Glossary of EM.Cube's Standard Geometric Objects
Contents
- 1 Box Tool
- 2 Cylinder Tool
- 3 Cone Tool
- 4 Pyramid Tool
- 5 Sphere Tool
- 6 Ellipsoid Tool
- 7 Torus Tool
- 8 Generating Platonic Solids
- 9 Rectangle Strip Tool
- 10 Circle Strip Tool
- 11 Radial Strip Tool
- 12 Ellipse Strip Tool
- 13 Triangle Strip Tool
- 14 Taper Strip Tool
- 15 Regular Polygon Tool
- 16 Spiral Strip Tool
- 17 Polystrip Tool
- 18 NURBS Strip Tool
- 19 Generating Complex Surfaces
- 20 Line Tool
- 21 Circle Tool
- 22 Super-Quadratic Curve Tool
- 23 Parabola Tool
- 24 Hyperbola Tool
- 25 Spiral Curve Tool
- 26 Helix Tool
- 27 Polyline Tool
- 28 NURBS Curve Tool
- 29 Generating Complex Curves
- 30 Point Tool
- 31 Fractal Tree Tool
Box Tool
MENU: Object → Solid → Box
TO DRAW A BOX:
- Activate the Box Tool.
- Left-click to establish the first bottom vertex.
- Drag the mouse away from the first vertex to establish the desired base plane area. Left-click a second time to establish the opposite bottom vertex.
- Drag the mouse up and away from the base plane to set the desired height. Left-click a third time to complete the box.
PYTHON COMMAND: box(label,x0,y0,z0,base_x,base_y,height[,cap_top,cap_bottom])
BOX PARAMETERS
| Parameter Name | Value Type | Units | Default Value | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LCS_X | real numeric | project units | - | X-coordinates of base |
| LCS_Y | real numeric | project units | - | Y-coordinates of base |
| LCS_Z | real numeric | project units | - | Z-coordinates of base |
| rot_X | real numeric | degrees | - | local rotation about X-axis |
| rot_Y | real numeric | degrees | - | local rotation about Y-axis |
| rot_Z | real numeric | degrees | - | local rotation about Z-axis |
| size_X | real numeric | project units | - | dimension along X-axis |
| size_Y | real numeric | project units | - | dimension along Y-axis |
| size_Z | real numeric | project units | - | dimension along Z-axis |
| fix_center_X | Boolean | - | TRUE | fixes X-coordinate of base |
| fix_center_Y | Boolean | - | TRUE | fixes Y-coordinate of base |
| cap_top | Boolean | - | TRUE | places a cap at top |
| cap_bottom | Boolean | - | TRUE | places a cap at bottom base |
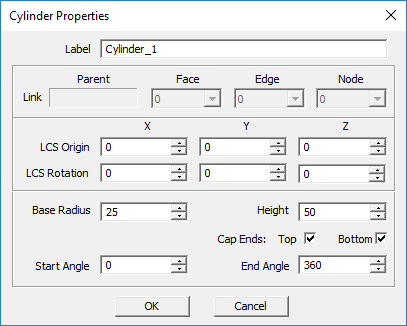
Cylinder Tool
MENU: Object → Solid → Cylinder
TO DRAW A CYLINDER:
- Activate the Cylinder Tool.
- Left-click to establish the center of the bottom base.
- Drag the mouse away from the origin to create the desired base radius. Left-click a second time to establish the cylinder's base.
- Drag the mouse up and away from the active work plane to establish the cylinder's height. Left-click a third time to complete the cylinder.
PYTHON COMMAND: cylinder(label,x0,y0,z0,radius,height[,start_angle,end_angle,cap_top,cap_bottom])
CYLINDER PARAMETERS
| Parameter Name | Value Type | Units | Default Value | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LCS_X | real numeric | project units | - | X-coordinates of base |
| LCS_Y | real numeric | project units | - | Y-coordinates of base |
| LCS_Z | real numeric | project units | - | Z-coordinates of base |
| rot_X | real numeric | degrees | - | local rotation about X-axis |
| rot_Y | real numeric | degrees | - | local rotation about Y-axis |
| rot_Z | real numeric | degrees | - | local rotation about Z-axis |
| base_radius | real numeric | project units | - | - |
| height | real numeric | project units | - | - |
| start_angle | real numeric | degrees | 0 | start azimuth angle |
| end_angle | real numeric | degrees | 360 | end azimuth angle |
| cap_top | Boolean | - | TRUE | places a cap at top |
| cap_bottom | Boolean | - | TRUE | places a cap at bottom base |
Cone Tool
MENU: Object → Solid → Cone
TO DRAW A CONE:
- Activate the Cone Tool.
- Left-click to establish the cone's base plane origin.
- Drag away from the origin to define the base plane's radius. Left-click a second time to define the base plane.
- Drag the mouse away from the base plane to establish the height. Left-click a third time to complete the cone.
PYTHON COMMAND: cone(label,x0,y0,z0,base_radius,height[,top_radius,start_angle,end_angle,cap_top,cap_bottom])
CONE PARAMETERS
| Parameter Name | Value Type | Units | Default Value | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LCS_X | real numeric | project units | - | X-coordinates of base |
| LCS_Y | real numeric | project units | - | Y-coordinates of base |
| LCS_Z | real numeric | project units | - | Z-coordinates of base |
| rot_X | real numeric | degrees | - | local rotation about X-axis |
| rot_Y | real numeric | degrees | - | local rotation about Y-axis |
| rot_Z | real numeric | degrees | - | local rotation about Z-axis |
| base_radius | real numeric | project units | - | - |
| top_radius | real numeric | project units | 0 | - |
| height | real numeric | project units | - | - |
| start_angle | real numeric | degrees | 0 | start azimuth angle |
| end_angle | real numeric | degrees | 360 | end azimuth angle |
| cap_top | Boolean | - | TRUE | places a cap at top |
| cap_bottom | Boolean | - | TRUE | places a cap at bottom base |
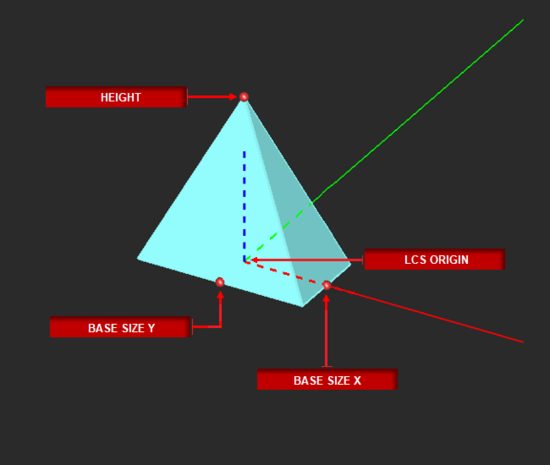
Pyramid Tool
MENU: Object → Solid → Pyramid
TO DRAW A PYRAMID:
- Activate the Pyramid Tool.
- Left-click to establish the first point of the rectangular base plane.
- Define the desired area of the base plane by dragging the mouse away from the first point. Left-click a second time to establish the base plane.
- Drag the mouse away from the base plane to establish the desired height. Left-click a third time to complete the pyramid.
PYTHON COMMAND: pyramid(label,x0,y0,z0,base_x,base_y,height[,top_x,top_y,cap_top,cap_bottom])
PYRAMID PARAMETERS
| Parameter Name | Value Type | Units | Default Value | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LCS_X | real numeric | project units | - | X-coordinates of base |
| LCS_Y | real numeric | project units | - | Y-coordinates of base |
| LCS_Z | real numeric | project units | - | Z-coordinates of base |
| rot_X | real numeric | degrees | - | local rotation about X-axis |
| rot_Y | real numeric | degrees | - | local rotation about Y-axis |
| rot_Z | real numeric | degrees | - | local rotation about Z-axis |
| base_size_X | real numeric | project units | - | - |
| base_size_Y | real numeric | project units | - | - |
| top_size_X | real numeric | project units | 0 | - |
| top_size_Y | real numeric | project units | 0 | - |
| height | real numeric | project units | - | - |
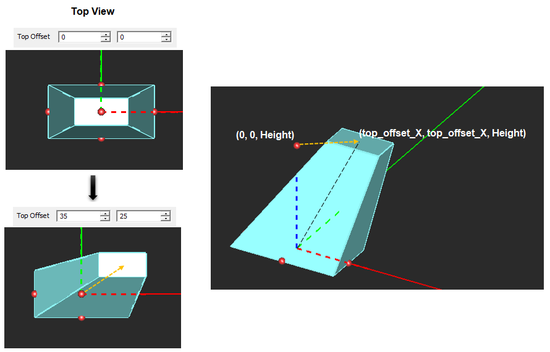
| top_offset_X | real numeric | project units | 0 | - |
| top_offset_Y | real numeric | project units | 0 | - |
| fix_center_X | Boolean | - | TRUE | fixes X-coordinate of base |
| fix_center_Y | Boolean | - | TRUE | fixes Y-coordinate of base |
| cap_top | Boolean | - | TRUE | places a cap at top |
| cap_bottom | Boolean | - | TRUE | places a cap at bottom base |
Sphere Tool
MENU: Object → Solid → Sphere
TO DRAW A SPHERE:
- Activate the Sphere Tool.
