Difference between revisions of "EM.Picasso"
Kazem Sabet (Talk | contribs) (→Visualizing the Far-Field Radiation Patterns) |
Kazem Sabet (Talk | contribs) (→Radar Cross Section of Planar Structures) |
||
| Line 404: | Line 404: | ||
=== Radar Cross Section of Planar Structures === | === Radar Cross Section of Planar Structures === | ||
| − | When a planar structure is excited by a plane wave source, the calculated far field data indeed represent the scattered fields of that planar structure. [[EM.Picasso]] can also calculate the radar cross section (RCS) of a planar target. Note that in this case the RCS is defined for a finite-sized target in the presence of an infinite background structure. The scattered θ and φ components of the far-zone electric field are indeed what you see in the 3D far field visualization of radiation (scattering) patterns. Instead of radiation or scattering patterns, you can instruct [[EM.Picasso]] to plot 3D visualizations of σ<sub>θ</sub>, σ<sub>φ</sub> and the total RCS | + | When a planar structure is excited by a plane wave source, the calculated far field data indeed represent the scattered fields of that planar structure. [[EM.Picasso]] can also calculate the radar cross section (RCS) of a planar target. Note that in this case the RCS is defined for a finite-sized target in the presence of an infinite background structure. The scattered θ and φ components of the far-zone electric field are indeed what you see in the 3D far field visualization of radiation (scattering) patterns. Instead of radiation or scattering patterns, you can instruct [[EM.Picasso]] to plot 3D visualizations of σ<sub>θ</sub>, σ<sub>φ</sub> and the total RCS. |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
[[Image:Info_icon.png|40px]] Click here to learn more about '''[[Data_Visualization_and_Processing#Visualizing_3D_RCS | Visualizing 3D RCS]]'''. | [[Image:Info_icon.png|40px]] Click here to learn more about '''[[Data_Visualization_and_Processing#Visualizing_3D_RCS | Visualizing 3D RCS]]'''. | ||
Revision as of 04:32, 10 August 2015
Contents
An EM.Picasso Primer
EM.Picasso in a Nutshell
EM.Picasso® is a versatile planar structure simulator for modeling and design of printed antennas, planar microwave circuits, and layered periodic structures. EM.Picasso's simulation engine is based on a 2.5-D full-wave Method of Moments (MoM) formulation that provides the ultimate modeling accuracy and computational speed for open-boundary multilayer structures. It can handle planar structures with arbitrary numbers of metal layouts, slot traces, vertical interconnects and lumped elements interspersed among different substrate layers.
EM.Picasso assumes that your planar structure has a substrate (background structure) of infinite lateral extents. Your substrate can be a dielectric half-space, or a single conductor-backed dielectric layer (as in microstrip components or patch antennas), or simply the unbounded free space, or any arbitrary multilayer stack-up configuration. In the special case of a free space substrate, EM.Picasso behaves similar to EM.Libera's Surface MoM simulator. In all the other cases, it is important to keep in mind the infinite extents of the background substrate structure. For example, you cannot use EM.Picasso to analyze a patch antenna with a finite-sized dielectric substrate, if the substrate edge effects are of concern in your modeling problem. EM.Tempo is recommended for the modeling of finite-sized substrates. Since EM.Picasso's Planar MoM simulation engine incorporates the Green's functions of the background structure into the analysis, only the finite-sized traces like microstrips and slots are discretized by the mesh generator. As a result, the size of EM.Picasso's computational problem is normally much smaller compared to the other techniques and solver. In addition, EM.Picasso generates a hybrid rectangular-triangular mesh of your planar structure with a large number of rectangular cells. This results in very fast computation times that oftentimes make up for the limited applications of EM.Picasso.
| |
EM.Picasso is the frequency-domain, full-wave Planar Module of EM.Cube, a comprehensive, integrated, modular electromagnetic modeling environment. EM.Picasso shares the visual interface, 3D parametric CAD modeler, data visualization tools, and many more utilities and features collectively known as CubeCAD with all of EM.Cube's other computational modules. |
![]() Click here to learn more about EM.Cube Modeling Environment.
Click here to learn more about EM.Cube Modeling Environment.
![]() Click here to learn more about the basic functionality of CubeCAD.
Click here to learn more about the basic functionality of CubeCAD.
An Overview of Planar Method of Moments
The Method of Moments (MoM) is a rigorous, full-wave numerical technique for solving open boundary electromagnetic problems. Using this technique, you can analyze electromagnetic radiation, scattering and wave propagation problems with relatively short computation times and modest computing resources. The method of moments is an integral equation technique; it solves the integral form of Maxwell’s equations as opposed to their differential forms that are used in the finite element or finite difference time domain methods.
In EM.Picasso, the background structure is usually a layered planar structure that consists of one or more laterally infinite material layers always stacked along the Z-axis. In other words, the dimensions of the layers are infinite along the X and Y axes. Metallic traces are placed at the boundaries between the substrate or superstrate layers. These are modeled by perfect electric conductor (PEC) traces or conductive sheet traces of finite thickness and finite conductivity. Some layers might be separated by infinite perfectly conducting ground planes. The two sides of a ground plane can be electromagnetically coupled through one or more slots (apertures). Such slots are modeled by magnetic surface currents. Furthermore, the metallic traces can be interconnected or connected to ground planes using embedded objects. Such objects can be used to model circuit vias, plated-through holes or dielectric inserts. These are modeled as volume polarization currents.
In a planar MoM simulation, the unknown electric and magnetic currents are discretized as a collection of elementary currents with small finite spatial extents. As a result, the governing integral equations reduce to a system of linear algebraic equations, whose solution determines the amplitudes of all the elementary currents defined over the planar structure's mesh. Once the total currents are known, you can calculate the fields everywhere in the structure.
![]() Click here to learn more about the theory of Planar Method of Moments.
Click here to learn more about the theory of Planar Method of Moments.
Building a Planar Structure
Understanding the Background Structure
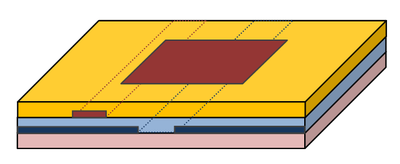
EM.Picasso is intended for constructing and modeling planar layered structures. By a planar structure we mean one that contains a background substrate of laterally infinite extents, made up of one or more material layers all stacked up vertically along the Z-axis. Objects of finite size are then interspersed among these substrate layers. The background structure in EM.Picasso is called the "Layer Stack-up". The layer stack-up is always terminated from the top and bottom by two infinite half-spaces. The terminating half-spaces might be the free space, or a perfect conductor (PEC ground), or any material medium. Most planar structures used in RF and microwave applications such as microstrip-based components have a PEC ground at their bottom. Some structures like stripline components require two bounding grounds (PEC half-spaces) both at their top and bottom.
Planar Object Types
EM.Picasso groups objects by their trace type and their hierarchical location in the substrate layer stack-up. All the planar objects belonging to the same trace group are located on the same substrate layer boundary and have the same color. All the embedded objects belonging to the same embedded set lie inside the same substrate layer and have the same color and same material composition.
EM.Picasso provides the following types of objects for building a planar layered structure:
- PEC Traces: These represent infinitesimally thin metallic planar objects that are deposited or metallized on or between substrate layers. PEC objects are modeled by surface electric currents.
- Slot Traces: These are used to model slots and apertures in PEC ground planes. Slot objects are always assumed to lie on an infinite horizontal PEC ground plane with zero thickness (which is not explicitly displayed in the project workspace). They are modeled by surface magnetic currents.
- Conductive Sheet Traces: These represent imperfect metals. They have a finite conductivity and a very small thickness. A surface impedance boundary condition is enforced on the surface of such traces.
- PEC Via Sets: These are metallic objects such as shorting pins, interconnect vias, plated-through holes, etc. that are grouped together as prismatic object sets. The embedded objects are modeled as vertical volume conduction currents.
- Embedded Dielectric Sets: These are prismatic dielectric objects inserted inside a substrate layer. You can define a finite permittivity and conductivity for such objects, but their height is always the same as the height of their host layer. The embedded dielectric objects are modeled as vertical volume polarization currents.
![]() Click here to learn more about Planar Traces & Object Types.
Click here to learn more about Planar Traces & Object Types.
