Difference between revisions of "Digital Tutorial Lesson 1: Examining Logic Gates"
Kazem Sabet (Talk | contribs) (→Using Live Digital Timing Diagrams) |
Kazem Sabet (Talk | contribs) (→Using Live Digital Timing Diagrams) |
||
| Line 88: | Line 88: | ||
Also note that "'''Step Size'''" is different from "'''Step Ceiling'''". Step size specifies how large each time step of the simulation is when using the "Simulation Stepping" feature. Step Size does not factor into the simulation when running the engine in "'''Walk'''" or "'''Run'''" modes, where the simulation engine itself decides how large a step to take. On the other hand, Step Ceiling is the maximum value that you specify for the automatically calculated time step when a simulation is "Walked" or "Run". | Also note that "'''Step Size'''" is different from "'''Step Ceiling'''". Step size specifies how large each time step of the simulation is when using the "Simulation Stepping" feature. Step Size does not factor into the simulation when running the engine in "'''Walk'''" or "'''Run'''" modes, where the simulation engine itself decides how large a step to take. On the other hand, Step Ceiling is the maximum value that you specify for the automatically calculated time step when a simulation is "Walked" or "Run". | ||
| − | To set the step size, go to '''Simulate Menu''' and select the "'''Time Options...'''" to open the Simulation Time Options Dialog. Or click the button labeled {{key|...}} on the '''[[Main toolbar|[[Main toolbar|[[Main toolbar|[[Main toolbar|[[Main toolbar|[[Main toolbar|[[Main toolbar|[[Main toolbar|[[Main toolbar|[[Main toolbar|[[Main toolbar|[[Main toolbar|[[Main toolbar|[[Main toolbar|[[Main toolbar|Main Toolbar]]]]]]]]]]]]]]]]]]]]]]]]]]]]]]''' on the left of the Run button as shown in the figure below. You can also use the keyboard shortcut "Ctrl+I" to open this dialog, which is shown below: | + | To set the step size, go to '''Simulate Menu''' and select the "'''Time Options...'''" to open the Simulation Time Options Dialog. Or click the button labeled {{key|...}} on the '''[[Main toolbar|[[Main toolbar|[[Main toolbar|[[Main toolbar|[[Main toolbar|[[Main toolbar|[[Main toolbar|[[Main toolbar|[[Main toolbar|[[Main toolbar|[[Main toolbar|[[Main toolbar|[[Main toolbar|[[Main toolbar|[[Main toolbar|[[Main toolbar|Main Toolbar]]]]]]]]]]]]]]]]]]]]]]]]]]]]]]]]''' on the left of the Run button as shown in the figure below. You can also use the keyboard shortcut "Ctrl+I" to open this dialog, which is shown below: |
<table> | <table> | ||
| Line 188: | Line 188: | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
| − | When Input 3 jumps to 1 at t = 180ns, it takes the NAND gate a propagation delay of | + | When Input 3 jumps to 1 at t = 180ns, it takes the NAND gate A2 a propagation delay of 7ns to fall from its 1 state down to 0. Similarly, it takes the Inverter gate A4 an additional propagation delay of 12ns to rise from its 0 state up to 1. This makes a total delay of 19ns as you can see from the graph. At t = 240ns, the reverse of these events happens and gate A2 and A4 undergo the opposite transition types. The total propagation delay is still 19ns, and therefore, the output drops from 1 to 0 at t = 259ns. These events are summarized in the table below. |
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 199: | Line 199: | ||
! scope="col"| Total Delay | ! scope="col"| Total Delay | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 180ns | + | | t = 180ns |
| H -> L | | H -> L | ||
| 7ns | | 7ns | ||
| Line 206: | Line 206: | ||
| 19ns | | 19ns | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 240ns | + | | t = 240ns |
| L -> H | | L -> H | ||
| 11ns | | 11ns | ||
Revision as of 14:13, 22 September 2015
Contents
What You Will Learn
In this tutorial you will use generic inverter gates and two-input NAND gates to build a three-input AND circuit. You will learn how to define digital inputs and outputs and use RF.Spice's live digital timing diagrams. It is assumed that by this time you have already completed the first few analog tutorial lessons and are comfortable with navigating the RF.Spice A/D Workshop.