- Left-click to establish the origin point. Drag the mouse outward from the origin to establish the radius.
- Left-click a second time to complete the sphere.
PYTHON COMMAND: sphere(label,x0,y0,z0,radius[,start_angle,end_angle])
SPHERE PARAMETERS
| Parameter Name | Value Type | Units | Default Value | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LCS_X | real numeric | project units | - | X-coordinates of base |
| LCS_Y | real numeric | project units | - | Y-coordinates of base |
| LCS_Z | real numeric | project units | - | Z-coordinates of base |
| rot_X | real numeric | degrees | - | local rotation about X-axis |
| rot_Y | real numeric | degrees | - | local rotation about Y-axis |
| rot_Z | real numeric | degrees | - | local rotation about Z-axis |
| radius | real numeric | project units | - | - |
| start_angle | real numeric | degrees | 0 | start azimuth angle |
| end_angle | real numeric | degrees | 360 | end azimuth angle |
Ellipsoid Tool
MENU: Object → Solid → Ellipsoid
TO DRAW AN ELLIPSOID:
- Activate the Ellipsoid Tool.
- Left-click to define the first X-radius anchor point.
- Drag the mouse to the desired length. left-click a second time to define the ending X-radius anchor point.
- Drag the mouse away from the X radius to establish the desired Y-radius. Left-click a third time to define the Y radius.
- Drag the mouse away from the active plane to define the Z radius. Left-click a fourth time to complete the ellipsoid.
PYTHON COMMAND: ellipsoid(label,x0,y0,z0,radius_x,radius_y,radius_z[,start_angle,end_angle])
ELLIPSOID PARAMETERS
| Parameter Name | Value Type | Units | Default Value | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LCS_X | real numeric | project units | - | X-coordinates of base |
| LCS_Y | real numeric | project units | - | Y-coordinates of base |
| LCS_Z | real numeric | project units | - | Z-coordinates of base |
| rot_X | real numeric | degrees | - | local rotation about X-axis |
| rot_Y | real numeric | degrees | - | local rotation about Y-axis |
| rot_Z | real numeric | degrees | - | local rotation about Z-axis |
| radius_X | real numeric | project units | - | - |
| radius_Y | real numeric | project units | - | - |
| radius_Z | real numeric | project units | - | - |
| start_angle | real numeric | degrees | 0 | start azimuth angle |
| end_angle | real numeric | degrees | 360 | end azimuth angle |
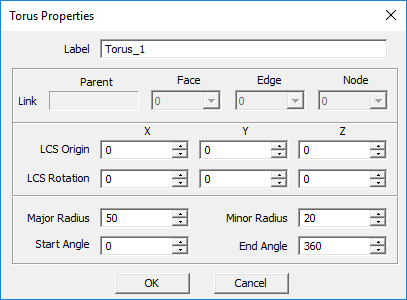
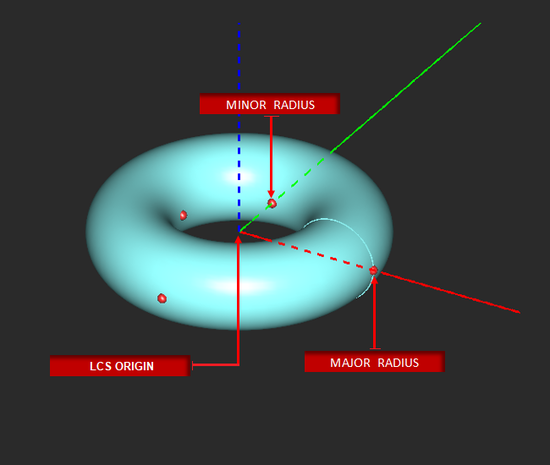
Torus Tool
MENU: Object → Solid → Torus
TO DRAW A TORUS:
- Activate the Torus Tool.
- Left-click to define the center point.
- Drag the mouse away from the origin and left-click a second time to establish the Major Radius of the torus.
- Drag the mouse away from the Major Radius construction path to establish the Minor Radius. Left-click a third time to complete the torus.
PYTHON COMMAND: torus(label,x0,y0,z0,radius_major,radius_minor[,start_angle,end_angle])
TORUS PARAMETERS
| Parameter Name | Value Type | Units | Default Value | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LCS_X | real numeric | project units | - | X-coordinates of base |
| LCS_Y | real numeric | project units | - | Y-coordinates of base |
| LCS_Z | real numeric | project units | - | Z-coordinates of base |
| rot_X | real numeric | degrees | - | local rotation about X-axis |
| rot_Y | real numeric | degrees | - | local rotation about Y-axis |
| rot_Z | real numeric | degrees | - | local rotation about Z-axis |
| major_radius | real numeric | project units | - | - |
| minor_radius | real numeric | project units | - | - |
| start_angle | real numeric | degrees | 0 | start azimuth angle |
| end_angle | real numeric | degrees | 360 | end azimuth angle |
Generating Platonic Solids
Besides EM.Cube's standard solid objects, i.e. box, cylinder, cone, pyramid, sphere, ellipsoid, and torus, you can use Solid Generator ![]() to create five types of Platonic solid objects:
to create five types of Platonic solid objects:
- Tetrahedron
- Hexahedron
- Octahedron
- Dodecahedron
- Icosahedron
A icosahedron with side length 20 (scale = 10).
- Click the Solid Generator
 button of the Object Toolbar or select Menu
button of the Object Toolbar or select Menu 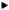 Object
Object  Solid
Solid  Solid Generator to open the Solid Generator Dialog.
Solid Generator to open the Solid Generator Dialog.
- Select one of the five platonic solid types Tetrahedron, Hexahedron Octahedron, Dodecahedron, or Icosahedron.
- The dialog shows the number of faces, edges, nodes and the side length of the standard platonic solid of the selected type. Specify the Scale based on the displayed Side Length.
- Before you create the solid and add it to the Navigation Tree, you have an opportunity to preview it. To do so, click the Preview button of the dialog. A yellow ghost of the solid appears in the Project Workspace. You can change the range or modify the function at this time. Once you are satisfied with the generated solid, click the Create to finalize its creation and add it to the list of object on the Navigation Tree.
Rectangle Strip Tool
MENU: Object → Surface → Rectangle Strip
TO DRAW A RECTANGLE STRIP:
- Activate the Rectangle Strip Tool.
- Left-click to establish the X/Y axial triangulation point.
- Drag the mouse outward from this point to define the desired area of the rectangle strip. Left-click a second time to complete the shape.
PYTHON COMMAND: rect_strip(label,x0,y0,z0,side_x,side_y)
RECTANGLE STRIP PARAMETERS
| Parameter Name | Value Type | Units | Default Value | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LCS_X | real numeric | project units | - | X-coordinates of base |
| LCS_Y | real numeric | project units | - | Y-coordinates of base |
| LCS_Z | real numeric | project units | - | Z-coordinates of base |
| rot_X | real numeric | degrees | - | local rotation about X-axis |
| rot_Y | real numeric | degrees | - | local rotation about Y-axis |
| rot_Z | real numeric | degrees | - | local rotation about Z-axis |
| side_X | real numeric | project units | - | dimension along X-axis |
| side_Y | real numeric | project units | - | dimension along Y-axis |
| fix_center_X | Boolean | - | TRUE | fixes X-coordinate of base |
| fix_center_Y | Boolean | - | TRUE | fixes Y-coordinate of base |
| rect_loop | Boolean | - | FALSE | if TRUE, creates a rectangular loop |
| loop_width | real numeric | project units | - | - |
Circle Strip Tool
MENU: Objects → Surfaces → Circle Strip
TO DRAW A CIRCLE STRIP:
- Activate the Circle Strip Tool.
