Difference between revisions of "An Overview of Digital Circuit Simulation"
Kazem Sabet (Talk | contribs) (→Setting Up Digital Circuit Simulations) |
Kazem Sabet (Talk | contribs) (→Digital Bus Connectors) |
||
| (5 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 109: | Line 109: | ||
==Propagation Delays== | ==Propagation Delays== | ||
| − | |||
The propagation delay of a digital device is the time it takes for the signal to change at the output in response to a change at the input. Each output pin of a digital device has a propagation delay associated with it. The propagation delay of a pin can be affected by the circuit's default fixed delay, the circuit's default delay class, the specific pin's overriding delay or delay class, and the device model's maximum, minimum and typical delays. | The propagation delay of a digital device is the time it takes for the signal to change at the output in response to a change at the input. Each output pin of a digital device has a propagation delay associated with it. The propagation delay of a pin can be affected by the circuit's default fixed delay, the circuit's default delay class, the specific pin's overriding delay or delay class, and the device model's maximum, minimum and typical delays. | ||
The delay actually involves two values, a rise time and a fall time. TPLH (the low-to-high propagation delay) is the time from the input change time to the output change time when the output is going from low to high. TPHL (the high-to-low propagation delay) is the time from the input change time to the output change time when the output is going from high to low. Propagation delays are important because they determine the speed of your circuit, and in circuits with feedback and flip flops and registers, propagation delays can even affect whether or not your circuit works. A digital device's delays can be accessed from its property dialog. | The delay actually involves two values, a rise time and a fall time. TPLH (the low-to-high propagation delay) is the time from the input change time to the output change time when the output is going from low to high. TPHL (the high-to-low propagation delay) is the time from the input change time to the output change time when the output is going from high to low. Propagation delays are important because they determine the speed of your circuit, and in circuits with feedback and flip flops and registers, propagation delays can even affect whether or not your circuit works. A digital device's delays can be accessed from its property dialog. | ||
| − | [[File: | + | <table> |
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td> | ||
| + | [[File:b2MAN_Fig40.png|thumb|left|640px| Digital Inverter's property dialog.]] | ||
| + | </td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | </table> | ||
| + | |||
An example showing the delays for the 7404 inverter is shown in the figure on the right. In this case, TPLH = 8ns and TPHL = 12ns. You can see that as the input value changes from 0 to 1 at t = 20ns, the output value changes from 1 to 0 at t = 20 + TPLH = 28ns. subsequently, as the input value changes from 1 to 0 at t = 40ns, the output value changes from 0 to 1 at t = 40 + TPHL = 52ns. | An example showing the delays for the 7404 inverter is shown in the figure on the right. In this case, TPLH = 8ns and TPHL = 12ns. You can see that as the input value changes from 0 to 1 at t = 20ns, the output value changes from 1 to 0 at t = 20 + TPLH = 28ns. subsequently, as the input value changes from 1 to 0 at t = 40ns, the output value changes from 0 to 1 at t = 40 + TPHL = 52ns. | ||
| Line 120: | Line 126: | ||
Many digital parts store their states regardless of what is happening at their inputs until a specific input changes value in a specific direction. The 7474 D flip flop is such a device. Its D input can change, but the output will not change until the clock pin rises from zero to one. We call the activating change in the clock pin a "Trigger". For the trigger to work, the circuit must be stable (i.e., inputs must not change) for a specific time period before the trigger occurs. This time is called the "Setup Time". After the trigger, the inputs must be stable for a time period so that the new state is not disturbed. This post-trigger time period is called the "Hold Time". If either the set up or hold time specifications are violated, the program notifies the user and sets the device's output to indeterminate. | Many digital parts store their states regardless of what is happening at their inputs until a specific input changes value in a specific direction. The 7474 D flip flop is such a device. Its D input can change, but the output will not change until the clock pin rises from zero to one. We call the activating change in the clock pin a "Trigger". For the trigger to work, the circuit must be stable (i.e., inputs must not change) for a specific time period before the trigger occurs. This time is called the "Setup Time". After the trigger, the inputs must be stable for a time period so that the new state is not disturbed. This post-trigger time period is called the "Hold Time". If either the set up or hold time specifications are violated, the program notifies the user and sets the device's output to indeterminate. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <table> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td> | ||