Defining the Layer Stack-Up
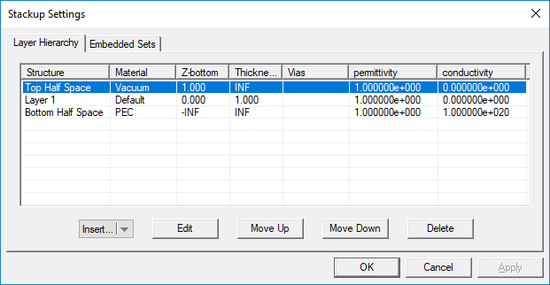
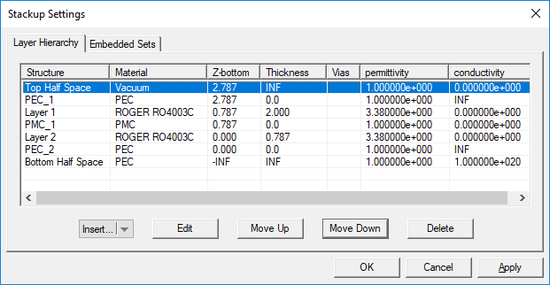
When you start a new project in EM.Picasso, there is always a default background structure that consists of a finite vacuum layer sandwiched between a vacuum top half-space and a PEC bottom half-space. Every time you open EM.Picasso or switched to it from EM.Cube's other modules, the Stack-up Settings Dialog opens up. This is where you define the entire background structure. Once you close this dialog, you can open it again by right clicking the Layer Stack-up item in the Computational Domain section of the navigation tree and selecting Layer Stack-up Settings... from the contextual menu. Or alternatively, you can select the menu item Simulate > Computational Domain > Layer Stack-up Settings...
The Stack-up Settings dialog has two tabs: Layer Hierarchy and Embedded Sets. The Layer Hierarchy tab has a table that shows all the background layers in hierarchical order from the top half-space to the bottom half-space. It also lists the material label of each layer, Z-coordinate of the bottom of each layer, its thickness (in project units) and material properties: permittivity (er), permeability (µr), electric conductivity (s) and magnetic conductivity (sm). There is also a column that lists the names of embedded object sets inside each substrate layer, if any.
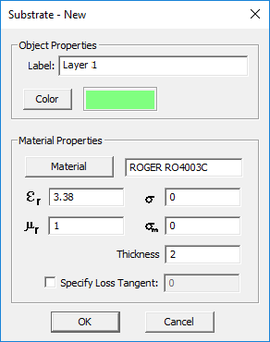
You can add new layers to your project's stack-up or delete its layers, or move layers up or down and thus change the layer hierarchy. To add a new background layer, click the arrow symbol on the Insert...button at the bottom of the dialog and select Substrate Layer from the button's dropdown list. A new dialog opens up where you can enter a label for the new layer and values for its material properties and thickness in project units.
You can delete a layer by selecting its row in the table and clicking the Delete button. To move a layer up and down, click on its row to select and highlight it. Then click either the Move Up or Move Down buttons consecutively to move the selected layer to the desired location in the stack-up. Note that you cannot delete or move the top or bottom half-spaces.
After creating a substrate layer, you can always edit its properties in the Layer Stack-up Settings dialog. Click on any layer's row in the table to select and highlight it and then click the Edit button. The substrate layer dialog opens up, where you can change the layer's label and assigned color. In the material properties section of the dialog, you can change the name of the material and its properties: permittivity (er), permeability (µr), electric conductivity (s) and magnetic conductivity (sm). To define electrical losses, you can either assign a value for electric conductivity (s), or alternatively, define a loss tangent for the material. In the latter case, check the box labeled "Specify Loss Tangent" and enter a value for it. In this case, the electric conductivity field becomes greyed out and reflects the corresponding s value at the center frequency of the project. You can also set the thickness of any substrate layer in the project units except for the top and bottom half-spaces.
![]() Click here to learn more about Defining Materials in EM.Cube.
Click here to learn more about Defining Materials in EM.Cube.
For better visualization of your planar structure, EM.Picasso displays a virtual domain in a default orange color to represent part of the infinite background structure. The size of this virtual domain is a quarter wavelength offset from the largest bounding box that encompasses all the finite objects in the project workspace. You can change the size of the virtual domain or its display color from the Domain Settings dialog, which you can access either by clicking the Computational Domain ![]() button of the Simulate Toolbar, or by selecting Simulate > Computational Domain > Domain Settings... from the Simulate Menu or by right clicking the Virtual Domain item of the Navigation Tree and selecting Domain Settings... from the contextual menu, or using the keyboard shortcut Ctrl+A. Keep in mind that the virtual domain is only for visualization purpose and does not affect the MoM simulation. The virtual domain also shows the substrate layers in translucent colors. If you assign different colors to your substrate layers, you have get a better visualization of multilayer virtual domain box surrounding your project structure.
button of the Simulate Toolbar, or by selecting Simulate > Computational Domain > Domain Settings... from the Simulate Menu or by right clicking the Virtual Domain item of the Navigation Tree and selecting Domain Settings... from the contextual menu, or using the keyboard shortcut Ctrl+A. Keep in mind that the virtual domain is only for visualization purpose and does not affect the MoM simulation. The virtual domain also shows the substrate layers in translucent colors. If you assign different colors to your substrate layers, you have get a better visualization of multilayer virtual domain box surrounding your project structure.
Defining Traces & Object Sets
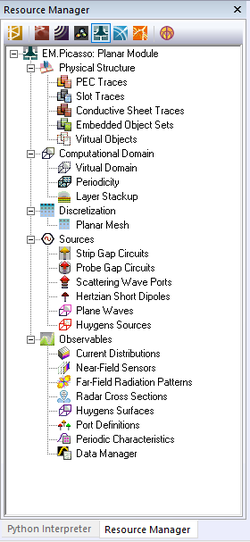
When you start a new project in Planar Module, the project workspace looks empty, and there are no finite objects in it. However, a default background structure is always present by default. Objects are defined as part of traces or embedded sets. Once defined, you can see a list of project objects in the Physical Structure section of the navigation tree.
Traces and object sets can be defined either from Layer Stack-up Settings dialog or from the navigation tree.
In the Layer Stack-up Settings dialog, you can add a new trace to the stack-up by clicking the arrow symbol on the Insert button of the dialog. You have to choose from Metal (PEC), Slot (PMC) or Conductive Sheet options. A respective dialog opens up, where you can enter a label and assign a color other than default ones. Once a new trace is defined, it is added, by default, to the top of the stack-up table underneath the top half-space. From here, you can move the trace down to the desired location on the layer hierarchy.
Every time you define a new trace, it is also added under the respective category in the Navigation Tree. Alternatively, you can define a new trace from the Navigation Tree by right clicking on one of the trace type names and selecting Insert New PEC Trace...or Insert New PMC Trace...or Insert New Conductive Sheet Trace...A respective dialog opens up for setting the trace properties. Once you close this dialog, it takes you directly to the Layer Stack-up Settings dialog so that you can set the right position of the trace on the stack-up.
Drawing & Managing Planar Objects
As soon as you start drawing geometrical objects in the project workspace, the Physical Structure section of the Navigation Tree gets populated. The names of traces are added under their respective trace type category, and the names of objects appear under their respective trace group. At any time, one and only one trace is active in the project workspace. An active trace is where all the new objects you draw belong to. When you define a new trace, it is set as active and you can immediately start drawing new objects on that trace. You can also set any trace active at any time by right clicking its name on the Navigation Tree and selecting Activate from the contextual menu. The name of the active trace is always displayed in bold letter in the Navigation Tree.
EM.Picasso has a special feature that makes construction of planar structures quite easy and straightforward. The active work plane of the project workspace is always set at the plane of the active trace. In EM.Cube's other modules, all objects are drawn in the XY plane (z = 0) by default. In Planar Module, all new objects are drawn on a horizontal plane that is located at the Z-coordinate of the currently active trace. As you change the active trace or add a new trace, you will also change the active work plane.
You can manage your project's layer hierarchy from the Layer Stack-up Settings dialog. You can add, delete and move around substrate layers, metallic and slot traces and embedded object sets. Metallic and slot traces can move among the interface planes between neighboring substrate layers. Embedded object sets including PEC vias and finite dielectric objects can move from substrate layer into another. When you delete a trace from the Layer Stack-up Settings dialog, all of its objects are deleted from the project workspace, too. You can also delete metallic and slot traces or embedded object sets from the Navigation Tree. To do so, right click on the name of the trace or object set in the Navigation Tree and select Delete from the contextual menu. You can also delete all the traces or object sets of the same type from the contextual menu of the respective type category in the Navigation Tree.