- Left-click to define the origin
- Drag the mouse away from the origin to establish the desired radius. Left-click a second time to complete the circle strip.
PYTHON COMMAND: circ_strip(label,x0,y0,z0,outer_radius,inner_radius[,start_angle,end_angle])
CIRCLE STRIP PARAMETERS
| Parameter Name | Value Type | Units | Default Value | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LCS_X | real numeric | project units | - | X-coordinates of base |
| LCS_Y | real numeric | project units | - | Y-coordinates of base |
| LCS_Z | real numeric | project units | - | Z-coordinates of base |
| rot_X | real numeric | degrees | - | local rotation about X-axis |
| rot_Y | real numeric | degrees | - | local rotation about Y-axis |
| rot_Z | real numeric | degrees | - | local rotation about Z-axis |
| outer_radius | real numeric | project units | - | circle's outer radius |
| inner_radius | real numeric | project units | 0 | inner radius creating a ring object |
| start_angle | real numeric | degrees | 0 | start azimuth angle |
| end_angle | real numeric | degrees | 360 | end azimuth angle |
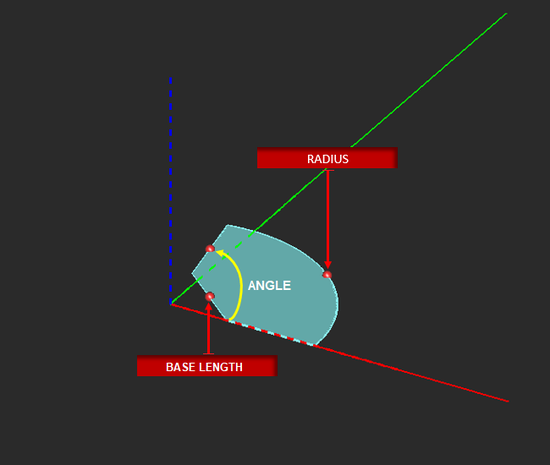
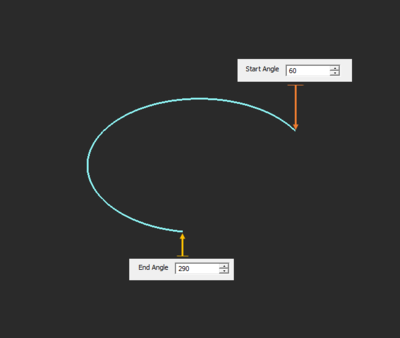
Radial Strip Tool
MENU: Object → Surface → Radial Strip
TO DRAW A RADIAL STRIP:
- Activate the Radial Strip Tool.
- Left-click to establish the origin point.
- Drag the mouse away from origin and left-click a second time to establish the radius and the first leg of the radial strip.
- Drag the mouse to the desired location to define the angle of the radial strip. Left-click a third time to complete the radial strip.
PYTHON COMMAND: radial_strip(label,x0,y0,z0,radius,base_lenght,angle)
RADIAL STRIP PARAMETERS
| Parameter Name | Value Type | Units | Default Value | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LCS_X | real numeric | project units | - | X-coordinates of base |
| LCS_Y | real numeric | project units | - | Y-coordinates of base |
| LCS_Z | real numeric | project units | - | Z-coordinates of base |
| rot_X | real numeric | degrees | - | local rotation about X-axis |
| rot_Y | real numeric | degrees | - | local rotation about Y-axis |
| rot_Z | real numeric | degrees | - | local rotation about Z-axis |
| radius | real numeric | project units | - | - |
| base_length | real numeric | project units | 0 | A nonzero value creates a flattened base |
| angle | real numeric | degrees | - | wedge angle |
Ellipse Strip Tool
MENU: Object → Surface → Ellipse Strip
TO DRAW AN ELLIPSE STRIP:
- Activate the Ellipse Strip Tool.
- Left-click to establish the X/Y axis origin.
- Drag the mouse away from the origin to the desired location. Left-click a second time to create the ellipse.
PYTHON COMMAND: ellipse_strip(label,x0,y0,z0,radius_x,radius_y[,start_angle,end_angle])
ELLIPSE STRIP PARAMETERS
| Parameter Name | Value Type | Units | Default Value | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LCS_X | real numeric | project units | - | X-coordinates of base |
| LCS_Y | real numeric | project units | - | Y-coordinates of base |
| LCS_Z | real numeric | project units | - | Z-coordinates of base |
| rot_X | real numeric | degrees | - | local rotation about X-axis |
| rot_Y | real numeric | degrees | - | local rotation about Y-axis |
| rot_Z | real numeric | degrees | - | local rotation about Z-axis |
| radius_X | real numeric | project units | - | radius along X-axis |
| radius_Y | real numeric | project units | - | radius along Y-axis |
| start_angle | real numeric | degrees | 0 | start azimuth angle |
| end_angle | real numeric | degrees | 360 | end azimuth angle |
| fix_center_X | Boolean | - | TRUE | fixes X-coordinate of base |
| fix_center_Y | Boolean | - | TRUE | fixes Y-coordinate of base |
Triangle Strip Tool
MENU: Object → Surface → Triangle Strip
TO DRAW A TRIANGLE STRIP:
- Activate the Triangle Strip Tool.
- Left-click to establish the triangles origin.
- Drag away from the origin and left-click a second time to define Leg 1 of the triangle.
- Drag away from leg 1, left-click a third time to define Leg 2 and complete the triangle.
NOTES, SPECIAL CASES OR EXCEPTIONS: Side 1 establish the length of first leg of the triangle. Side 2 establishes the length of the second leg of the triangle Angle defines the opening angle of the origin vertex (the angle between leg one and leg two). Hold down the Shift key while positioning the third point of the triangle to constrain the origin angle to 15º increments.
PYTHON COMMAND: triangle_strip(label,x0,y0,z0,side1,side2,angle)
TRIANGLE STRIP PARAMETERS
| Parameter Name | Value Type | Units | Default Value | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LCS_X | real numeric | project units | - | X-coordinates of base |
| LCS_Y | real numeric | project units | - | Y-coordinates of base |
| LCS_Z | real numeric | project units | - | Z-coordinates of base |
| rot_X | real numeric | degrees | - | local rotation about X-axis |
| rot_Y | real numeric | degrees | - | local rotation about Y-axis |
| rot_Z | real numeric | degrees | - | local rotation about Z-axis |
| side_1 | real numeric | project units | - | - |
| side_2 | real numeric | project units | 0 | - |
| angle | real numeric | degrees | - | wedge angle |
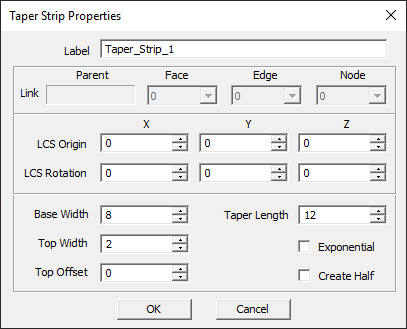
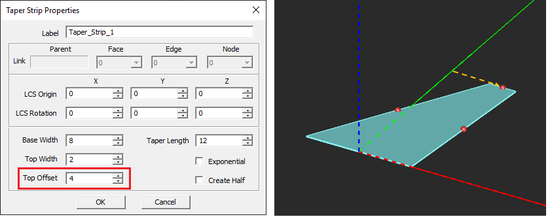
Taper Strip Tool
MENU: Object → Surface → Taper Strip
TO DRAW A TAPER STRIP:
- Activate the Taper Strip Tool.
- Left-click to establish the base length midpoint.
- Drag outward from this point to define the desired length and angle of the base side. Left-click a second time to define the base.
- To establish the height, drag the mouse away from the base to the desired location. Left-click a third time to complete the Taper Strip.
NOTES, SPECIAL CASES OR EXCEPTIONS: Taper Length establishes the distance between the base and top sides of the trapezoid. If the Exponential check box is checked, the two slanted sides of the trapezoid are replaced by exponential curves passing through the same vertices.
