialog. Once the PO simulation starts, a new dialog called Output Window opens up that reports the various stages of PO simulation, displays the running time and shows the percentage of completion for certain tasks during the PO simulation process. A prompt announces the completion of the PO simulation. At this time, EM.Cube generates a number of output data files that contain all the computed simulation data. These include current distributions, near field data, far field radiation pattern data as well bi-static or mono-static radar cross sections (RCS) if the structure is excited by a plane wave source.
button of the Simulate Toolbar or select Menu > Simulate > Run...or use the keyboard shortcut Ctrl+R. To start the simulation click the Run button of this dialog. Once the PO simulation starts, a new dialog called Output Window opens up that reports the various stages of PO simulation, displays the running time and shows the percentage of completion for certain tasks during the PO simulation process. A prompt announces the completion of the PO simulation. At this time, EM.Cube generates a number of output data files that contain all the computed simulation data. These include current distributions, near field data, far field radiation pattern data as well bi-static or mono-static radar cross sections (RCS) if the structure is excited by a plane wave source.
Setting The Numerical Parameters
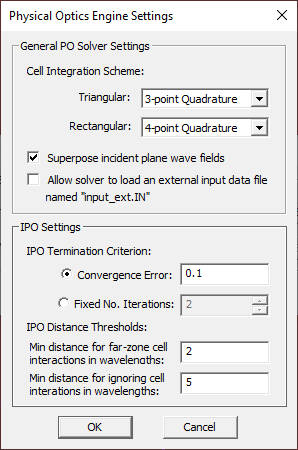
Before you run a PO simulation, you can change some of the PO simulation engine settings. While in the EM.Illumina's Simulation Run Dialog, click the Settings button next to the Select Engine dropdown list. In the Physical Optics Engine Settings Dialog, there are two options for Solver Type: Iterative and GOPO. The default option is Iterative. The GOPO solver is a zero-order PO simulator that uses Geometrical Optics (GO) to determine the lit and shadow cells in the structure's mesh. For the termination of the IPO solver, there are two options: Convergence Error and Maximum Number of Iterations. The default Termination Criterion is based on convergence error, which has a default value of 0.1 and can be changed to any desired accuracy. The convergence error is defined as the L2 norm of the normalized residual error in the combined J/M current solution of the entire discretized structure from one iteration to the next. Note that for this purpose, the magnetic currents are scaled by η0 in the residual error vector.
You can also use higher- or lower-order integration schemes for the calculation of field integrals. EM.Cube's PO simulation engine uses triangular cells for the mesh of the physical surface structures and rectangular cells for discretization of Huygens sources and surfaces. For integration of triangular cells, you have three options: 7-Point Quadrature, 3-Point Quadrature and Constant. For integration of rectangular cells, too, you have three options: 9-Point Quadrature, 4-Point Quadrature and Constant.