By default, the last defined trace or embedded object set is active. You can activate any trace or embedded object set at any time for drawing new objects. You can move one or more selected objects from any trace or embedded object set to another group of the same type or of different type. First select an object in the project workspace or in the Navigation Tree. Then, right click on the highlighted selection and select Move To > from the contextual menu. This opens another sub-menu containing Planar and a list of all the other EM.Cube modules that have already defined object groups. Select Planar or any other available module, and yet another sub-menu opens up with a list of all the available traces and embedded object sets already defined in your project. Select the desired group, and all the selected objects will move to that group. When selecting multiple objects from the Navigation Tree, make sure that you hold the keyboard's Shift Key or Ctrl Key down while selecting a group's name from the contextual menu.
Planar Module's Rules & Limitations
- Terminating PEC ground planes at the top or bottom of a planar structure are defined as PEC top or bottom half-spaces, respectively.
- A PEC ground plane placed in the middle of a substrate stack-up requires at least one slot object to provide electromagnetic coupling between its top and bottom sides. In this case, a PMC trace is rather introduced at the given Z-plane, which implies the presence of an infinite PEC ground although it is not explicitly indicated in the Navigation Tree.
- Metallic and slot traces cannot coexist on the same Z-plane. However, you can stack up multiple PEC and conductive sheet traces at the same Z-coordinate. Similarly, multiple PMC traces can be placed at the same Z-coordinate.
- Metallic and slot traces are strictly defined at the interface planes between substrate layers. To define a suspended metallic trace in a substrate layer (as in the case of the center conductor of a stripline), you must split the dielectric layer into two thinner layers and place your PEC trace at the interface between them.
- The current version of the Planar MoM simulation engine is based on a 2.5-D MoM formulation. Only vertical volume currents and no circumferential components are allowed on embedded objects. The 2.5-D assumption holds very well in two cases: (a) when embedded objects are very thin with a very small cross section (with lateral dimensions less than 2-5% of the material wavelength) or (b) when embedded objects are very short and sandwiched between two closely spaced PEC traces or grounds from the top and bottom.
- The current release of EM.Cube allows any number of PEC via sets collocated in the same substrate layer. However, you can define only one embedded dielectric object set per substrate layer, and no vias sets collocated in the same layer. Note that the single set can host an arbitrary number of embedded dielectric objects of the same material properties.
Planar module does not allow construction of 3D CAD objects. Instead, you draw the cross section of prismatic objects as planar surface objects parallel to the XY plane. EM.Cube then automatically extrudes these cross sections and constructs and displays 3D prisms over them. The prisms extend all the way across the thickness of the host substrate layer.
Discretizing Planar Structures
Understanding the Planar MoM Mesh
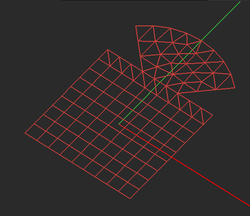
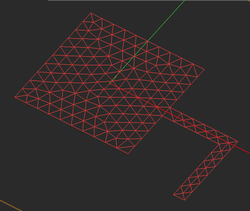
The method of moments (MoM) discretizes all the finite-sized objects of a planar structure (excluding the background structure) into a set of elementary cells. The accuracy of the MoM numerical solution depends greatly on the quality and resolution of the generated mesh. As a rule of thumb, a mesh density of about 20-30 cells per effective wavelength usually yields satisfactory results. Yet, for structures with lots of fine geometrical details or for highly resonant structures, higher mesh densities may be required. Also, the particular simulation data that you seek in a project also influence your choice of mesh resolution. For example, far field characteristics like radiation patterns are less sensitive to the mesh density than field distributions on a structure with a highly irregular shape and a rugged boundary.
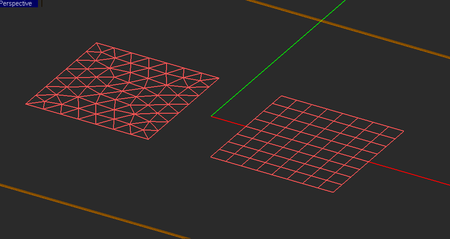
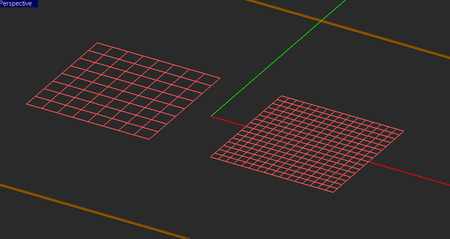
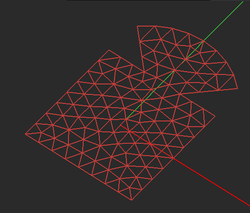
EM.Picasso generates two types of mesh for a planar structure: a pure triangular and a hybrid triangular-rectangular. In both case, EM.Picasso attempts to create a highly regular mesh, in which most of the cells have almost equal areas. The hybrid mesh type tries to produce as many rectangular cells as possible especially in the case of objects with rectangular or linear boundaries. In connection or junction areas between adjacent objects or close to highly curved boundaries, the use of triangular cells is clearly inevitable. EM.Picasso's default mesh type is hybrid. The uniformity or regularity of mesh is an important factor in warranting a stable MoM numerical solution.
The mesh density gives a measure of the number of cells per effective wavelength that are placed in various regions of your planar structure. The higher the mesh density, the more cells are created on the geometrical objects. Keep in mind that only the finite-sized objects of your structure are discretized. The free-space wavelength is defined as [math]\lambda_0 = \tfrac{2\pi f}{c}[/math], where f is the center frequency of your project and c is the speed of light in the free space. The effective wavelength is defined as [math]\lambda_{eff} = \tfrac{\lambda_0}{\sqrt{\varepsilon_{eff}}}[/math], where eeff is the effective permittivity. By default, EM.Picasso generates a hybrid mesh with a mesh density of 20 cells per effective wavelength. The effective permittivity is defined differently for different types of traces and embedded object sets. This is to make sure that enough cells are placed in areas that might feature higher field concentration. For PEC and conductive sheet traces, the effective permittivity is defined as the larger of the permittivity of the two substrate layers just above and below the metallic trace. For slot traces, the effective permittivity is defined as the mean (average) of the permittivity of the two substrate layers just above and below the metallic trace. For embedded object sets, the effective permittivity is defined as the largest of the permittivities of all the substrate layers and embedded dielectric sets.
Generating, Viewing & Customizing a Planar Mesh
You can generate and view a planar mesh by clicking the Show Mesh ![]() button of the Simulate Toolbar or by selecting Menu > Simulate > Discretization > Show Mesh or using the keyboard shortcut Ctrl+M. When the mesh of the planar structure is displayed in EM.Cube’s project workspace, its "Mesh View" mode is enabled. In this mode you can perform view operations like rotate view, pan or zoom, but you cannot create new objects or edit existing ones. To exit the mesh view mode, press the keyboard's Esc Key or click the Show Mesh
button of the Simulate Toolbar or by selecting Menu > Simulate > Discretization > Show Mesh or using the keyboard shortcut Ctrl+M. When the mesh of the planar structure is displayed in EM.Cube’s project workspace, its "Mesh View" mode is enabled. In this mode you can perform view operations like rotate view, pan or zoom, but you cannot create new objects or edit existing ones. To exit the mesh view mode, press the keyboard's Esc Key or click the Show Mesh ![]() button once again.
button once again.
Once a mesh is generated, it stays in the memory until the structure is changed or the mesh density or other settings are modified. Every time you view mesh, the one in the memory is displayed. You can force EM.Picasso to create a new mesh from the ground up by selecting Menu > Simulate > Discretization > Regenerate Mesh or by right clicking on the Planar Mesh item in the Discretization section of the navigation tree and selecting Regenerate from the contextual menu.