PYTHON COMMAND: taper_strip(label,x0,y0,z0,base_width,top_width,length,is_expo)
TAPER STRIP PARAMETERS
| Parameter Name | Value Type | Units | Default Value | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LCS_X | real numeric | project units | - | X-coordinates of base |
| LCS_Y | real numeric | project units | - | Y-coordinates of base |
| LCS_Z | real numeric | project units | - | Z-coordinates of base |
| rot_X | real numeric | degrees | - | local rotation about X-axis |
| rot_Y | real numeric | degrees | - | local rotation about Y-axis |
| rot_Z | real numeric | degrees | - | local rotation about Z-axis |
| base_width | real numeric | project units | - | - |
| taper_length | real numeric | project units | - | - |
| top_width | real numeric | project units | - | - |
| top_offset | real numeric | project units | 0 | A zero value creates an isosceles triangle |
| exponential | Boolean | - | FALSE | creates an exponential taper transition |
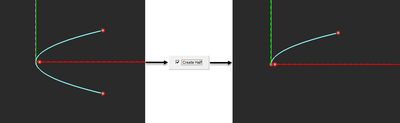
| create-half | Boolean | - | FALSE | keeps left half of taper strip only |
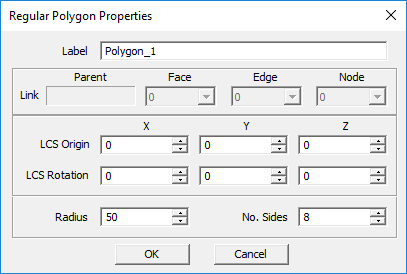
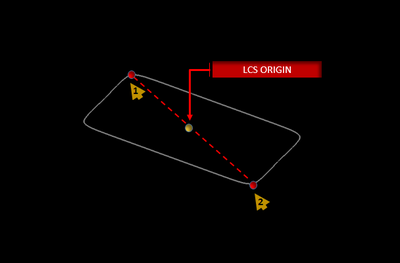
Regular Polygon Tool
MENU: Object → Surface → Regular Polygon
TO DRAW A REGULAR POLYGON:
- Activate the Regular Polygon Tool.
- Left-click to create the origin of the Regular Polygon.
- Drag away from the origin and left-click a second time to define the Regular Polygon's diameter.
- Drag the mouse to increase or decrease the number of sides desired. Left-click a third time to finish drawing the Regular Polygon.
NOTES, SPECIAL CASES OR EXCEPTIONS: This tool creates a regular polygon with an arbitrary number of sides within a circumscribing circle of a specified radius.
PYTHON COMMAND: polygon_reg(label,x0,y0,z0,radius,n_sides)
REGULAR POLYGON PARAMETERS
| Parameter Name | Value Type | Units | Default Value | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LCS_X | real numeric | project units | - | X-coordinates of base |
| LCS_Y | real numeric | project units | - | Y-coordinates of base |
| LCS_Z | real numeric | project units | - | Z-coordinates of base |
| rot_X | real numeric | degrees | - | local rotation about X-axis |
| rot_Y | real numeric | degrees | - | local rotation about Y-axis |
| rot_Z | real numeric | degrees | - | local rotation about Z-axis |
| radius | real numeric | project units | - | radius of circumscribing circle |
| side_count | integer numeric | - | - | number of side of regular polygon |
| top_width | real numeric | project units | - | - |
Spiral Strip Tool
MENU: Object → Surface → Spiral Strip
TO DRAW A SPIRAL STRIP:
- Activate the Spiral Strip Tool.
- Left-click to establish the origin of the Spiral Strip's inner-radius.
- Drag away from the origin to expand the inner radius. Left-click a second time to set the inner radius and create the starting point for the outer radius.
- Drag the mouse away from the second point to expand the outer radius (or closer to contract the radius). Left-click a third time to complete the spiral.
NOTES, SPECIAL CASES OR EXCEPTIONS: Checking the Inner Taper box creates a rounded taper at the inner edge of each spiral arm by drawing an exponential curve from a user-defined edge inset point to that edge's opposite corner vertex. Checking the Outer Taper box creates a rounded taper at the outer edge of each spiral arm by drawing an exponential curve from a user-defined edge inset point to that edge's opposite corner vertex.. Inset Distance establishes an imaginary offset point positioned away from the corner vertex from the inner or outer edge. The Inner Radius setting is not available when the Dual Arm option is enabled.
PYTHON COMMAND: spiral_strip(label,x0,y0,z0,width,radius_inner,radius_outer,n_turns,spiral_dir,is_dual)
SPIRAL STRIP PARAMETERS
| Parameter Name | Value Type | Units | Default Value | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LCS_X | real numeric | project units | - | X-coordinates of base |
| LCS_Y | real numeric | project units | - | Y-coordinates of base |
| LCS_Z | real numeric | project units | - | Z-coordinates of base |
| rot_X | real numeric | degrees | - | local rotation about X-axis |
| rot_Y | real numeric | degrees | - | local rotation about Y-axis |
| rot_Z | real numeric | degrees | - | local rotation about Z-axis |
| inner_radius | real numeric | project units | - | - |
| outer_radius | real numeric | project units | - | - |
| strip_width | real numeric | project units | - | - |
| turns | integer numeric | project units | 2 | number of spiral turns |
| ccw | Boolean | - | TRUE | if TRUE, creates counterclockwise right-handedness |
| dual_arm | Boolean | - | FALSE | creates a dual-arm spiral |
| inner_taper | Boolean | - | FALSE | if TRUE, tapers spiral strip from inner end |
| inner_inset | real numeric | project units | 0 | when inner_taper is TRUE, a nonzero value creates inner inset |
| outer_taper | Boolean | - | FALSE | if TRUE, tapers spiral strip from outer end |
| outer_inset | real numeric | project units | 0 | when outer_taper is TRUE, a nonzero value creates outer inset |
| taper_pointing | list: {inward, outward} | - | inward | sets the direction spiral's end tapers point to |
Polystrip Tool
MENU: Object → Surface → Polystrip
TO DRAW A POLYSTRIP:
- Activate the Polystrip Tool.
- Click anywhere on the active work plane to create nodes. The Polystrip's contour is rendered as soon as the second node is defined. A Polystrip must have at least three nodes.
- The Polystrip can be closed at any time by either double-clicking on the workplane to establish a closing node, or by pressing the C or ENTER key, which connects the last drawn node with the first. Once closed, the surface area is filled.
PYTHON COMMAND: polystrip(label,(x0,y0,z0),(x1,y1,z1) ... )
EDITING NODES
Each Polystrip node can be selected by clicking on it in the work plane. You can also force nodes to snap to the nearest grid point by activating Snap to Grid (View → Grid Settings).
DIALOG PARAMETERS
Index reports the unique order number of the currently selected node. Active Node shows the X, Y and Z coordinates of the currently selected node.
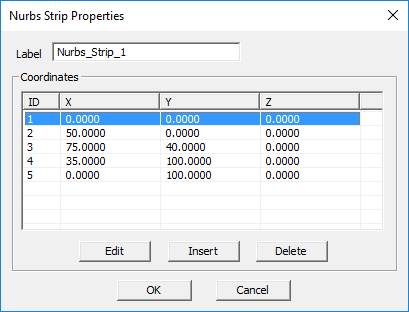
NURBS Strip Tool
MENU: Object → Surface → NURBS Strip
TO DRAW A NURBS STRIP:
- Activate the NURBS Strip Tool.
- Click anywhere on the active work plane to create nodes. The NURBs contour is rendered as soon as the second node is defined. A NURBS Strip must have at least three nodes.
- The NURBS Strip can be closed at any time by either double-clicking on the workplane to establish a closing node, or by pressing the C or ENTER key, which connects the last drawn node with the first. Once closed, the surface area is filled.
PYTHON COMMAND: nurbs_strip(label,(x0,y0,z0),(x1,y1,z1) ... )
EDITING NODES
Each NURBS Strip node can be selected by clicking on it in the work plane. You can also force nodes to snap to the nearest grid point by activating Snap to Grid (View → Grid Settings).
DIALOG PARAMETERS
Index reports the unique order number of the currently selected node. Active Node shows the X, Y and Z coordinates of the currently selected node.