Placing Digital Parts
To build your first digital circuit, you need the following parts:
| Part Name | Part Type | Part Value |
|---|---|---|
| In1 | Digital Input | 1-bit |
| In2 | Digital Input | 1-bit |
| In3 | Digital Input | 1-bit |
| Out1 | Digital Output | 1-bit |
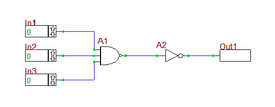
| A1 - A2 | Generic NAND Gate | Defaults |
| A3 - A4 | Generic Inverter Gate | Defaults |
Digital input and output ports are generic and virtual parts. You can get them from the "Digital I/O" submenu of the "Parts Menu". Or you can easily place them in your circuit by typing the keyboard shortcut N for Digital Input and the keyboard shortcut O for Digital Output. Similar to all other parts or devices, digital input and output ports have property dialogs that can be accessed by double-clicking on them. By default, the digital input and output takes 1-bit binary data in decimal format (rather then hexadecimal). The keyboard shortcut for the NAND gate is Alt+A, and keyboard shortcut for the inverter gate is Alt+O.
| |
You can use the keyboard's Space bar to "Repeat Place Device". |
Your project workspace at this point should like the figure below:
Finally, use one the wiring methods you learned in the earlier analog tutorial lessons to connect all the parts and I/O ports. At the end, you should have a digital circuit similar to the figure shown below. Straight wires can always be drawn by simply clicking on device pins and dragging a line out of the pins. For drawing bent lines and multi-segment lines, you have to use the Wire Tool.
Testing the Digital Circuit by Stepping Manually
Digital circuit simulation is a time domain simulation. Furthermore, it is an event-driven simulation. It means that the simulation engine waits for changes in the input(s) of the circuit and then updates the digital state of various nodes in response to those state changes. You can run a time domain simulation in three different modes: Step, Walk or Run. "Stepping" increments time a single time step at a time. "Walking" is faster than stepping and increments time by multiple steps at a time determined using a "Walk Factor". "Running" is equivalent to the analog live simulation and continues indefinitely until you pause it or stop it and reset. The first thing you always do in a digital simulation is to set the time step size.
Also note that "Step Size" is different from "Step Ceiling". Step size specifies how large each time step of the simulation is when using the "Simulation Stepping" feature. Step Size does not factor into the simulation when running the engine in "Walk" or "Run" modes, where the simulation engine itself decides how large a step to take. On the other hand, Step Ceiling is the maximum value that you specify for the automatically calculated time step when a simulation is "Walked" or "Run".
To set the step size, go to Simulate Menu and select the "Time Options..." to open the Simulation Time Options Dialog. Or click the button labeled ... on the [[Main toolbar|[[Main toolbar|[[Main toolbar|[[Main toolbar|[[Main toolbar|[[Main toolbar|[[Main toolbar|[[Main toolbar|[[Main toolbar|[[Main toolbar|[[Main toolbar|[[Main toolbar|[[Main toolbar|[[Main toolbar|[[Main toolbar|Main Toolbar]]]]]]]]]]]]]]]]]]]]]]]]]]]]]] on the left of the Run button as shown in the figure below. You can also use the keyboard shortcut "Ctrl+I" to open this dialog, which is shown below:
Set the "Time Step" to 20n, leave the "Walk Factor" at the default value of 2 and close the dialog. Now start the digital simulation by "Stepping" your digital circuit. Click the "Step" ![]() button of the Main Toolbar or select "Step" from the "Simulate Menu" or simply use the keyboard shortcut Ctrl+H. The simulation time will increase to 20ns, and the output’s value will change to 0. Note that all your three inputs have initial values of 0. The state of your circuit is shown in the figure below on the left. Next, change the value of Input 1 to 1 and leave the Input 2 and Input 3 at 0. During a live simulation, you can change the values of inputs by clicking on their Up Arrow and Down Arrow buttons at their right end. Note that by changing the input values, the output doesn't change immediately. This is because the engine is waiting for you to step the time to compute the next state of the circuit. Click the "Step"
button of the Main Toolbar or select "Step" from the "Simulate Menu" or simply use the keyboard shortcut Ctrl+H. The simulation time will increase to 20ns, and the output’s value will change to 0. Note that all your three inputs have initial values of 0. The state of your circuit is shown in the figure below on the left. Next, change the value of Input 1 to 1 and leave the Input 2 and Input 3 at 0. During a live simulation, you can change the values of inputs by clicking on their Up Arrow and Down Arrow buttons at their right end. Note that by changing the input values, the output doesn't change immediately. This is because the engine is waiting for you to step the time to compute the next state of the circuit. Click the "Step" ![]() button or type Ctrl+H one more time. The simulation time increases to 40ns, but the output’s value stays at 0. This is expected as a three-input AND circuit requires all three inputs to be 1 to have an output of 1. The state of the circuit at t = 40s is shown below in the middle figure. Finally, change the values of Input 2 and Input 3 to 1. Step the simulation to 60ns. This time, the output changes to 1 as shown below in the figure on the right. Note that at each time step, the state of all the wires including the output of the NAND gate is displayed on the circuit. The binary states are shown in small black box labels. You can also tell the state of a wire from its color. Blue is 0 and red is 1.
button or type Ctrl+H one more time. The simulation time increases to 40ns, but the output’s value stays at 0. This is expected as a three-input AND circuit requires all three inputs to be 1 to have an output of 1. The state of the circuit at t = 40s is shown below in the middle figure. Finally, change the values of Input 2 and Input 3 to 1. Step the simulation to 60ns. This time, the output changes to 1 as shown below in the figure on the right. Note that at each time step, the state of all the wires including the output of the NAND gate is displayed on the circuit. The binary states are shown in small black box labels. You can also tell the state of a wire from its color. Blue is 0 and red is 1.