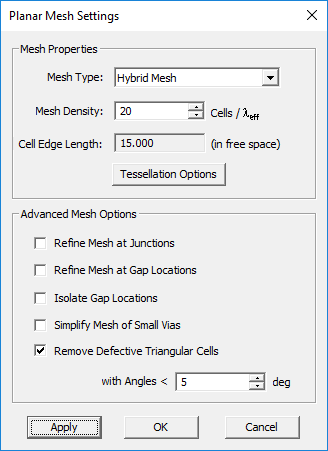
You can change the settings of the planar mesh including the mesh type and density from the Planar Mesh Settings Dialog. You can also change these settings while in the mesh view mode, and you can update the changes to view the new mesh. To open the mesh settings dialog, either click the Mesh Settings ![]() button of the Simulate Toolbar or select Menu > Simulate > Discretization > Mesh Settings..., or by right click on the Planar Mesh item in the Discretization section of the Navigation Tree and select Mesh Settings... from the contextual menu, or use the keyboard shortcut Ctrl+G. You can change the mesh algorithm from the dropdown list labeled Mesh Type, which offers two options: Hybrid and Triangular. You can also enter a different value for Mesh Density in cells per effective wavelength (λeff). For each value of mesh density, the dialog also shows the average "Cell Edge Length" in the free space. To get an idea of the size of mesh cells on the traces and embedded object sets, divide this edge length by the square root of the effective permittivity a particular trace or set. Click the Apply button to make the changes effective.
button of the Simulate Toolbar or select Menu > Simulate > Discretization > Mesh Settings..., or by right click on the Planar Mesh item in the Discretization section of the Navigation Tree and select Mesh Settings... from the contextual menu, or use the keyboard shortcut Ctrl+G. You can change the mesh algorithm from the dropdown list labeled Mesh Type, which offers two options: Hybrid and Triangular. You can also enter a different value for Mesh Density in cells per effective wavelength (λeff). For each value of mesh density, the dialog also shows the average "Cell Edge Length" in the free space. To get an idea of the size of mesh cells on the traces and embedded object sets, divide this edge length by the square root of the effective permittivity a particular trace or set. Click the Apply button to make the changes effective.
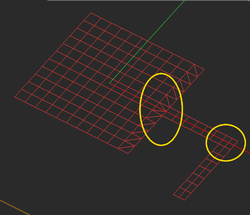
A Note on the Junction Mesh
The integrity of the planar mesh and its continuity in the junction areas where adjacent objects are connected directly affects the simulation results. The most important rule of object connections in EM.Picasso is that only objects belonging to the same trace can be connected to one another. If two objects belong to the same trace (residing on the same Z-plane) and have a common overlap area, EM.Picasso first merges the two objects using the "Boolean Union" operation and converts them into a single object for the purpose of meshing. EM.Picasso's hybrid planar mesh generator has some additional rules:
- If two connected rectangular objects have the same side dimensions along the common linear edge with perfect alignment, a rectangular junction mesh is produced.
- If two connected rectangular objects have different side dimensions along the common linear edge or have edge offset, a set of triangular cells is generated along the edge of the object with the large side.
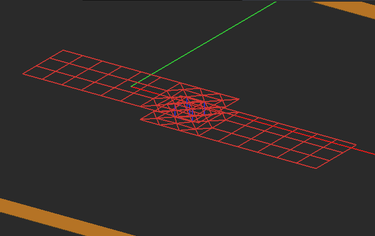
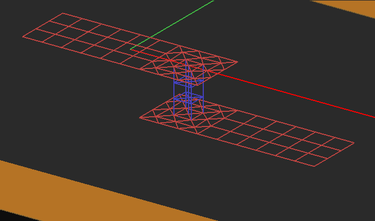
- Rectangular objects that contain gap source or lumped elements, always have a rectangular mesh around the gap area.
If an embedded object like an interconnect via is located under or above a metallic trace or connected from both top and bottom, it is critical to create mesh continuity between the embedded object and its connected metallic traces. In other words, the generated mesh must ensure current continuity between the vertical volume currents and horizontal surface currents. EM.Picasso’s planar mesh generator automatically handles situations of this kind and generates all the required connection meshes.
Refining the Planar Mesh Locally
It is very important to apply the right mesh density to capture all the geometrical details of your planar structure. This is especially true for "field discontinuity" regions such as junction areas between objects of different side dimensions, where larger current concentrations are usually observed at sharp corners, or at the connection areas between metallic traces and PEC vias, as well as the areas around gap sources and lumped elements, as these create voltage or current discontinuities. For large planar structures, using a higher mesh density may not always be a practical option since it will quickly lead to a very large MoM matrix and thus growing the size of the numerical problem. EM.Picasso provides several ways of controlling the mesh of a planar structure locally.
The Planar Mesh Settings dialog gives a few options for customizing your planar mesh around geometrical and field discontinuities. You can check the check box labeled "Refine Mesh at Junctions", which increases the mesh resolution at the connection area between rectangular objects. Or you can check the check box labeled "Refine Mesh at Gap Locations", which may prove particularly useful when gap sources or lumped elements are placed on a short transmission line connected from both ends. Or you can check the check box labeled "Refine Mesh at Vias", which increases the mesh resolution on the cross section of embedded object sets and at the connection regions of the metallic objects connected to them. EM.Picasso typically doubles the mesh resolution locally at the discontinuity areas when the respective boxes are checked.
You should always visually inspect EM.Picasso's default generated mesh to see if the current mesh settings have produced an acceptable mesh. You may often need to change the mesh density or other parameters and regenerate the mesh. Sometimes EM.Picasso's default mesh may contain very narrow triangular cells due to very small angles between two edges. In some rare cases, extremely small triangular cells may be generated, whose area is a small fraction of the average mesh cell. These cases typically happen at the junctions and other discontinuity regions or at the boundary of highly irregular geometries with extremely fine details. In such cases, increasing or decreasing the mesh density by one or few cells per effective wavelength often resolves that problem and eliminates those defective cells. Nonetheless, EM.Picasso's planar mesh generator offers an option to identify the defective triangular cells and either delete them or cure them. By curing we mean removing a narrow triangular cell and merging its two closely spaced nodes to fill the crack left behind. EM.Picasso by default deletes or cures all the triangular cells that have angles less than 10º. Sometimes removing defective cells may inadvertently cause worse problems in the mesh. You may choose to disable this feature and uncheck the box labeled "Remove Defective Triangular Cells" in the Planar Mesh Settings dialog. You can also change the value of the minimum allowable cell angle.
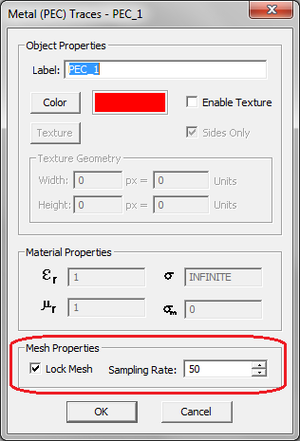
Another way of local mesh control is to lock the mesh density of certain traces or object sets. The mesh density that you specify in the Planar Mesh Settings dialog is a global parameter and applies to all the traces and embedded object sets in your project. However, you can lock the mesh of individual PEC, PMC and conductive sheet traces or embedded objects sets. In that case, the locked mesh density takes precedence over the global density. Note that locking mesh of object groups, in principle, is different than refining the mesh at discontinuities. In the latter case, the mesh of connection areas is affected. However, objects belonging to different traces cannot be connected to one another. Therefore, locking mesh can be useful primarily for isolated object groups that may require a higher (or lower) mesh resolution. You can lock the local mesh density by accessing the property dialog of a specific trace or embedded object set and checking the box labeled Lock Mesh. This will enable the Mesh Density box, where you can accept the default global value or set any desired new value.
Excitation Sources
Your planar structure must be excited by some sort of a signal source that induces electric currents on metal parts and magnetic currents on slot traces. The excitation source you choose depends on the observables you seek in your project. EM.Picasso provides the following source types for exciting planar structures:
- Gap Sources
- Probe Sources
- De-embedded Sources
- Short Dipole Sources
- Plane Wave Sources
- Huygens Sources
For antennas and planar circuits, where you typically define one or more ports, you usually use lumped sources. A lumped source is indeed a gap discontinuity that is placed on the path of an electric or magnetic current flow, where a voltage or current source is connected to inject a signal. Gap sources are placed across metal or slot traces. Probe sources are placed across vertical PEC vias. A de-embedded source is a special type of gap source that is placed near the open end of an elongated metal or slot trace to create a standing wave pattern, from which the scattering parameters can be calculated accurately. To calculate the scattering characteristics of a planar structure, e.g. its radar cross section (RCS), you excite it with a plane wave source. Short dipole sources are used to explore propagation of points sources along a layered structure. Huygens sources are virtual equivalent sources that capture the radiated electric and magnetic fields from another structure possibly in another EM.Cube computational module and bring them as a new source to excite your planar structure.
![]() Click here to learn more about Planar MoM Source Types.
Click here to learn more about Planar MoM Source Types.
![]() Click here to learn more about Using Source Arrays for Modeling Antenna Arrays.
Click here to learn more about Using Source Arrays for Modeling Antenna Arrays.