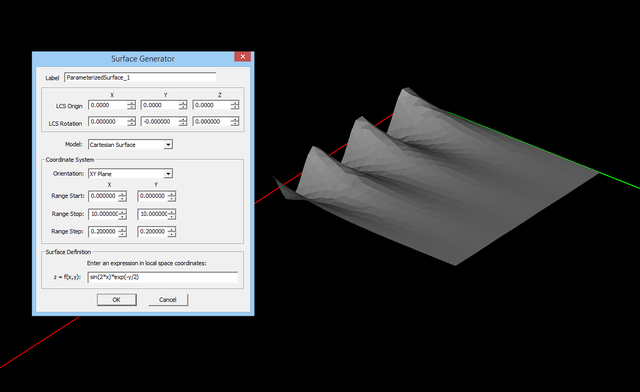
Generating Complex Surfaces
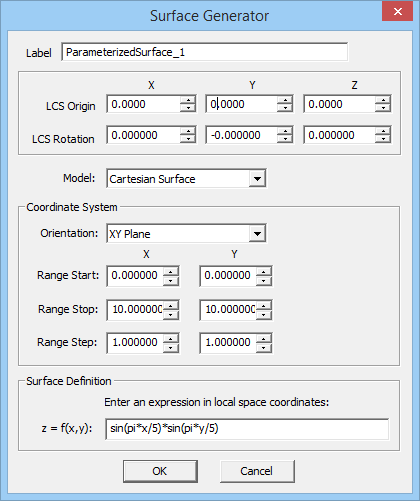
Besides EM.Cube's standard planar objects, i.e. rectangle strip, circle strip, radial strip, ellipse strip, triangle strip, taper strip, regular polygon, spiral strip, polystrip and NURBS strip, you can use Surface Generator ![]() to create a large variety of other surface objects. Practically, any imaginable planar or non-planar surface can be synthesized in EM.Cube. These include:
to create a large variety of other surface objects. Practically, any imaginable planar or non-planar surface can be synthesized in EM.Cube. These include:
A mathematical surface defined by z = sin(2*x)*exp(-y/2): (left) polymesh version, (right) smooth generic surface version.
- Click the Surface Generator
 button of the Object Toolbar to open the Curve Generator Dialog.
button of the Object Toolbar to open the Curve Generator Dialog.
- From the Model dropdown list, select the Custom Function, which is the default option. Also specify the Orientation of the surface, which is the XY principal plane by default.
- Specify the range of the surface including Start, Stop and Step values along the two specified dimensions.
- In the "Parameters" section, define the function representing the surface. This has the form z = f(x,y) in XY Plane, x = f(y,z) in YZ Plane or y = f(z,x) in ZX Plane.
- As in the previous case, you can choose between the two Polymesh or Generic Surface options. You can also preview the curve before finalizing its creation.
Line Tool
MENU: Object → Curve → Line
TO DRAW A LINE:
- Activate the Line Tool.
- left click anywhere on the workplane to begin drawing the line.
- left-click a second time to complete the line.
NOTES, SPECIAL CASES OR EXCEPTIONS: When the check box Lock Center is checked, changing the line's length expands or shrinks it equally from both ends. To create a line perpendicular to the current work plane, hold down the Alt key while dragging the mouse to establish the line's end point.
PYTHON COMMAND: line(label,x0,y0,z0,len[,dir])
LINE PARAMETERS
| Parameter Name | Value Type | Units | Default Value | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LCS_X | real numeric | project units | - | X-coordinates of base |
| LCS_Y | real numeric | project units | - | Y-coordinates of base |
| LCS_Z | real numeric | project units | - | Z-coordinates of base |
| rot_X | real numeric | degrees | - | local rotation about X-axis |
| rot_Y | real numeric | degrees | - | local rotation about Y-axis |
| rot_Z | real numeric | degrees | - | local rotation about Z-axis |
| length | real numeric | project units | - | - |
| fix_center | Boolean | - | FALSE | fixes midpoint coordinates |
Circle Tool
MENU: Object → Curve → Circle
TO DRAW A CIRCLE:
- Activate the Circle Tool.
- Left-click at the desired location on the active grid to establish the origin.
- Drag your mouse away from the origin to set the desired radius.
- Left click a second time to complete the circle.
PYTHON COMMAND: circle(label,x0,y0,z0,radius,start_angle,end_angle)
CIRCLE PARAMETERS
| Parameter Name | Value Type | Units | Default Value | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LCS_X | real numeric | project units | - | X-coordinates of base |
| LCS_Y | real numeric | project units | - | Y-coordinates of base |
| LCS_Z | real numeric | project units | - | Z-coordinates of base |
| rot_X | real numeric | degrees | - | local rotation about X-axis |
| rot_Y | real numeric | degrees | - | local rotation about Y-axis |
| rot_Z | real numeric | degrees | - | local rotation about Z-axis |
| radius | real numeric | project units | - | - |
| start_angle | real numeric | degrees | 0 | start azimuth angle |
| end_angle | real numeric | degrees | 360 | end azimuth angle |
Super-Quadratic Curve Tool
MENU: Object → Curve → Super-quadratic Curve
TO DRAW A SUPER-QUADRATIC CURVE:
- Activate the Super-Quadratic Curve Tool.
- Left-click to establish the initial X/Y diameter triangulation point.
- Drag the mouse away from this point to define the desired size.
- Left-click a second time to complete the superquad.
NOTES, SPECIAL CASES OR EXCEPTIONS: The parameter Order changes the radius of the four corners of the super-quadratic curve. The second-order super-quadratic curve (n = 2) corresponds to an ellipse. Entering a higher value for the order decreases the corner radius and make the curve look like a rectangle with rounded corners. Checking the Rectangle box creates a rectangular curve with no corner rounding.
PYTHON COMMAND: superquad(label,x0,y0,z0,diam_x,diam_y,order)
SUPER-QUADRATIC CURVE PARAMETERS
| Parameter Name | Value Type | Units | Default Value | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LCS_X | real numeric | project units | - | X-coordinates of base |
| LCS_Y | real numeric | project units | - | Y-coordinates of base |
| LCS_Z | real numeric | project units | - | Z-coordinates of base |
| rot_X | real numeric | degrees | - | local rotation about X-axis |
| rot_Y | real numeric | degrees | - | local rotation about Y-axis |
| rot_Z | real numeric | degrees | - | local rotation about Z-axis |
| diameter_X | real numeric | project units | - | diameter along X-axis |
| diameter_Y | real numeric | project units | - | diameter along Y-axis |
| order | integer numeric | degrees | 2 | a higher order resembles a rectangle with rounded corners |
| is_rectangle | Boolean | - | FALSE | if TRUE, draws a rectangle |
| fix_center_X | Boolean | - | TRUE | fixes X-coordinate of base |
| fix_center_Y | Boolean | - | TRUE | fixes Y-coordinate of base |
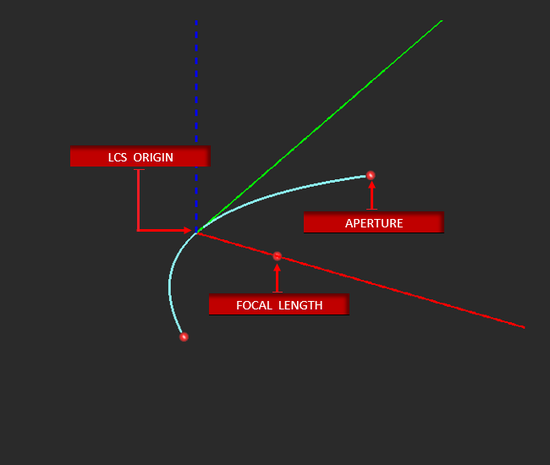
Parabola Tool
MENU: Object → Curve → Parabola
TO DRAW A PARABOLA:
- Activate the Parabola Tool.
- Left-click to set the Focal Point.
- Drag away from the focal point and left-click a second time to set the desired Offset.
- Drag and left-click a third time to complete the Parabolic Curve.
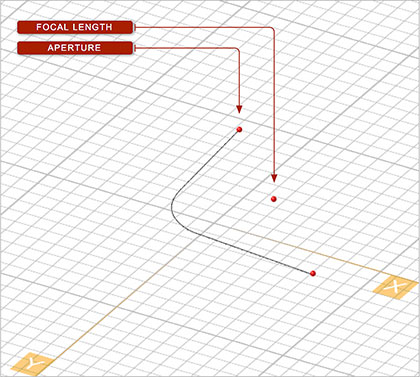
NOTES, SPECIAL CASES OR EXCEPTIONS: The parameters Axial Length and Aperture adjust the size of the opening of the parabola. Changing the value of either one automatically adjusts the value of the other. Checking the box labeled Create Half bisects the parabola and removes its bottom half. You can revolve the resulting half-curve to create a paraboloid.