| + | [[File:b2MAN_Fig39.png|thumb|left|720px| Propagation delay of the digital inverter circuit.]] | ||
| + | </td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | </table> | ||
==Initial Circuit State== | ==Initial Circuit State== | ||
| Line 129: | Line 143: | ||
A digital clock is a periodic pulse generator similar to the analog square wave generator. Many digital devices such as flip flops require a clock for their operation. From a clock's property dialog, you can change its default name and set its period as well as its pulse width. The pulse width is the duration of the high (1) portion of the signal in each period. The clock input itself must have a period of a certain duration in order for dynamic devices to operate properly. This minimum period is expressed in its inverted form as the maximum frequency of a digital device. | A digital clock is a periodic pulse generator similar to the analog square wave generator. Many digital devices such as flip flops require a clock for their operation. From a clock's property dialog, you can change its default name and set its period as well as its pulse width. The pulse width is the duration of the high (1) portion of the signal in each period. The clock input itself must have a period of a certain duration in order for dynamic devices to operate properly. This minimum period is expressed in its inverted form as the maximum frequency of a digital device. | ||
| − | |||
==Digital Bus Connectors== | ==Digital Bus Connectors== | ||
| Line 135: | Line 148: | ||
You can edit the pin connections of bus connectors. By default, the wires coming into splitters and combiners are distributed automatically in the following manner. The wires connected to the top pin become the least significant bits of the splitter or combiner. The rest of the wires coming into the splitter or combiner are placed into the higher bits of the splitter or combiner. After the circuit state is updated, the splitter or combiner will display the bit numbers of the wires. The wire distribution can be customized by turning off the "Auto Distribute" checkbox in the bus connector's property dialog and entering the pin numbers manually. The first leg will use the wires in the first dialog box, etc. For example, if you have a 1-to-2 splitter, you can specify that you want bit 0 of the net to go onto the lower pin of the bus connector and bit 1 of the net to go to the upper pin. Multiple bits can be specified for each pin using colons and commas to group bits. | You can edit the pin connections of bus connectors. By default, the wires coming into splitters and combiners are distributed automatically in the following manner. The wires connected to the top pin become the least significant bits of the splitter or combiner. The rest of the wires coming into the splitter or combiner are placed into the higher bits of the splitter or combiner. After the circuit state is updated, the splitter or combiner will display the bit numbers of the wires. The wire distribution can be customized by turning off the "Auto Distribute" checkbox in the bus connector's property dialog and entering the pin numbers manually. The first leg will use the wires in the first dialog box, etc. For example, if you have a 1-to-2 splitter, you can specify that you want bit 0 of the net to go onto the lower pin of the bus connector and bit 1 of the net to go to the upper pin. Multiple bits can be specified for each pin using colons and commas to group bits. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <table> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td> | ||
| + | [[File:b2MAN_Fig41.png|thumb|left|480px| Bus Connector's property dialog.]] | ||
| + | </td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | </table> | ||
==Additional Considerations== | ==Additional Considerations== | ||
Latest revision as of 15:25, 10 November 2016
![]() Back to RF.Spice A/D Wiki Gateway
Back to RF.Spice A/D Wiki Gateway
Contents
- 1 The Main Differences Between Analog and Digital Circuit Simulations
- 2 Wire and Pin Values (Level & Strength)
- 3 How Does the Digital Simulation Engine Work?
- 4 Setting Up Digital Circuit Simulations
- 5 Propagation Delays
- 6 Initial Circuit State
- 7 Digital Clocks
- 8 Digital Bus Connectors
- 9 Additional Considerations
The Main Differences Between Analog and Digital Circuit Simulations
Analog devices and circuits operate in a continuous domain, where node voltages and branch currents can take arbitrary (positive or negative) values. These quantities can be varied continuously as a function of time. In contrast, digital devices and circuits operate in a discrete domain, where the device pins and circuit nodes have a binary state of either HIGH (1) or LOW (0) at any given instant of time. A digital circuit must have at least a digital input and a digital output with one or more digital devices connected in between. The input/output ports and devices are connected through wires. Just like device pins, the wires, too, have a digital state at any instant of time. You control and set the state of the input devices. B2.Spice’s digital simulator then determines the state of the wires and other device pins including the digital outputs.