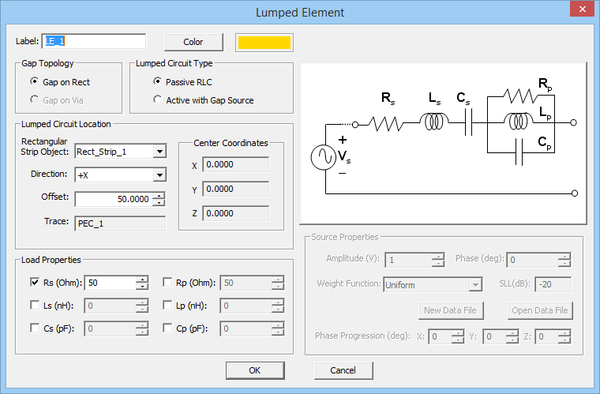
Modeling Lumped Elements in EM.Picasso
Lumped elements are components, devices, or circuits whose overall dimensions are very small compared to the wavelength. As a result, they are considered to be dimensionless compared to the dimensions of a mesh cell. In fact, a lumped element is equivalent to an infinitesimally narrow gap that is placed in the path of current flow, across which the device's governing equations are enforced. Using Kirkhoff's laws, these device equations normally establish a relationship between the currents and voltages across the device or circuit. Crossing the bridge to Maxwell's domain, the device equations must now be cast into a from o boundary conditions that relate the electric and magnetic currents and fields. EM.Picasso allows you to define passive circuit elements: Resistors (R), Capacitors (C), Inductors (L), and series and parallel combinations of them.
![]() Click here to learn more about Defining Lumped Elements.
Click here to learn more about Defining Lumped Elements.
![]() Click here for a general discussion of Linear Passive & Nonlinear Active Devices.
Click here for a general discussion of Linear Passive & Nonlinear Active Devices.
Defining Ports
Ports are used in a planar structure to order and index the sources for calculation of circuit parameters such as scattering (S), impedance (Z) and admittance (Y) parameters. In EM.Cube's Planar Module, you can use the following types of sources to define ports:
- Gap Sources
- Probe Sources
- Active Lumped Elements
- De-Embedded Sources
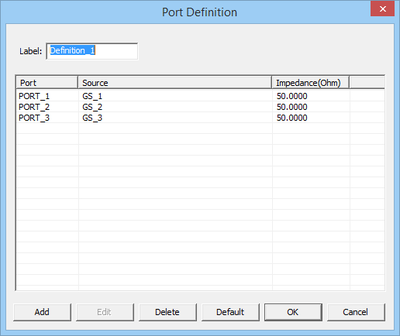
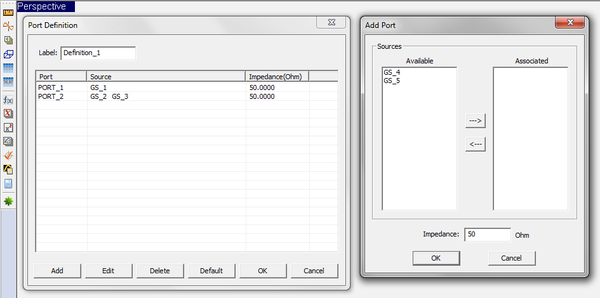
Ports are defined in the Observables section of the Navigation Tree. Right click on the Port Definition item of the Navigation Tree and select Insert New Port Definition... from the contextual menu. The Port Definition Dialog opens up, showing the default port assignments. If you have N sources in your planar structure, then N default ports are defined, with one port assigned to each source according to their order on the Navigation Tree. Note that your project can have mixed gap and probes sources as well as active lumped element sources.
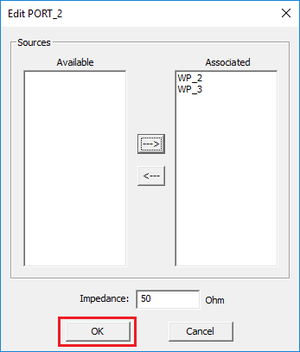
You can define any number of ports equal to or less than the total number of sources in your project. The Port List of the dialog shows a list of all the ports in ascending order, with their associated sources and the port's characteristic impedance, which is 50S by default. You can delete any port by selecting it from the Port List and clicking the Delete button of the dialog. Keep in mind that after deleting a port, you will have a source in your project without any port assignment and make sure that is what you intend. You can change the characteristic impedance of a port by selecting it from the Port List and clicking the Edit button of the dialog. This opens up the Edit Port dialog, where you can enter a new value in the box labeled Impedance.
![]() Click here to learn more about the theory of Computing Port Characteristics in Planar MoM.
Click here to learn more about the theory of Computing Port Characteristics in Planar MoM.
Modeling Coupled Ports
Sources can be coupled to each other to model coupled strip lines (CPS) on metal traces or coplanar waveguides (CPW) on slot traces. Similarly, probe sources may be coupled to each other. Coupling two or more sources does not change the way they excite a planar structure. It is intended only for the purpose of S parameter calculation. The feed lines or vias which host the coupled sources are usually parallel and aligned with one another and they are all grouped together as a single transmission line represented by a single port. This single "coupled" port then interacts with other coupled or uncoupled ports.
You couple two or more sources using the Port Definition Dialog. To do so, you need to change the default port assignments. First, delete all the ports that are to be coupled from the Port List of the dialog. Then, define a new port by clicking the Add button of the dialog. This opens up the Add Port dialog, which consists of two tables: Available sources on the left and Associated sources on the right. A right arrow (-->) button and a left arrow (<--) button let you move the sources freely between these two tables. You will see in the "Available" table a list of all the sources that you deleted earlier. You may even see more available sources. Select all the sources that you want to couple and move them to the "Associated" table on the right. You can make multiple selections using the keyboard's Shift and Ctrl keys. Closing the Add Port dialog returns you to the Port Definition dialog, where you will now see the names of all the coupled sources next to the name of the newly added port.
| |
It is your responsibility to set up coupled ports and coupled Transmission Lines properly. For example, to excite the desirable odd mode of a coplanar waveguide (CPW), you need to create two rectangular slots parallel to and aligned with each other and place two gap sources on them with the same offsets and opposite polarities. To excite the even mode of the CPW, you use the same polarity for the two collocated gap sources. Whether you define a coupled port for the CPW or not, the right definition of sources will excite the proper mode. The couple ports are needed only for correct calculation of the port characteristics. |
Running Planar MoM Simulations
The first step of planning a planar MoM simulation is defining your planar structure. This consists of the background structure plus all the finite-sized metal and slot trace objects and possibly embedded metal or dielectric objects that are interspersed among the substrate layers. The background stack-up is defined in the Layer Stack-up dialog, which automatically opens up as soon as you enter the Planar Module. The metal and slot traces and embedded object sets are listed in the Navigation Tree, which also shows all the geometrical (CAD) objects you draw in the project workspace under each object group at different Z-planes.
The next step is to decide on the excitation scheme. If your planar structure has one or more ports and you seek to calculate its port characteristics, then you have to choose one of the lumped source types or a de-embedded source. If you are interested in the scattering characteristics of your planar structure, then you must define a plane wave source. Before you can run a planar MoM simulation, you also need to decide on the project's observables. These are the simulation data that you expect EM.Cube to generate as the outcome of the numerical simulation. EM.Cube's Planar Module offers the following observables:
- Current Distribution
- Field Sensors
- Far Fields (Radiation Patterns or Radar Cross Section)
- Huygens Surfaces
- Port Characteristics
- Periodic Characteristics
If you run a simulation without having defined any observables, no data will be generated at the end of the simulation. Some observables require a certain type of excitation source. For example, port characteristics will be calculated only if the project contains a port definition, which in turn requires the existence of at least one gap or probe or de-embedded source. The periodic characteristics (reflection and transmission coefficients) are calculated only if the structure has a periodic domain and excited by a plane wave source.
Planar Module's Simulation Modes
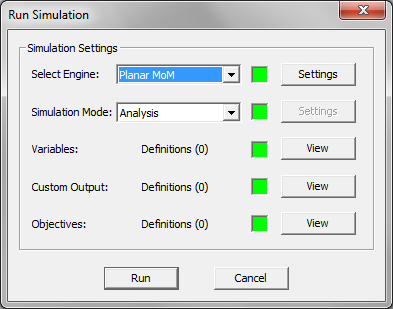
The simplest simulation type in EM.Cube is an analysis. In this mode, the planar structure in your project workspace is meshed at the center frequency of the project. EM.Cube generates an input file at this single frequency, and the Planar MoM simulation engine is run once. Upon completion of the planar MoM simulation, a number of data files are generated depending on the observables you have defined in your project. An analysis is a single-run simulation.