PYTHON COMMAND: parabola(label,x0,y0,z0,focal_length,axial_length,half_only)
PARABOLA PARAMETERS
| Parameter Name | Value Type | Units | Default Value | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LCS_X | real numeric | project units | - | X-coordinates of base |
| LCS_Y | real numeric | project units | - | Y-coordinates of base |
| LCS_Z | real numeric | project units | - | Z-coordinates of base |
| rot_X | real numeric | degrees | - | local rotation about X-axis |
| rot_Y | real numeric | degrees | - | local rotation about Y-axis |
| rot_Z | real numeric | degrees | - | local rotation about Z-axis |
| focal_length | real numeric | project units | - | - |
| axial_length | real numeric | project units | - | - |
| aperture | real numeric | degrees | - | is determined automatically by focal and axial lengths or can be set independently |
| create_half | Boolean | - | FALSE | if TRUE, draws the left half only |
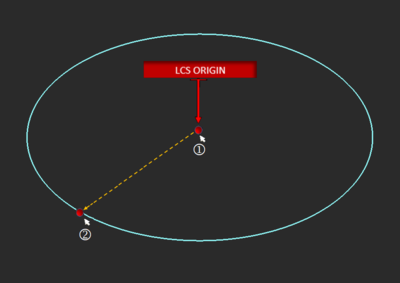
Hyperbola Tool
MENU: Object → Curve → Hyperbola
TO DRAW A HYPERBOLA:
- Activate the Hyperbola Tool.
- Left-click to define the X-radius origin. Construction guides will appear to aid in the drawing process.
- Drag the mouse away from the origin to establish the desired X-radius. Left-click a second time.
- To establish the Y-radius and the hyperbola's leg length, drag the mouse to the desired location and left-click to complete the Hyperbola.
PYTHON COMMAND: hyperbola(label,x0,y0,z0,diam_x,diam_y,axial_length,half_only)
HYPERBOLA PARAMETERS
| Parameter Name | Value Type | Units | Default Value | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LCS_X | real numeric | project units | - | X-coordinates of base |
| LCS_Y | real numeric | project units | - | Y-coordinates of base |
| LCS_Z | real numeric | project units | - | Z-coordinates of base |
| rot_X | real numeric | degrees | - | local rotation about X-axis |
| rot_Y | real numeric | degrees | - | local rotation about Y-axis |
| rot_Z | real numeric | degrees | - | local rotation about Z-axis |
| diameter_X | real numeric | project units | - | diameter along X-axis |
| diameter_Y | real numeric | project units | - | diameter along Y-axis |
| axial_length | real numeric | project units | - | - |
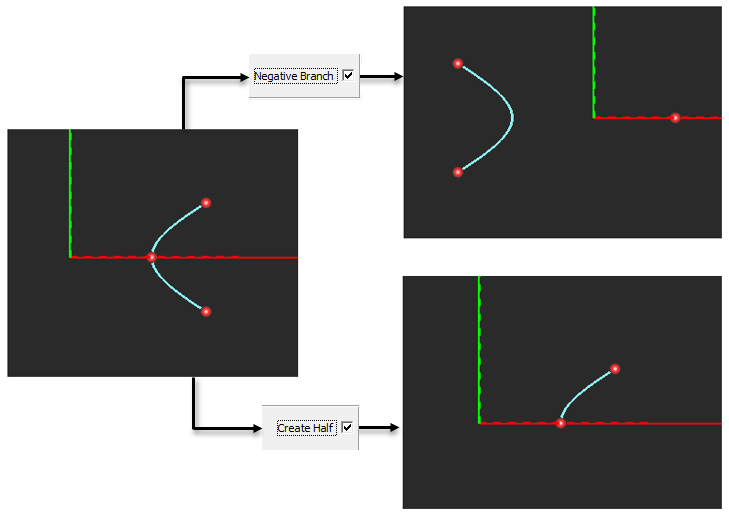
| create_half | Boolean | - | FALSE | if TRUE, draws one half of one branch only |
| negative_branch | - | FALSE | if TRUE, draws the negative branch only |
DIALOG PROPERTIES
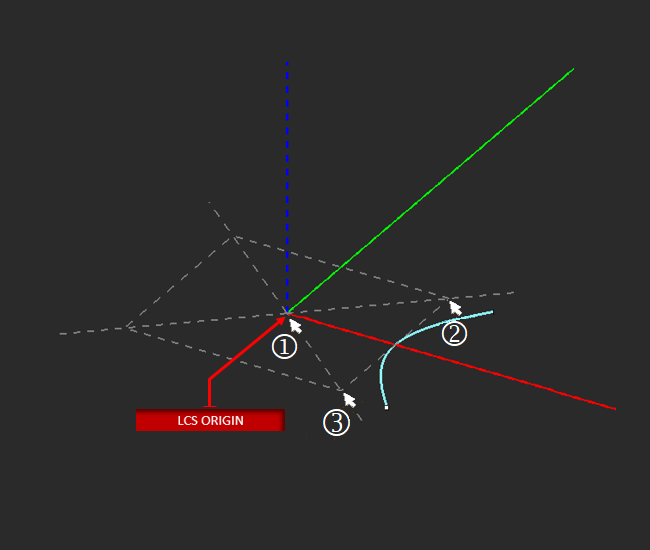
X Diameter Y Diameter Axial Length establishes the distance between the start and end points of the hyperbolic curve.
Neg. Branch create a mirrored version of the hyperbolic curve. Create Half bisects and removes the bottom half of the hyperbolic curve. You can revolve the resulting curve to create a hyperbolic dish.
EDIT HANDLES
Edit handles, available in shape edit mode, allow you to modify common shape attributes using your mouse. The diagram on the left provides a reference of the parameters controlled by the resize (RED) edit handles. Edit handles turn blue when the mouse cursor hovers on top of them. This color change indicates that the handle is active. Click and drag on any active handle to reshape the object.
Spiral Curve Tool
MENU: Object → Curve → Spiral
TO DRAW A SPIRAL CURVE:
- Activate the Spiral Curve Tool.
- Left-click to establish the inner-radial origin of the Spiral.
- Drag away from the origin to expands the inner radius (drag inward toward the origin to reduces the inner radius).
- Left-click a second time to set the inner radius and create the anchor point for the outer radius.
- Drag the mouse away from the second point to expand the outer radius or closer to reduce the radius.
- Left-click a third time to complete the spiral.