A digital circuit simulation is an event-driven, time-domain simulation. You can define an arbitrary time step for your live digital simulation and increment the simulation time discretely, one step at a time, and manually change the state of the input(s) at each time step. It is recommended to use a time step of 20ns, which is typical for many commercially available digital devices. Or you can initiate a digital source and define a preset binary data sequence as your input, and then run a transient analysis of your digital circuit over the duration of your data sequence.
The binary states of 1 and 0 indeed represent high and low voltages (typically 3V/5V and 0V) , respectively, at the pins of a digital device. When the input pin of a digital device changes its state, for example, from low to high, the device’s output pin does not change its state instantaneously. It takes a finite amount of time for the device to react to the state change. This is called the propagation delay. Digital devices may have different propagation delays for change of state from low to high (TPLH) or change of state from high to low (TPHL). As you connect and cascade many digital devices, these propagation delays add up and amount to a sizable delay time. In high-speed digital circuits, where state changes may occur very fast, the accumulated propagation delays may create serious operational problems.
![]() RF.Spice A/D Digital Tutorial Lessons Gateway
RF.Spice A/D Digital Tutorial Lessons Gateway
Wire and Pin Values (Level & Strength)
Each wire or each device pin has both a logic level & a strength that together make its value at any instant of time. RF.Spice A/D supports 3 signal levels and 4 signal strengths, giving a total of 12 different values. The possible logic levels are high (1), low (0), and indeterminate (x). The possible strengths are strong (s), resistive (r), high impedance (z), and initial unknown (?), in order by their strength, from strongest to weakest. If one pin of a wire is generating a strong-high signal and the other pin is generating resistive-low, then the strong level will dominate, and the result will be a strong-high wire value.
The value that a pin propagates can differ from the value of the wire it is attached to if the wire is also attached to other pins which are propagating different values. In this case, the wire must resolve the competing values to come up with a single wire value. An indeterminate level resolved with anything else is indeterminate. An initial unknown level resolved with any other level is set equal to the other level. A high resolved with a low results in indeterminate. Pins will propagate indeterminate levels when there is not enough information at the inputs of a device to generate known outputs.
The digital circuit simulator must interpret the circuit before a simulation can begin. For example, it must determine which device pins are logically connected to which wires. To make the program run quickly, the circuit interpretation is performed only when necessary. As a result, while you are editing the circuit, the outputs may sometimes show incorrect values, or the bus widths may be incorrect. If you step the time or change an input value, then the circuit state will be updated correctly.
How Does the Digital Simulation Engine Work?
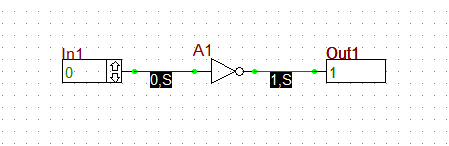
Rather than giving a theoretical account of the workings of the digital simulation engine, here we present an example. The circuit used for this example will be the simple inverter function given below.
Assuming that the initial conditions are set to indeterminate level and strength, all wires and pins will be preset to the indeterminate state with unknown strengths. As soon as the simulation starts, however, the input port will send a message to the simulation engine that its pin's value should be 0, causing the program's wire change list to be appended with the first wire's ID (0). The program will then process the wire changes. That is, the value of wire 0 is calculated to be 0, and the wire's value is passed to each of the pins that connected to it. Since the input to the inverter was previously unknown, and its new value is a strong 0, the input pin will be appended to the device input change list.