EM.Cube offers a number of multi-run simulation modes. In such cases, the Planar MoM simulation engine is run multiple times. At each engine run, certain parameters are varied and a collection of simulation data are generated. At the end of a multi-run simulation, you can graph the simulation results in EM.Grid or you can animate the 3D simulation data from the Navigation Tree. For example, in a frequency sweep, the frequency of the project is varied over its specified bandwidth. Port characteristics are usually plotted vs. frequency, representing your planar structure's frequency response. In an angular sweep, the θ or φ angle of incidence of a plane wave source is varied over their respective ranges. EM.Cube's Planar Module currently provides the following types of multi-run simulation modes:
- Frequency Sweep
- Parametric Sweep
- Optimization
- HDMR Sweep
Figure 1: Selecting a simulation mode in Planar Module's Simulation Run dialog.
Running A Planar MoM Analysis
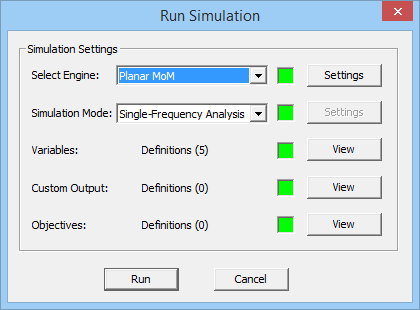
To run a planar MoM analysis of your project structure, open the Run Simulation Dialog by clicking the Run ![]() button on the Simulate Toolbar or select Menu > Simulate > Run or use the keyboard shortcut Ctrl+R. The Analysis option of the Simulation Mode dropdown list is selected by default. Once you click the Run button, the simulation starts. A new window, called the Output Window, opens up that reports the different stages of simulation and the percentage of the tasks completed at any time. After the simulation is successfully completed, a message pops up and reports the end of simulation. In certain cases like calculating scattering parameters of a circuit or reflection / transmission characteristics of a periodic surface, some results are also reported in the Output Window. At the end of a simulation, you need to click the Close button of the Output Window to return to the project workspace.
button on the Simulate Toolbar or select Menu > Simulate > Run or use the keyboard shortcut Ctrl+R. The Analysis option of the Simulation Mode dropdown list is selected by default. Once you click the Run button, the simulation starts. A new window, called the Output Window, opens up that reports the different stages of simulation and the percentage of the tasks completed at any time. After the simulation is successfully completed, a message pops up and reports the end of simulation. In certain cases like calculating scattering parameters of a circuit or reflection / transmission characteristics of a periodic surface, some results are also reported in the Output Window. At the end of a simulation, you need to click the Close button of the Output Window to return to the project workspace.
Figure 1: Planar Module's Simulation Run dialog.
Stages Of A Planar MoM Analysis
EM.Cube's Planar MoM simulation engine uses a particular formulation of the method of moments called mixed potential integral equation (MPIE). Due to high-order singularities, the dyadic Green's functions for electric fields generated by electric currents as well as the dyadic Green's functions for magnetic fields generated by magnetic currents have very slow convergence behaviors. Instead of using these slowly converging dyadic Green's function, the MPIE formulation uses vector and scalar potentials. These include vector electric potential A(r), scalar electric potential KΦ(r), vector magnetic potential F(r) and scalar magnetic potential KΨ(r). These potentials have singularities of lower orders. As a result, they coverage relatively faster. The speed of their convergence is further increased drastically using special singularity extraction techniques.
A planar MoM simulation consists of two major stages: matrix fill and linear system inversion. In the first stage, the moment matrix and excitation vector are calculated. In the second stage, the MoM system of linear equations is inverted using one of the several available matrix solvers to find the unknown coefficients of all the basis functions. The unknown electric and magnetic currents are linear superpositions of all these elementary solutions. These can be visualized in EM.Cube using the current distribution observables. Having determined all the electric and magnetic currents in your planar structure, EM.Cube can then calculate the near fields on prescribed planes. These are introduced as field sensor observables. The near-zone electric and magnetic fields are calculated using a spectral domain formulation of the dyadic Green's functions. Finally the far fields of the planar structure are calculated in the spherical coordinate system. These calculations are performed using the asymptotic form of the dyadic Green's functions using the "stationary phase method".
Setting Numerical Parameters
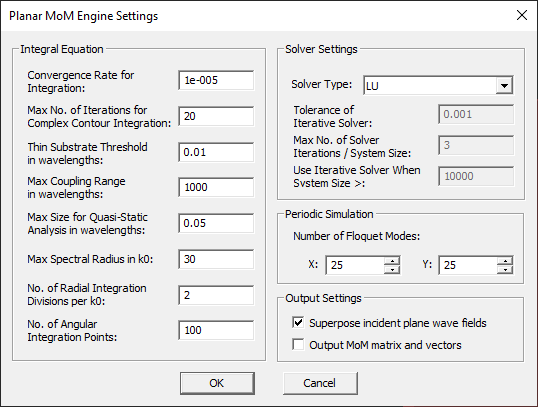
A planar MoM simulation involves a number of numerical parameters that take preset default values unless you change them. You can access these parameters and change their values by clicking the Settings button next to the Select Engine dropdown list in the Planar Module's Simulation Run dialog. In most cases, you do not need to open this dialog and you can leave all the default numerical parameter values intact. However, it is useful to familiarize yourself with these parameters, as they may affect the accuracy of your numerical results.
The Planar MoM Engine Settings Dialog is organized in a number of sections. Here we describe some of the numerical parameters. The "Matrix Fill" section of the dialog deals with the operations involving the dyadic Green's functions. You can set a value for the Convergence Rate for Integration, which is 1E-5 by default. This is used for the convergence test of all the infinite integrals in the calculation of the Hankel transform of spectral-domain dyadic Green's functions. When the substrate is lossy, the surface wave poles are captured in the complex integration plane using contour deformation. You can change the maximum number of iterations involved in this deformed contour integration, whose default value is 20. When the substrate is very thin with respect to the wavelength, the dyadic Green's functions exhibit numerical instability. Additional singularity extraction measures are taken to avoid numerical instability but at the expense of increased computation time. By default, a thin substrate layer is defined to a have a thickness less than 0.01λeff, where λeff is the effective wavelength. You can modify the definition of "Thin Substrate" by entering a value for Thin Substrate Threshold different than the default 0.01. The parameter Max Coupling Range determines the distance threshold in wavelength between the observation and source points after which the Green's interactions are neglected. This distance by default is set to 1,000 wavelengths. For electrically small structures, the phase variation across the structure may be negligible. In such cases, a fast quasi-static analysis can be carried out. You can set this threshold in wavelengths in the box labeled Max Dimensions for Quasi-Static Analysis.
In the "Spectral Domain Integration" section of the dialog, you can set a value to Max Spectral Radius in k0, which has a default value of 30. This means that the infinite spectral-domain integrals in the spectral variable kρ are pre-calculated and tabulated up to a limit of 30k0, where k0 is the free space propagation constant. These integrals may converge much faster based on the specified Convergence Rate for Integration described earlier. However, in certain cases involving highly oscillatory integrands, much larger integration limits like 100k0 might be needed to warrant adequate convergence. For spectral-domain integration along the real kρ axis, the interval [0, Nk0] is subdivided into a large number of sub-intervals, within each an 8-point Gauss-Legendre quadrature is applied. The next parameter, No. Radial Integration Divisions per k0, determines how small these intervals should be. By default, 2 divisions are used for the interval [0, k0]. In other words, the length of each integration sub-interval is k0/2. You can increase the resolution of integration by increasing this value above 2. Finally, instead of 2D Cartesian integration in the spectral domain, a polar integration is performed. You can set the No. of Angular Integration Points, which has a default value of 100.
Figure 1: The Planar MoM Engine Settings dialog.
Planar Module's Linear System Solvers
After the MoM impedance matrix [Z] (not to be confused with the impedance parameters) and excitation vector [V] have been computed through the matrix fill process, the planar MoM simulation engine is ready to solve the system of linear equations:
- [math] \mathbf{[Z]}_{N\times N} \cdot \mathbf{[I]}_{N\times 1} = \mathbf{[V]}_{N\times 1} [/math]
where [I] is the solution vector, which contains the unknown amplitudes of all the basis functions that represent the unknown electric and magnetic currents of finite extents in your planar structure. In the above equation, N is the dimension of the linear system and equal to the total number of basis functions in the planar mesh. EM.Cube's linear solvers compute the solution vector[I] of the above system. You can instruct EM.Cube to write the MoM matrix and excitation and solution vectors into output data files for your examination. To do so, check the box labeled "Output MoM Matrix and Vectors" in the Matrix Fill section of the Planar MoM Engine Settings dialog. These are written into three files called mom.dat1, exc.dat1 and soln.dat1, respectively.