Using Live Digital Timing Diagrams
RF.Spice A/D allows you to view the state of your digital inputs and outputs graphically in real time using "Live Timing Diagrams". The digital timing diagram appears at the bottom of the Workshop just like a regular graph. However, these are interactive "live" graphs that change and expand with every time step. For this part of the lesson, you keep the value of "Time Step" at 20ns. First, reset your simulation engine by clicking the "Stop/Reset" ![]() button of the Main Toolbar. Also reset the values of all the three inputs to 0.
button of the Main Toolbar. Also reset the values of all the three inputs to 0.
To activate the timing diagrams, click the "Show/Hide Live Digital Timing Diagrams" ![]() button of the Schematic Toolbar. Nothing happens immediately because you haven't started a digital simulation yet. Here is the game plan that you will follow next. You will set the values of each input to 1 sequentially, one at a time. You will increment three time steps between any two actions or events. Then, you will revert the values of the three inputs back to 0 sequentially, one at a time, in the reverse order, until all the three inputs are 0 again. The following table shows the timing of the events:
button of the Schematic Toolbar. Nothing happens immediately because you haven't started a digital simulation yet. Here is the game plan that you will follow next. You will set the values of each input to 1 sequentially, one at a time. You will increment three time steps between any two actions or events. Then, you will revert the values of the three inputs back to 0 sequentially, one at a time, in the reverse order, until all the three inputs are 0 again. The following table shows the timing of the events:
| Time | Input 1 | Input 2 | Input 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0ns | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 60ns | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 120ns | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 180ns | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 240ns | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 300ns | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 360ns | 0 | 0 | 0 |
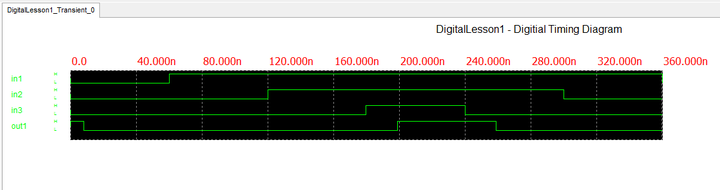
Start the digital simulation with all zero inputs and increment three time steps to 60ns. You will see that four timing diagrams appear at the bottom of the Workshop, one for each input and one for the output. In general every input and output port will have a timing diagram. Then, change the value of Input 1 to 1. Step again and you will see that the timing diagrams immediately get updated because the input states have now changed. Increment two more time steps to 120ns. Then, change the value of Input 2 to 1. Follow this recipe according to the above event table with 60ns intervals until all inputs are set to 0 again. The timing diagrams get updated after each change of state and the final diagrams are shown in the figure below. Note that your timing diagram may expand too long to fit into the bottom graph window. In that case, click on the title of the graph window tab to make it the active window. The toolbar changes accordingly. Then click the "Zoom Out Horizontal" ![]() button of the Graph Toolbar to shrink the diagram until it has the right size for viewing.
button of the Graph Toolbar to shrink the diagram until it has the right size for viewing.
| |
The timing diagram updates only when there is a change of states of the inputs. |
With a closer look at the output timing diagram, you will be able to see the propagation delay between the input and output ports. For example, at t = 180ns, when all three inputs are 1, you would expect to see the output to jump at 1. However, it takes about 19ns for this to happen (at t = 199ns). To understand this, double-click on the NAND gate A2 and inverter gate A4 to open up their property dialogs as shown below. You will see that the generic NAND gate has a "Low-to-High Propagation Delay" of 11ns and a "High-to-Low Propagation Delay" of 7ns. The generic inverter gate has a "Low-to-High Propagation Delay" of 12ns and a "High-to-Low Propagation Delay" of 8ns.
When Input 3 jumps to 1 at t = 180ns, it takes the NAND gate A2 a propagation delay of 7ns to fall from its 1 state down to 0. Similarly, it takes the Inverter gate A4 an additional propagation delay of 12ns to rise from its 0 state up to 1. This makes a total delay of 19ns as you can see from the graph. At t = 240ns, the reverse of these events happens and gate A2 and A4 undergo the opposite transition types. The total propagation delay is still 19ns, and therefore, the output drops from 1 to 0 at t = 259ns. These events are summarized in the table below.
| Time | A2 Transition Type | A2 Transition Delay | A4 Transition Type | A4 Transition Delay | Total Delay |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| t = 180ns | H -> L | 7ns | L -> H | 12ns | 19ns |
| t = 240ns | L -> H | 11ns | H -> L | 8ns | 19ns |