The next step is to process the device input change list. That is to calculate the output of the inverter. Since the input is 0, and the simulation code for the inverter says that the input should be inverted and placed at the output, the output should be 1. However, the output is delayed by 8ns, the TPLH time of the inverter. So the output pin is appended to the future change list along with the time the pin will change (8ns) and the value it will change to (1, Strong). The device's "Future Change List" will now look like this:
| Time | Device | Pin | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 8ns | 7404 | output | Strong 1 |
All of this happens at time t = 0. Wire 0 now has a value of zero, and both the output pin of the input port and the input pin of the inverter have values of 0. Assuming that the simulator is running, the next step is to advance the time to the point of the next state change. From the future change list, we see that the next change is at the time t = 8ns, so time is forwarded to 8ns. Now, the future change is realized, i.e., the output pin of the inverter changes value to a strong 1, and the wire connected to it, wire 1, is put on the wire change list. Then the wire change list is processed. First, the wire's value is calculated. Since the output pin is a strong 1 and the input to the output port is still unknown, the wire's value is calculated to be a strong 1. The devices that are connected to wire 1 are put on the device input change list, and the connected pins' values are set to strong 1. Finally, the output probe's state is recalculated. Since the output probe's input pin is a strong 1, the output probe displays 1.
This example is very simple, yet it illustrates the workings of the digital circuit simulation engine. Note that the simulator doesn't have to continually check for signal changes at every nanosecond, but rather it keeps track of future events which in turn drive the simulator. Reset Time, Go, Step, and changing an input value all update the circuit state if necessary once you have changed the circuit.
Setting Up Digital Circuit Simulations
Setting the Input
The simplest input device for digital circuits is the "Digital Input" with the keyboard shortcut N. For the basic input port, click on the up and down arrows with the selection arrow to toggle its value between 0 and 1. Or double click on the input port to open the device's property dialog and set or change the input's value. RF.Spice A/D offers a number of other input devices for digital simulation. With the "Toggle Switch", click on the switch to change its value. The button changes with each click of the mouse. The "DIP8 Switch" has eight output pins, each of which are controlled by a separate switch. Clicking on the switches will toggle their output values. With the hexadecimal "Keypad", click on one of the 16 buttons to select a value from 0, 1, ..., 9, A, B, ..., F. A "Digital Source" allows you to define a sequence of binary values as a function of time (or time step index).
For input devices, the logical value, number of bits available, decimal or hexadecimal format, and name of the device can be edited. Choose "Assert High" or "Assert Low" to determine the polarity setting of the device.
Setting the Output
The simplest output device for digital circuits is the "Digital Output" with the keyboard shortcut O. A digital probe device does the same function. All input and output port logic levels are shown in the input and output ports in hexadecimal notation. For single wire probes, the probe values 1 and 0 mean logical High and logical Low. The value ? means indeterminate, i.e. the program cannot determine the signal value. A strength of S is a strong signal, strength R is for resistive strength, Z for High Impedance, and ? for unknown strength.
If "Circuit Animation" is activated for digital simulation, you will see the logical state of all wire during a simulation as text. If "Circuit Animation" is turned off, you can view the logic level and strength of any wire in the schematic window by using the "Probe Tool". You can access this tool either from the Schematic Toolbar or from Edit Menu or simply using the keyboard shortcut Ctrl+Alt+P. In the "Probe Mode", place the tip of the logic probe on any wire and depress the left mouse button to see its logic level and strength. If the logic probe is probing a digital bus, then the value of the bus is the hexadecimal value calculated by making bit 0 of the bus the least significant bit.
For output devices, the device name and decimal or hexadecimal format can be edited. Choose "Assert High" or "Assert Low" to determine the polarity setting of the device.
Running a Live Interactive Digital Simulation
Set up the input values and set the time step you desire from the Simulation Time Options dialog. To open this dialog, click the Step Interval Settings ![]() button on the Main Toolbar, or select the Time Options item of the Simulate Menu, or use the keyboard shortcut Ctrl+I. A typical time step for digital circuit simulations is 20ns. Click the Step
button on the Main Toolbar, or select the Time Options item of the Simulate Menu, or use the keyboard shortcut Ctrl+I. A typical time step for digital circuit simulations is 20ns. Click the Step ![]() button to start the simulation. The simulation time is incremented by one time step. The current time is displayed in the simulation toolbar next to the control buttons. You can view the logical state of the wires and device pint either using the logic Probe Tool or by Circuit Animation. The values of input and output devices are displayed, too. You can change the values of input devices in real time. Click the Step
button to start the simulation. The simulation time is incremented by one time step. The current time is displayed in the simulation toolbar next to the control buttons. You can view the logical state of the wires and device pint either using the logic Probe Tool or by Circuit Animation. The values of input and output devices are displayed, too. You can change the values of input devices in real time. Click the Step ![]() button once again to increment the time by another time step. The Walk button starts the simulation but increases the simulation time by the walk factor, which can be set in the Simulation > Time Options menu. Click the Strop/Reset
button once again to increment the time by another time step. The Walk button starts the simulation but increases the simulation time by the walk factor, which can be set in the Simulation > Time Options menu. Click the Strop/Reset ![]() button to reset the time to t = 0.