There are a large number of numerical methods for solving systems of linear equations. These methods are generally divided into two groups: direct solvers and iterative solvers. Iterative solvers are usually based on matrix-vector multiplications. Direct solvers typically work faster for matrices of smal to medium size (N<3,000). EM.Cube's Planar Module offers five linear solvers:
- LU Decomposition Method
- Biconjugate Gradient Method (BiCG)
- Preconditioned Stabilized Biconjugate Gradient Method (BCG-STAB)
- Generalized Minimal Residual Method (GMRES)
- Transpose-Free Quasi-Minimum Residual Method (TFQMR)
Of the above list, LU is a direct solver, while the rest are iterative solvers. BiCG is a relatively fast iterative solver, but it works only for symmetric matrices. You cannot use BiCG for periodic structures or planar structures that contain both metal and slot traces at different planes, as their MoM matrices are not symmetric. The three solvers BCG-STAB, GMRES and TtFQMR work well for both symmetric and asymmetric matrices and they also belong to a class of solvers called Krylov Sub-space Methods. In particular, the GMRES method always provides guaranteed unconditional convergence.
EM.Cube's Planar Module, by default, provides a "Automatic" solver option that picks the best method based on the settings and size of the numerical problem. For linear systems with a size less than N = 3,000, the LU solver is used. For larger systems, BiCG is used when dealing with symmetric matrices, and GMRES is used for asymmetric matrices. If the size of the linear system exceeds N = 15,000, the sparse version of the iterative solvers is used, utilizing a row-indexed sparse storage scheme. You can override the automatic solver option and manually set you own solver type. This is done using the Solver Type dropdown list in the "Linear System Solver" section of the Planar MoM Engine Settings dialog. There are also a number of other parameters related to the solvers. The default value of Tolerance of Iterative Solver is 1E-3, which can be increased for more ill-conditioned systems. The maximum number of iterations is usually expressed as a multiple of the systems size. The default value of Max No. of Solver Iterations / System Size is 3. For extremely large systems, sparse versions of iterative solvers are used. In this case, the elements of the matrix are thresholded with respect to the larges element. The default value of Threshold for Sparse Solver is 1E-6, meaning that all the matrix elements whose magnitude is less than 1E-6 times the large matrix elements are set equal to zero. There are two more parameters that are related to the Automatic Solver option. These are " User Iterative Solver When System Size >" with a default value of 3,000 and " Use SParse Storage When System Size > " with a default value of 15,000. In other words, you control the automatic solver when to switch between direct and iterative solvers and when to switch to the sparse version of iterative solvers.
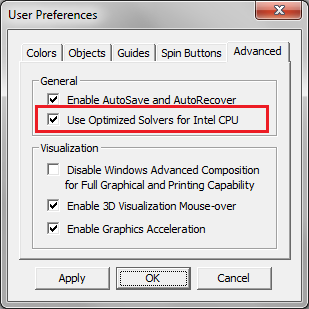
If your computer has an Intel CPU, then EM.Cube offers special versions of all the above linear solvers that have been optimized for Intel CPU platforms. These optimal solvers usually work 2-3 time faster than their generic counterparts. When you install EM.Cube, the option to use Intel-optimized solvers is already enabled. However, you can disable this option (e.g. if your computer has a non-Intel CPU). To do that, open the EM.Cube's Preferences Dialog from Menu > Edit > Preferences or using the keyboard shortcut Ctrl+H. Select the Advanced tab of the dialog and uncheck the box labeled " Use Optimized Solvers for Intel CPU".
Running Uniform and Adaptive Frequency Sweeps
In a frequency sweep, the operating frequency of a planar structure is varied during each sweep run. EM.Cube's Planar Module offers two types of frequency sweep: Uniform and Adaptive. In a uniform frequency sweep, the frequency range and the number of frequency samples are specified. The samples are equally spaced over the frequency range. At the end of each individual frequency run, the output data are collected and stored. At the end of the frequency sweep, the 3D data can be visualized and/or animated, and the 2D data can be graphed in EM.Grid.
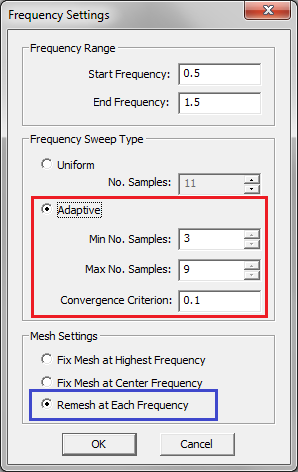
To run a uniform frequency sweep, open the Simulation Run Dialog, and select the Frequency Sweep option from the dropdown list labeled Simulation Mode. When you choose the frequency sweep option, the Settings button next to the simulation mode dropdown list becomes enabled. Clicking this button opens the Frequency Settings dialog. The Frequency Rangeis initially set equal to your project's center frequency minus and plus half bandwidth. But you can change the values of Start Frequencyand End Frequency as well as the Number of Samples. The dialog offers two options for Frequency Sweep Type: Uniform or Adaptive. Select the former type. It is very important to note that in a MoM simulation, changing the frequency results in a change of the mesh of the structure, too. This is because the mesh density is defined in terms of the number of cells per effective wavelength. By default, during a frequency sweep, EM.Cube fixes the mesh density at the highest frequency, i.e., at the "End Frequency". This usually results in a smoother frequency response. You have the option to fix the mesh at the center frequency of the project or let EM.Cube "remesh" the planar structure at each frequency sample during a frequency sweep. You can make one of these three choices using the radio button in the Mesh Settings section of the dialog. Closing the Frequency Settings dialog returns you to the Simulation Run dialog, where you can start the planar MoM frequency sweep simulation by clicking the Run button.
Frequency sweeps are often performed to study the frequency response of a planar structure. In particular, the variation of scattering parameters like S11 (return loss) and S21 (insertion loss) with frequency are of utmost interest. When analyzing resonant structures like patch antennas or planar filters over large frequency ranges, you may have to sweep a large number of frequency samples to capture their behavior with adequate details. The resonant peaks or notches are often missed due to the lack of enough resolution. EM.Cube's Planar Module offers a powerful adaptive frequency sweep option for this purpose. It is based on the fact that the frequency response of a physical, causal, multiport network can be represented mathematically using a rational function approximation. In other words, the S parameters of a circuit exhibit a finite number of poles and zeros over a given frequency range. EM.Cube first starts with very few frequency samples and tries to fit rational functions of low orders to the scattering parameters. Then, it increases the number of samples gradually by inserting intermediate frequency samples in a progressive manner. At each iteration cycle, all the possible rational functions of higher orders are tried out. The process continues until adding new intermediate frequency samples does not improve the resolution of the "Sij" curves over the given frequency range. In that case, the curves are considered as having converged.
You must have defined one or more ports for your planar structure run an adaptive frequency sweep. Open the Frequency Settings dialog from the Simulation Run dialog and select the Adaptive option of Frequency Sweep Type. You have to set values for Minimum Number of Samples and Maximum Number of Samples. Their default values are 3 and 9, respectively. You also set a value for the Convergence Criterion, which has a default value of 0.1. At each iteration cycle, all the S parameters are calculated at the newly inserted frequency samples, and their average deviation from the curves of the last cycle is measured as an error. When this error falls below the specified convergence criterion, the iteration is ended. If EM.Cube reaches the specified maximum number of iterations and the convergence criterion has not yet been met, the program will ask you whether to continue the process or exit it and stop.
Working with EM.Picasso Simulation Data
EM.Picasso's Output Simulation Data
Depending on the source type and the types of observables defined in a project, a number of output data are generated at the end of a planar MoM simulation. Some of these data are 2D by nature and some are 3D. The output simulation data generated by EM.Picasso can be categorized into the following groups:
- Port Characteristics: S, Z and Y Parameters and Voltage Standing Wave Ratio (VSWR)
- Radiation Characteristics: Radiation Patterns, Directivity, Total Radiated Power, Axial Ratio, Main Beam Theta and Phi, Radiation Efficiency, Half Power Beam Width (HPBW), Maximum Side Lobe Level (SLL), First Null Level (FNL), Front-to-Back Ratio (FBR), etc.