PYTHON COMMAND: spiral_curve(label,x0,y0,z0,radius_inner,radius_outer,nturns,spiral_dir,is_dual)
SPIRAL CURVE PARAMETERS
| Parameter Name | Value Type | Units | Default Value | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LCS_X | real numeric | project units | - | X-coordinates of base |
| LCS_Y | real numeric | project units | - | Y-coordinates of base |
| LCS_Z | real numeric | project units | - | Z-coordinates of base |
| rot_X | real numeric | degrees | - | local rotation about X-axis |
| rot_Y | real numeric | degrees | - | local rotation about Y-axis |
| rot_Z | real numeric | degrees | - | local rotation about Z-axis |
| inner_radius | real numeric | project units | - | - |
| outer_radius | real numeric | project units | - | - |
| turns | integer numeric | project units | 2 | number of spiral turns |
| ccw | Boolean | - | TRUE | if TRUE, creates counterclockwise right-handedness |
| dual_arm | Boolean | - | FALSE | creates a dual-arm spiral |
DIALOG PROPERTIES
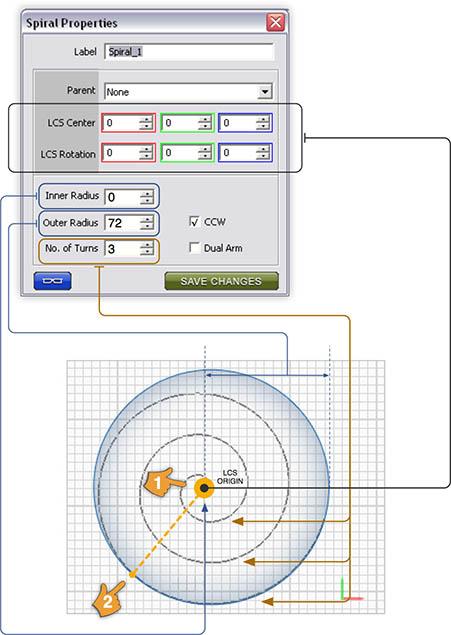
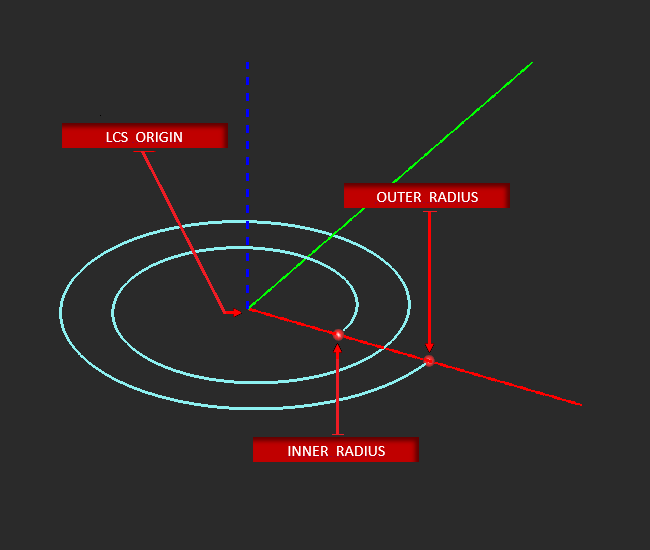
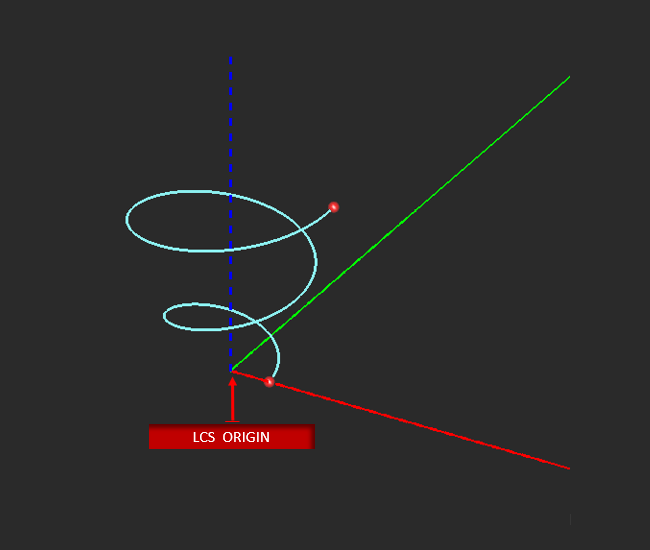
Inner Radius defines the distance between the spiral's origin and the starting point of each spiral arm. Outer Radius sets the distance each spiral arm will radiate outward from the inner radius. Number of Turns defines the number of spiral revolutions of each arm Counter Clockwise (CCW) flips the clockwise drawing direction of the spiral arms.
The X, Y, Z LCS coordinates originate at the center of the spiral.
EDIT HANDLES
Edit handles, available in shape edit mode, allow you to modify common shape attributes using your mouse. The diagram on the left provides a reference of the parameters controlled by the resize (RED) edit handles. Edit handles turn blue when the mouse cursor hovers on top of them. This color change indicates that the handle is active. Click and drag on any active handle to reshape the object.
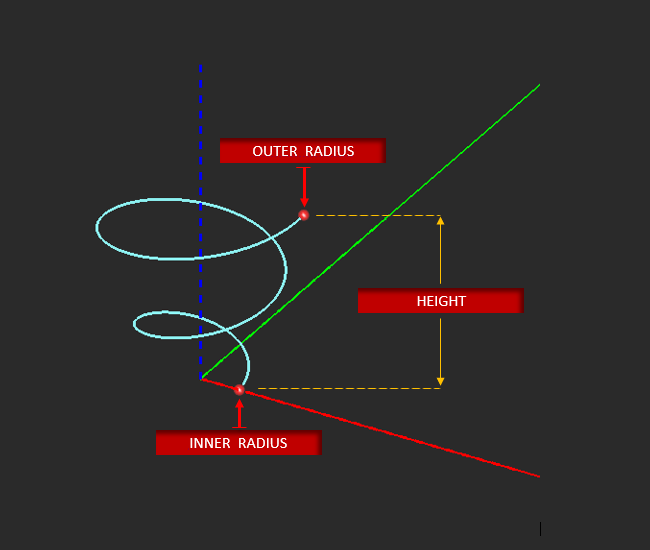
Helix Tool
MENU: Object → Curve → Helix
TO DRAW A HELIX:
- Activate the Helix Tool.
- Left-click to establish the origin of the inner-radius.
- Drag away from the origin to expand the inner radius, (toward it to contract the inner radius).
- Left-click a second time to set the inner radius and to establish the anchor point from which you will set the height of the helix.
- Drag your cursor "up" and away from the second anchor point to increase the height of the helix.
- Left-click a third time to complete the helix.
PYTHON COMMAND: helix(label,x0,y0,z0,radius_inner,radius_outer,height,nturns,helix_dir)
HELIX PARAMETERS
| Parameter Name | Value Type | Units | Default Value | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LCS_X | real numeric | project units | - | X-coordinates of base |
| LCS_Y | real numeric | project units | - | Y-coordinates of base |
| LCS_Z | real numeric | project units | - | Z-coordinates of base |
| rot_X | real numeric | degrees | - | local rotation about X-axis |
| rot_Y | real numeric | degrees | - | local rotation about Y-axis |
| rot_Z | real numeric | degrees | - | local rotation about Z-axis |
| inner_radius | real numeric | project units | same as outer radius | - |
| outer_radius | real numeric | project units | - | - |
| height | real numeric | project units | - | - |
| turns | integer numeric | project units | 2 | number of spiral turns |
| ccw | Boolean | - | TRUE | if TRUE, creates counterclockwise right-handedness |
DIALOG PARAMETERS
Inner Radius defines the distance between the spiral's origin and the starting point of each spiral arm. Outer Radius sets the distance each spiral arm will radiate outward from the inner radius. Number of Turns defines the number of spiral revolutions of each arm Height establishes the elevation of the outer radius of the helix. Counter Clockwise (CCW) flips the clockwise drawing direction of the spiral arms.
The X, Y, Z LCS coordinates originate at the base center of the helix.
SNAP POINT EDIT HANDLES
Edit handles, available in shape edit mode, allow you to modify common shape attributes using your mouse. The diagram on the left provides a reference of the parameters controlled by the resize (RED) edit handles.
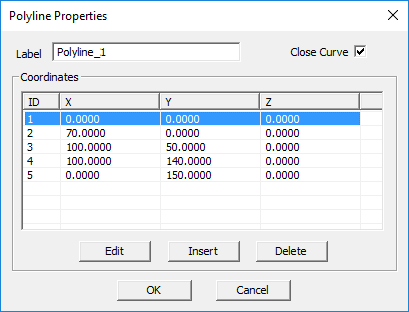
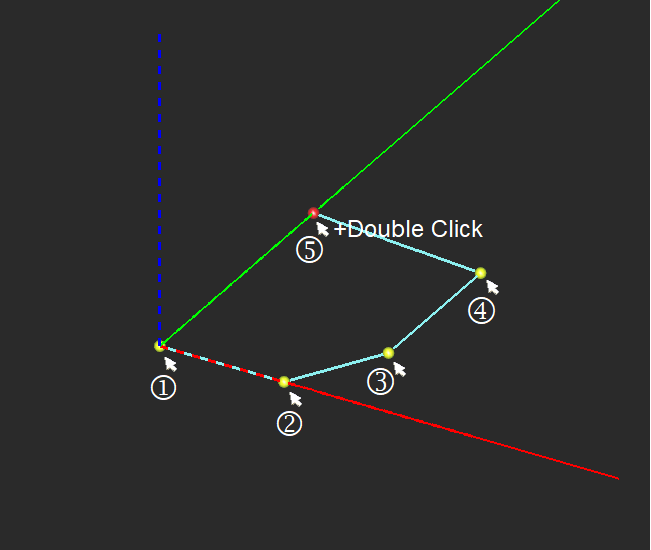
Polyline Tool
MENU: Object → Curve → Polyline
TO DRAW A POLYLINE:
- Activate the Polyline Tool.
- Click anywhere on the active work plane to create nodes. The Polyline's contour is rendered as soon as the second node is defined. A Polyline must have at least two nodes.
- The Polyline can be closed at any time by either double-clicking on the workplane to establish a closing node, or by pressing the C or ENTER key, which connects the last drawn node with the first.