button to reset the time to t = 0.
With RF.Spice A/D you can also view live digital timing diagrams during a live digital simulation. Click on the "Show/Hide Live Digital Timing Diagram" ![]() button in the Schematic Toolbar. Initially nothing happens. A soon as the digital simulation starts, a graph window opens up at the bottom of the screen that shows live timing diagrams for all the input and output devices. As you continue to step the time, these graphs expand. Similar to other graphs, the digital timing diagrams have their own settings dialogs in the Toolbox. Note that the timing diagrams are updated only when a change occurs in your circuit.
button in the Schematic Toolbar. Initially nothing happens. A soon as the digital simulation starts, a graph window opens up at the bottom of the screen that shows live timing diagrams for all the input and output devices. As you continue to step the time, these graphs expand. Similar to other graphs, the digital timing diagrams have their own settings dialogs in the Toolbox. Note that the timing diagrams are updated only when a change occurs in your circuit.
Running a Digital Simulation as a Transient Test
A live simulation is indeed a perpetual (time-domain) transient simulation. If your digital input values are known in advance as a function of time or time step index, you can alternatively run a transient test of your digital circuit. In this case, you need a digital source as your input. You can use one ore more digital probes for the output. The results will appear as timing diagrams in a graph window at the end of the transient test.
Propagation Delays
The propagation delay of a digital device is the time it takes for the signal to change at the output in response to a change at the input. Each output pin of a digital device has a propagation delay associated with it. The propagation delay of a pin can be affected by the circuit's default fixed delay, the circuit's default delay class, the specific pin's overriding delay or delay class, and the device model's maximum, minimum and typical delays.
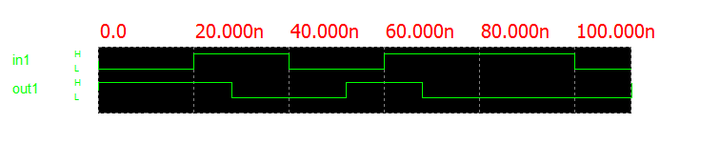
The delay actually involves two values, a rise time and a fall time. TPLH (the low-to-high propagation delay) is the time from the input change time to the output change time when the output is going from low to high. TPHL (the high-to-low propagation delay) is the time from the input change time to the output change time when the output is going from high to low. Propagation delays are important because they determine the speed of your circuit, and in circuits with feedback and flip flops and registers, propagation delays can even affect whether or not your circuit works. A digital device's delays can be accessed from its property dialog.
An example showing the delays for the 7404 inverter is shown in the figure on the right. In this case, TPLH = 8ns and TPHL = 12ns. You can see that as the input value changes from 0 to 1 at t = 20ns, the output value changes from 1 to 0 at t = 20 + TPLH = 28ns. subsequently, as the input value changes from 1 to 0 at t = 40ns, the output value changes from 0 to 1 at t = 40 + TPHL = 52ns.
RF.Spice A/D does not vary propagation delays depending on which input has changed value. For example, in an adder, when the carry-in input changes, the outputs respond more quickly than when other inputs change value. RF.Spice A/D cannot model this effect. Also, RF.Spice A/D cannot model delays when the output changes from indeterminate to low differently from changes from high to low. In the 74126 Bus Buffer with 3-State Outputs, for example, the time it takes for the output to change from its high impedance state to low (TPZL) is typically 15ns, while the time to change from high to low (TPHL) is typically 7ns. RF.Spice A/D does not allow specification of TPZL, so it uses TPHL in place of TPZL.