- Scattering Characteristics: Bi-static and Mono-static Radar Cross Section (RCS)
- Periodic Characteristics: Reflection and Transmission Coefficients
- Current Distributions: Electric and magnetic current amplitude and phase on all metal and slot traces and embedded objects
- Near-Field Distributions: Electric and magnetic field amplitude and phase on specified planes and their central axes
Examining Port Characteristics
If your planar structure is excited by gap sources or probe sources or de-embedded sources, and one or more ports have been defined, the planar MoM engine calculates the scattering, impedance and admittance (S/Z/Y) parameters of the designated ports. The scattering parameters are defined based on the port impedances specified in the project's Port Definition dialog. If more than one port has been defined in the project, the S/Z/Y matrices of the multiport network are calculated.
At the end of a planar MoM simulation, the values of S/Z/Y parameters and VSWR data are calculated and reported in the output message window. The S, Z and Y parameters are written into output ASCII data files of complex type with a ".CPX" extension. Every file begins with a header consisting of a few comment lines that start with the "#" symbol. The complex values are arranged into two columns for the real and imaginary parts. In the case of multiport structures, every single element of the S/Z/Y matrices is written into a separate complex data file. For example, you will have data files like S11.CPX, S21.CPX, ..., Z11.CPX, Z21.CPX, etc. The VSWR data are saved to an ASCII data file of real type with a ".DAT" extension called, VSWR.DAT.
If you run an analysis, the port characteristics have single complex values, which you can view using EM.Cube's data manager. However, there are no curves to graph. You can plot the S/Z/Y parameters and VSWR data when you have data sets, which are generated at the end of any type of sweep including a frequency sweep. In that case, the ".CPX" files have multiple rows corresponding to each value of the sweep parameter (e.g. frequency). EM.Cube's 2D graph data are plotted in EM.Grid, a versatile graphing utility. You can plot the port characteristics directly from the Navigation Tree. Right click on the Port Definition item in the Observables section of the Navigation Tree and select one of the items: Plot S Parameters, Plot Y Parameters, Plot Z Parameters, or Plot VSWR. In the first three cases, another sub-menu gives a list of individual port parameters.
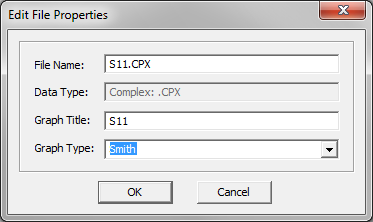
In particular, it may be useful to plot the Sii parameters on a Smith chart. To change the format of a data plot, select it in the Data Manager and click its Edit button. In the Edit File Dialog, choose one of the options provided in the dropdown list labeled Graph Type.
![]() Click here to learn more about Graphing Port Characteristics.
Click here to learn more about Graphing Port Characteristics.
![]() Click here to learn more about Rational Interpolation of Scattering Parameters.
Click here to learn more about Rational Interpolation of Scattering Parameters.
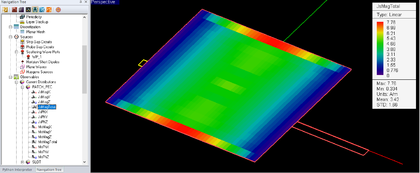
Visualizing Current Distributions
Electric and magnetic currents are the fundamental output data of a planar MoM simulation. After the numerical solution of the MoM linear system, they are found using the solution vector [I] and the definitions of the electric and magnetic vectorial basis functions:
- [math] \mathbf{[X]}_{N\times 1} = \begin{bmatrix} I^{(J)} \\ \\ V^{(M)} \end{bmatrix} \quad \Rightarrow \quad \begin{cases} \mathbf{J(r)} = \sum_{n=1}^N I_n^{(J)} \mathbf{f_n^{(J)} (r)} \\ \\ \mathbf{M(r)} = \sum_{k=1}^K V_k^{(M)} \mathbf{f_k^{(M)} (r)} \end{cases} [/math]
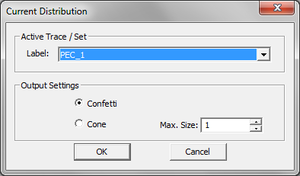
Note that currents are complex vector quantities. Each electric or magnetic current has three X, Y and Z components, and each complex component has a magnitude and phase. You can visualize the surface electric currents on metal (PEC) and conductive sheet traces, surface magnetic currents on slot (PMC) traces and vertical volume currents on the PEV vias and embedded dielectric objects. 3D color-coded intensity plots of electric and magnetic current distributions are visualized in the project workspace, superimposed on the surface of physical objects. In order to view the current distributions, you must first define them as observables before running the planar MoM simulation. At the top of the Current Distribution dialog and in the section titled Active Trace / Set, you can select a trace or embedded object set where you want to observe the current distribution.
| |
You have to define a separate current distribution observable for each individual trace or embedded object set. |
![]() Click here to learn more about Visualizing 3D Current Distribution Maps.
Click here to learn more about Visualizing 3D Current Distribution Maps.
Visualizing the Near Fields

![]() Click here to learn more about Defining a Field Sensor Observable.
Click here to learn more about Defining a Field Sensor Observable.
![]() Click here to learn more about Visualizing 3D Near Field Maps.
Click here to learn more about Visualizing 3D Near Field Maps.
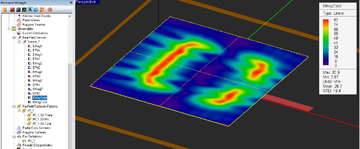
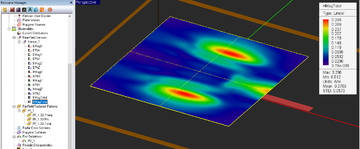
Computing Radiation Pattern of Planar Structures
Even though EM.Pplanar MoM engine does not need a radiation box, you still have to define a "Far Field" observable for radiation pattern calculation. This is because far field calculations take time and you have to instruct EM.Cube to perform these calculations. To define a far field, right click the Far Fields item in the Observables section of the Navigation Tree and select Insert New Radiation Pattern.... The Radiation Pattern Dialog opens up. You may accept the default settings, or you can change the value of Angle Increment, which is expressed in degrees. You can also choose to Normalize 2D Patterns. In that case, the maximum value of a 2D paten graph will have a value of 1; otherwise, the actual far field values in V/m will be used on the graph.
Once a planar MoM simulation is finished, three far field items are added under the Far Field item in the Navigation Tree. These are the far field component in θ direction, the far field component in φ direction and the "Total" far field. The 2D radiation pattern graphs can be plotted from EM.Cube's Data Manager. A total of eight 2D radiation pattern graphs are available: 4 polar and 4 Cartesian graphs for the XY, YZ, ZX and user defined plane cuts.
![]() Click here to learn more about the theory of Far Field Computations.
Click here to learn more about the theory of Far Field Computations.
![]() Click here to learn more about the theory of Using Array Factors to Model Antenna Arrays .
Click here to learn more about the theory of Using Array Factors to Model Antenna Arrays .
![]() Click here to learn more about Visualizing 3D Radiation Patterns.
Click here to learn more about Visualizing 3D Radiation Patterns.
![]() Click here to learn more about Plotting 2D Radiation Graphs.
Click here to learn more about Plotting 2D Radiation Graphs.
Radar Cross Section of Planar Structures
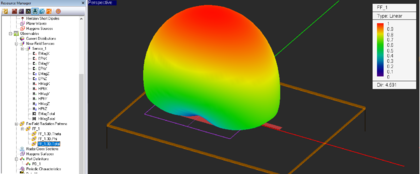
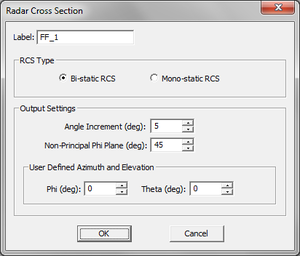
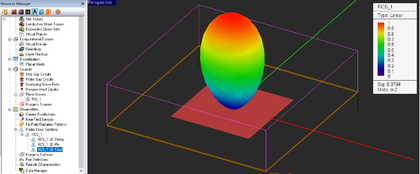
When a planar structure is excited by a plane wave source, the calculated far field data indeed represent the scattered fields of that planar structure. EM.Picasso can also calculate the radar cross section (RCS) of a planar target. Note that in this case the RCS is defined for a finite-sized target in the presence of an infinite background structure. The scattered θ and φ components of the far-zone electric field are indeed what you see in the 3D far field visualization of radiation (scattering) patterns. Instead of radiation or scattering patterns, you can instruct EM.Picasso to plot 3D visualizations of σθ, σφ and the total RCS.
![]() Click here to learn more about Visualizing 3D RCS.
Click here to learn more about Visualizing 3D RCS.
![]() Click here to learn more about Plotting 2D RCS Graphs.
Click here to learn more about Plotting 2D RCS Graphs.