PYTHON COMMAND: polyline(label,(x0,y0,z0),(x1,y1,z1) ... )
EDITING NODES
Each Polyline node can be selected by clicking on it in the work plane. You can also force nodes to snap to the nearest grid point by activating Snap to Grid (View → Grid Settings).
If the polyline shape was originally drawn unclosed, you can place a checkmark in the Close option box to connect the first drawn anchor point with the last drawn anchor point. Closing the "loop" allows you to fill the polyline shape, creating a planar object whose perimeter and surface area matches the drawn polyline's outline.
DIALOG PARAMETERS
Index reports the unique order number of the currently selected node. Active Node shows the X, Y and Z coordinates of the currently selected node.
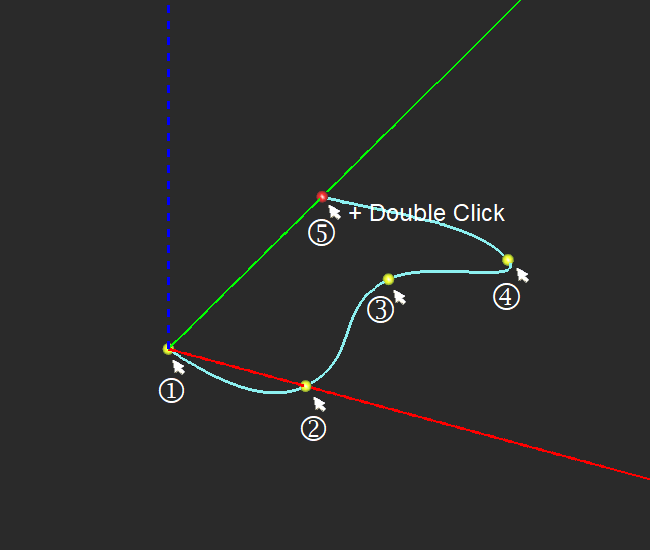
NURBS Curve Tool
MENU: Object → Curve → NURBS
TO DRAW A NURBS CURVE:
- Activate the NURBS Curve Tool.
- Click anywhere on the active work plane to create nodes. The contour of the NURBs Curve is rendered as soon as the second node is defined. A NURBs Curve must have at least two nodes.
- The NURBs Curve can be closed at any time by either double-clicking on the workplane to establish a closing node, or by pressing the C or ENTER key, which connects the last drawn node with the first.
PYTHON COMMAND: nurbs_curve(label,(x0,y0,z0),(x1,y1,z1) ... )
EDITING NODES
Each NURBs Curve node can be selected by clicking on it in the work plane. You can also force nodes to snap to the nearest grid point by activating Snap to Grid (View → Grid Settings).
If the NURBs Curve shape was originally drawn unclosed, you can place a checkmark in the Close option box to connect the first drawn anchor point with the last drawn anchor point. Closing the "loop" allows you to fill the polyline shape, creating a planar object whose perimeter and surface area matches the drawn polyline's outline.
DIALOG PARAMETERS
Index reports the unique order number of the currently selected node. Active Node shows the X, Y and Z coordinates of the currently selected node.
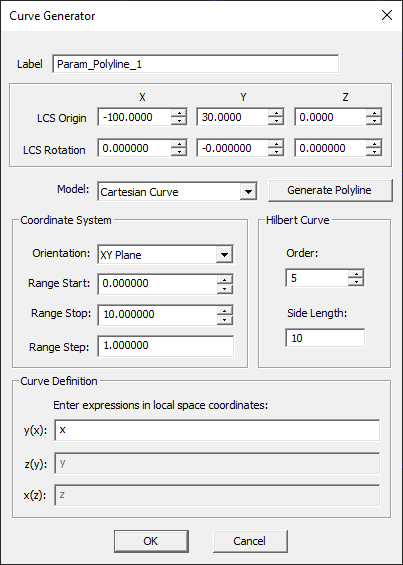
Generating Complex Curves
Besides EM.CUBE's standard curve objects, i.e. line, circle, super-quadratic curve, parabola, hyperbola, spiral curve and helix, you can use Curve Generator ![]() to create a large variety of other curve objects. Practically, any imaginable curve can be synthesized in EM.CUBE. These include:
to create a large variety of other curve objects. Practically, any imaginable curve can be synthesized in EM.CUBE. These include:
- Planar Cartesian curves represented by equation y = f(x).
- Planar polar curves represented by equation r = f(?).
- 3-D parametric curves represented by equations x = x(t), y = y(t), and z = z(t).
Moreover, you can create planar curves on any of the three principal XY, YZ or ZX planes.
- Click the Curve Generator
 button of the Object Toolbar or select Menu
button of the Object Toolbar or select Menu  Object
Object  Curve
Curve  Curve Generator to open the Curve Generator Dialog.
Curve Generator to open the Curve Generator Dialog.
- Select one of the three curve types Cartesian, Polar or Parametric. For the Cartesian type, also specify the Orientation, which is the XY principal plane by default.
- Specify the range of the curve. This includes Start, Stop and Step values. For polar curves, the angles are expressed in radians.
- In the "Parameters" section, define the function representing the curve. For the Cartesian type, this has the form y = f(x) in XY Plane, z = f(y) in YZ Plane or x = f(z) in ZX Plane. For polar curves, the function is defined as r = f(t), where t and r represent the angle and radius, respectively. For parametric curves, t is the parameter, and the x, y and z coordinates are all expressed as three functions of t.
- Curve Generator offers two options for the curve to be generated: Polyline or NURBS Curve. The latter is the default option. Change Curve Type if you want to create a polyline.
- Before you create the curve and add it to the Navigation Tree, you have an opportunity to preview it. To do so, click the Preview button of the dialog. A yellow ghost of the curve appears in the Project Workspace. You can change the range or modify the function at this time. Once you are satisfied with the generated curve, click the Create to finalize its creation and add it to the list of object on the Navigation Tree.
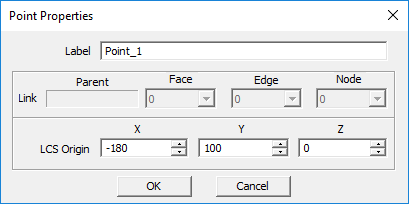
Point Tool
MENU: Object → Special → Point
TO DRAW A POINT:
- Activate the Point Tool.
- Left-click to establish the location of the point.
PYTHON COMMAND: point(label,x0,y0,z0)
POINT PARAMETERS
| Parameter Name | Value Type | Units | Default Value | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LCS_X | real numeric | project units | - | X-coordinate of point |
| LCS_Y | real numeric | project units | - | Y-coordinate of point |
| LCS_Z | real numeric | project units | - | Z-coordinate of point |
Fractal Tree Tool
MENU: Object → Special → Fractal Tree
TO DRAW A FRACTAL TREE:
- Activate the Fractal Tree Tool.
- Left-click to establish the location of the fractal tree. A default horizontal fractal tree appears in the project workspace.
- The Fractal Dialog opens up on the lower right corner of the screen. You have two options: fractal tree with linear or cylindrical branches. You can also set the number of fractal levels.
- Make sure to click the OK button of the dialog to complete the fractal construction.
PYTHON COMMAND: fractal_tree(label,x0,y0,z0,key_type,key_size,n_level,sep_angle,n_gen,prune_factor,thickness,thick_factor)
FRACTAL TREE PARAMETERS
| Parameter Name | Value Type | Units | Default Value | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LCS_X | real numeric | project units | - | X-coordinates of base |
| LCS_Y | real numeric | project units | - | Y-coordinates of base |
| LCS_Z | real numeric | project units | - | Z-coordinates of base |
| rot_X | real numeric | degrees | - | local rotation about X-axis |
| rot_Y | real numeric | degrees | - | local rotation about Y-axis |
| rot_Z | real numeric | degrees | - | local rotation about Z-axis |
| key_object_type | Line or Cylinder | - | Line | - |
| level_count | integer numeric | - | 3 | number of fractal levels |
| separation_angle | real numeric | degrees | 30 | angle between two adjacent branches |
| generation_factor | integer numeric | - | 3 | Number of new branches generated at each node |
| prune_factor | real numeric | - | 0 | A number between 0 and 1 representing the percentage of branches randomly deleted |
| thickness | real numeric | project units | 1 | diameter of branches |
| thickness_factor | real numeric | - | 0.2 | A number between 0 and 1 representing the percentage of tapering of each cylindrical branch upward |