Many digital parts store their states regardless of what is happening at their inputs until a specific input changes value in a specific direction. The 7474 D flip flop is such a device. Its D input can change, but the output will not change until the clock pin rises from zero to one. We call the activating change in the clock pin a "Trigger". For the trigger to work, the circuit must be stable (i.e., inputs must not change) for a specific time period before the trigger occurs. This time is called the "Setup Time". After the trigger, the inputs must be stable for a time period so that the new state is not disturbed. This post-trigger time period is called the "Hold Time". If either the set up or hold time specifications are violated, the program notifies the user and sets the device's output to indeterminate.
Initial Circuit State
You have certain level of control over the initial state of a digital circuit. The input pins of digital devices are always initialized to the Initial Unknown strength & level. You can set the initial state of the output pin of some digital devices such as latches and flip flops. This is done using the "IC" parameter of these devices, which usually has a default zero value.
Digital Clocks
A digital clock is a periodic pulse generator similar to the analog square wave generator. Many digital devices such as flip flops require a clock for their operation. From a clock's property dialog, you can change its default name and set its period as well as its pulse width. The pulse width is the duration of the high (1) portion of the signal in each period. The clock input itself must have a period of a certain duration in order for dynamic devices to operate properly. This minimum period is expressed in its inverted form as the maximum frequency of a digital device.
Digital Bus Connectors
In RF.Spice A/D, the digital data may consist of one or more bits. In the case of multi-bit data, you can use wires to represent digital buses. In other words, a digital bus is equivalent to a multi-bit wire. You can convert a digital bus to multiple single-bit wires using bus connectors. There are two types of bus connectors: Splitters and Combiners. RF.Spice A/D provides 1-to-2, 1-to-3, 1-to-4 and 1-to-8 splitters as well as 2-to-1, 3-to-1, 4-to-1 and 8-to-1 combiners.
You can edit the pin connections of bus connectors. By default, the wires coming into splitters and combiners are distributed automatically in the following manner. The wires connected to the top pin become the least significant bits of the splitter or combiner. The rest of the wires coming into the splitter or combiner are placed into the higher bits of the splitter or combiner. After the circuit state is updated, the splitter or combiner will display the bit numbers of the wires. The wire distribution can be customized by turning off the "Auto Distribute" checkbox in the bus connector's property dialog and entering the pin numbers manually. The first leg will use the wires in the first dialog box, etc. For example, if you have a 1-to-2 splitter, you can specify that you want bit 0 of the net to go onto the lower pin of the bus connector and bit 1 of the net to go to the upper pin. Multiple bits can be specified for each pin using colons and commas to group bits.
Additional Considerations
For some simple device models (i.e. nets and bus connectors), all that is editable are the name of the device in the library, and the EDIF name. For all functional devices, the title of the device, which appears above the device picture, may be edited in this dialog. Also, propagation delays may be edited for each pin capable of output. Power dissipation parameters, including Icc, the static current dissipated, and the dynamic parameters Cpd and Cin, are available. Parameters for fan-out violations, Iol, Ioh, Iil, and Iih are available here. For dynamic devices, the additional parameters of set-up and hold time and maximum clock frequency are available.
All digital devices in the circuit have unique models. For example, if you place two 7404 inverters in the circuit and change tplh for one of them, the other will still have its old tplh value. There is no way to share models in the digital mode of RF.Spice A/D. However, if you use mixed mode in RF.Spice A/D, then you can share models and changing one 7404 inverter's delays will change the delays for all 7404 inverters in the circuit unless you specify through the Edit->Options menu that all devices are unique.
The most obvious cause of an unknown output value is an unknown input. You should probe the inputs to the device to find which of its inputs if any is unknown, and continue backtracking to the source of the problem. The possible causes of unknown output values are unknown input values, set-up time violations, and hold-time violations. For example, if you are using a 7474 D flip-flop, and d changes at time 10, then the clock changes at time 25ns, the output will soon change to unknown because the 7474's set-up time requirement is 20ns. Edit the model for a register or flip flop to view its set up and hold time requirements.
![]() Back to RF.Spice A/D Wiki Gateway
Back to RF.Spice A/D Wiki Gateway